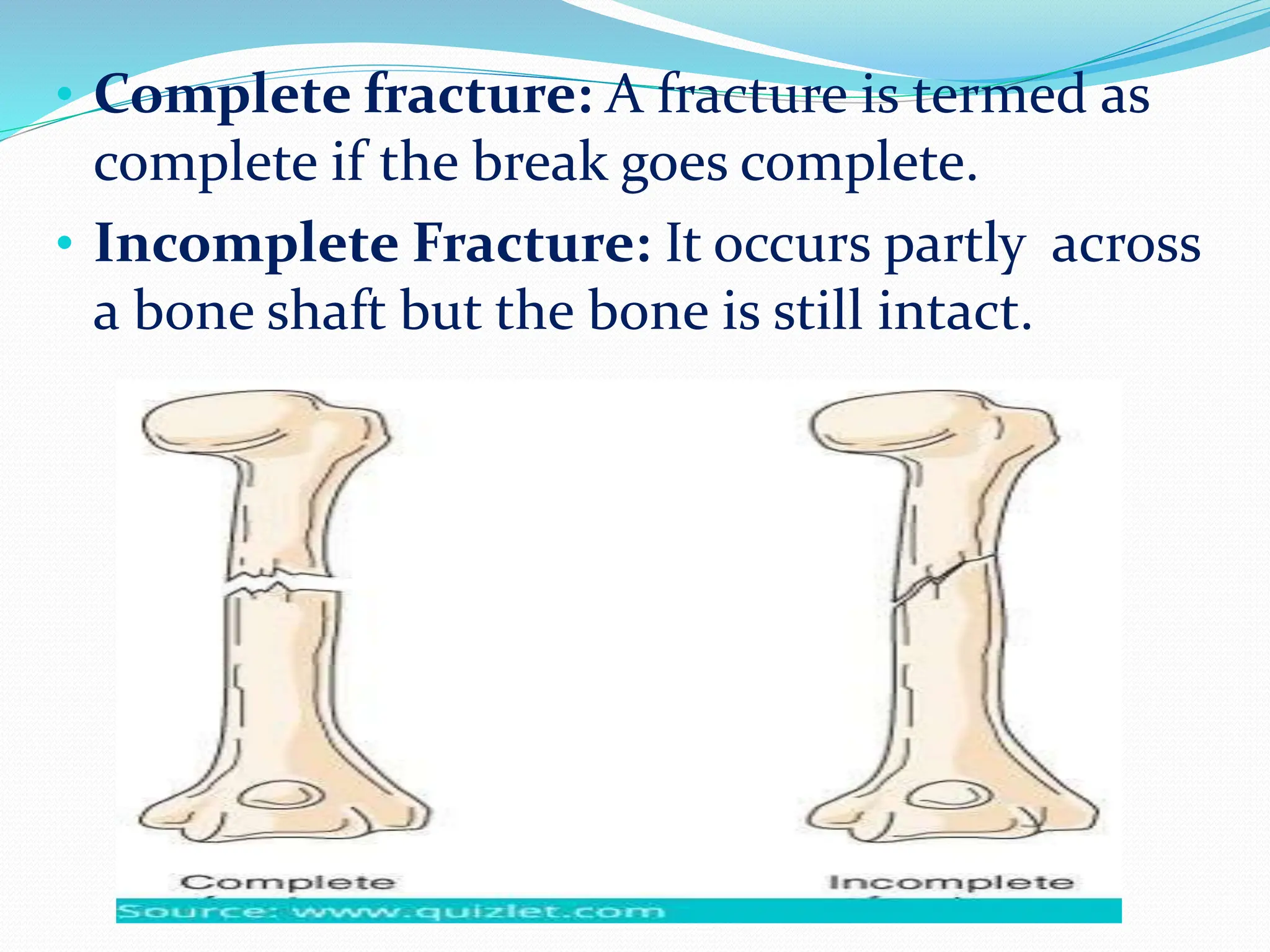
