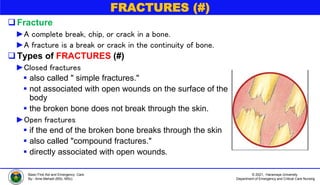
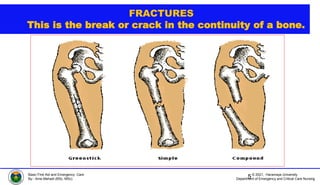
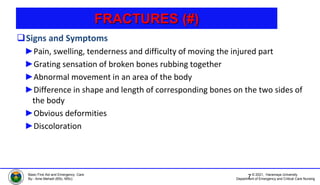
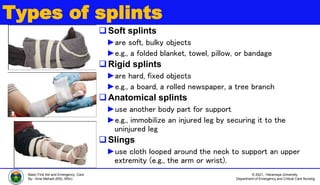
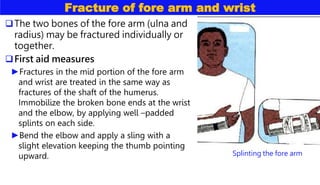
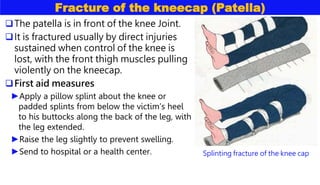
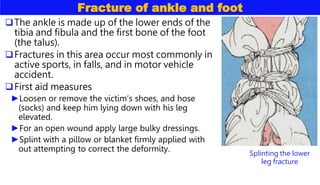
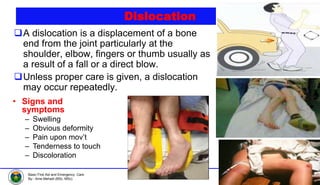
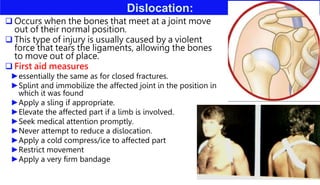
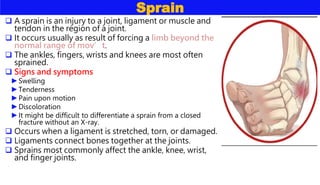
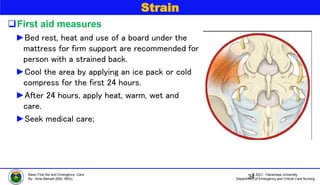
This document discusses various types of bone injuries including fractures, sprains, strains, and muscle cramps. It provides details on closed and open fractures, as well as green stick and complicated fractures. Signs and symptoms of fractures are outlined. First aid principles for fractures include immobilization, splinting, controlling bleeding if open, and seeking immediate medical help. Specific fractures of the skull, face, shoulder blade, collarbone, upper arm, elbow, and forearm are also described with appropriate first aid treatments.