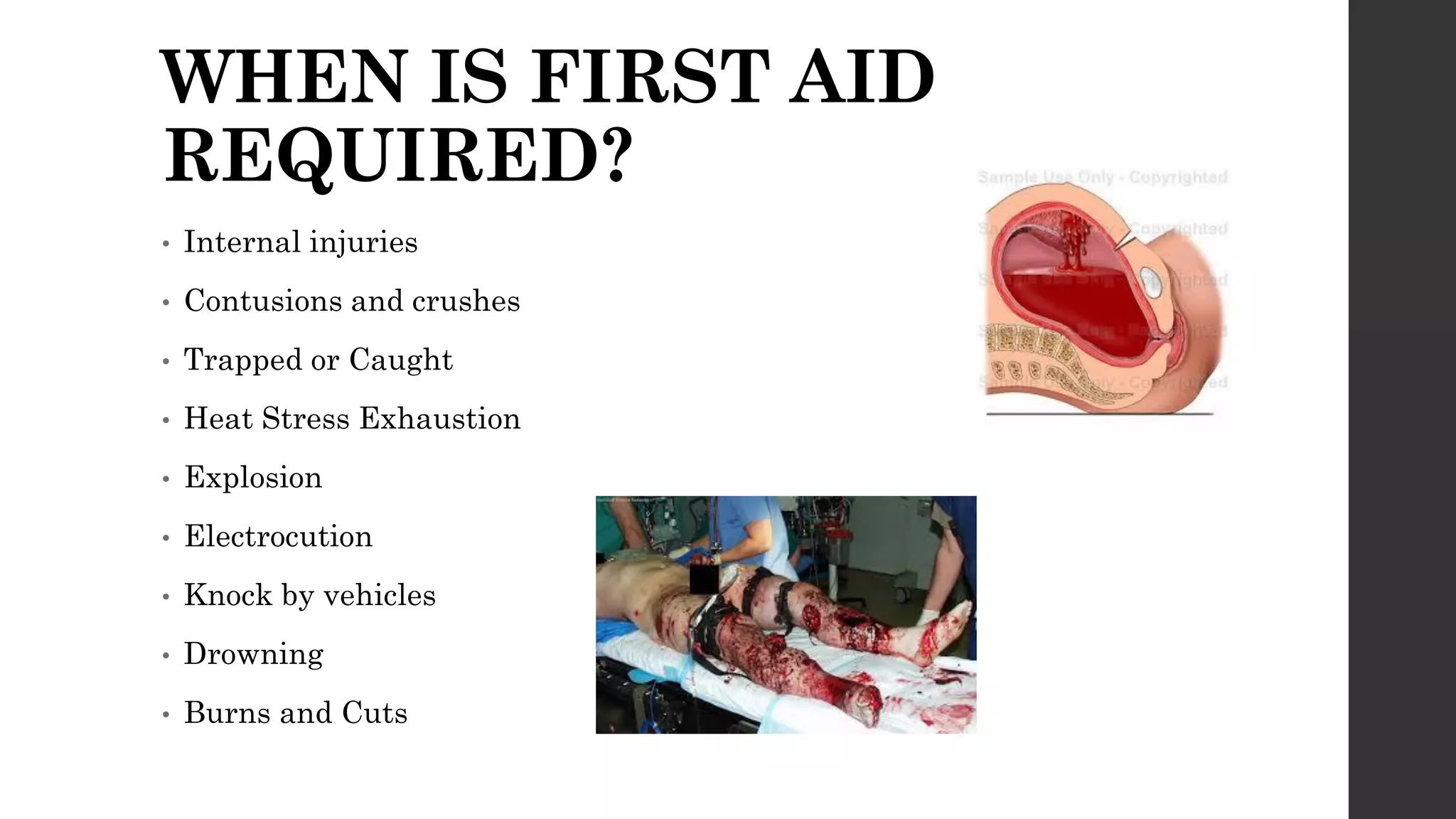
This document provides an introduction and overview of first aid. It defines first aid as immediate care for injured or ill individuals until medical treatment arrives. It outlines who can provide first aid, including police, firefighters, medical professionals, and the public. The document lists common reasons first aid may be required, such as injuries, illnesses, burns, and more. It describes the principles, goals, supplies, and responsibilities of first aid providers. Finally, it discusses the DRABC action plan for assessing life-threatening conditions in a victim.