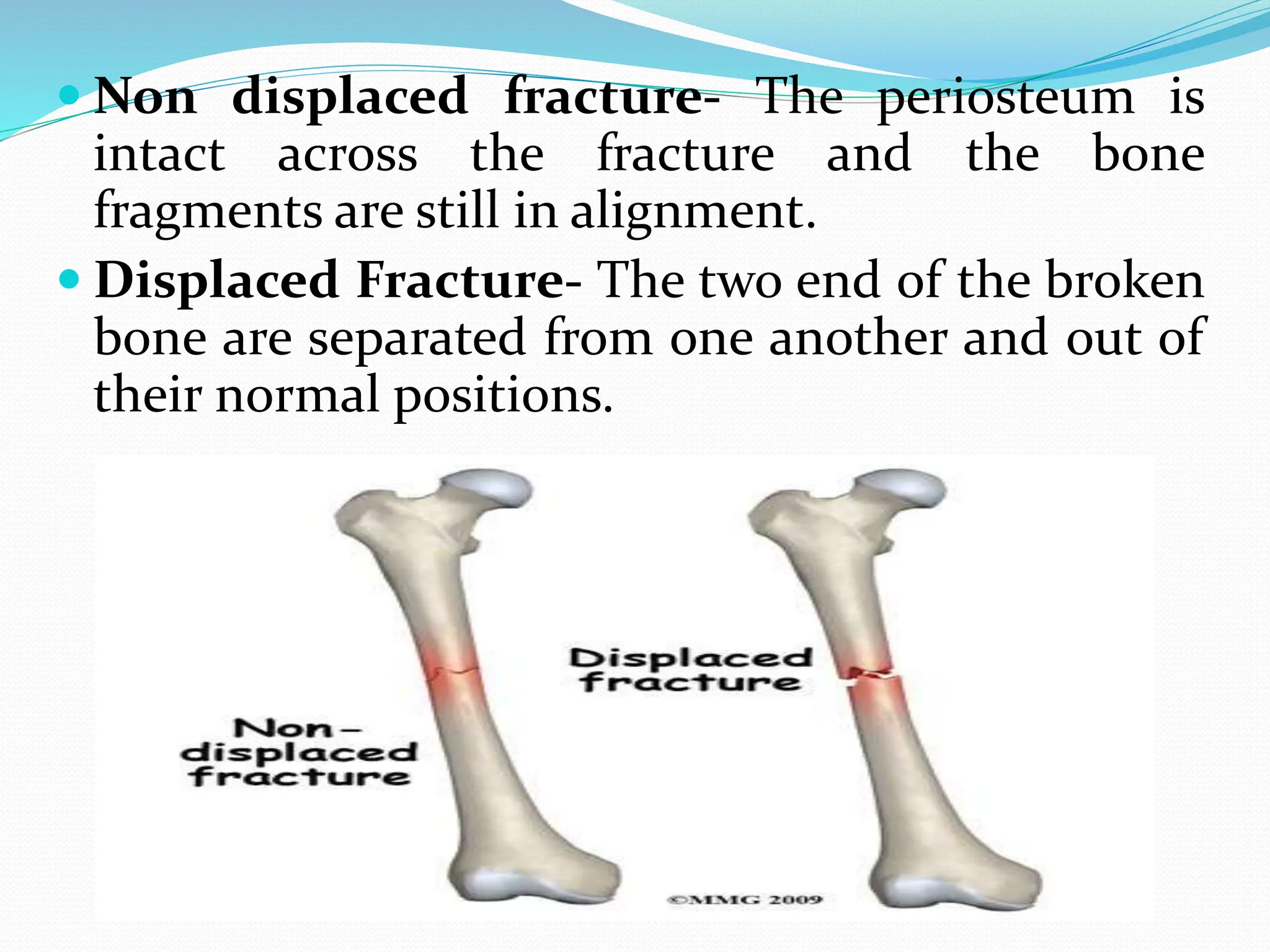
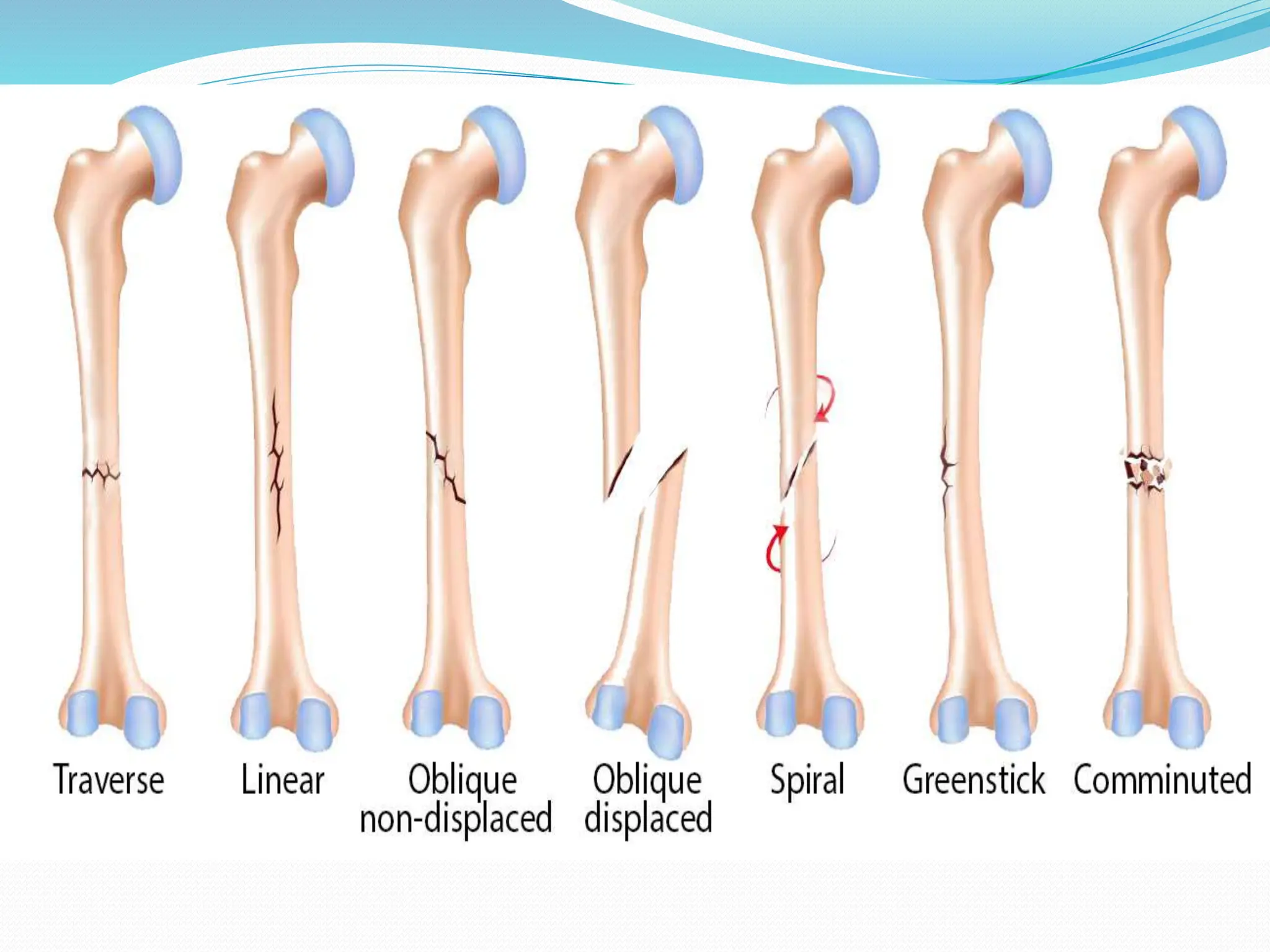
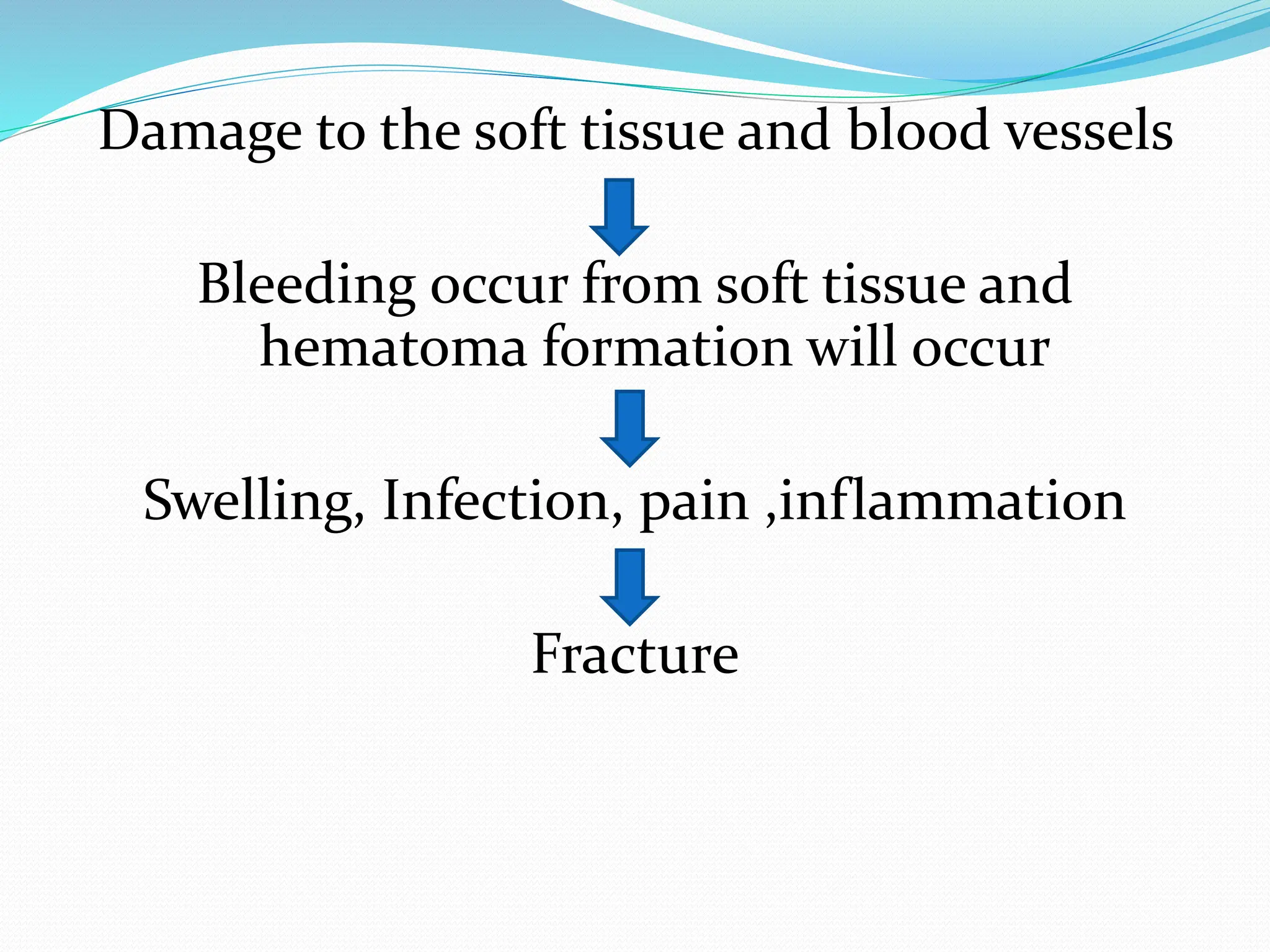
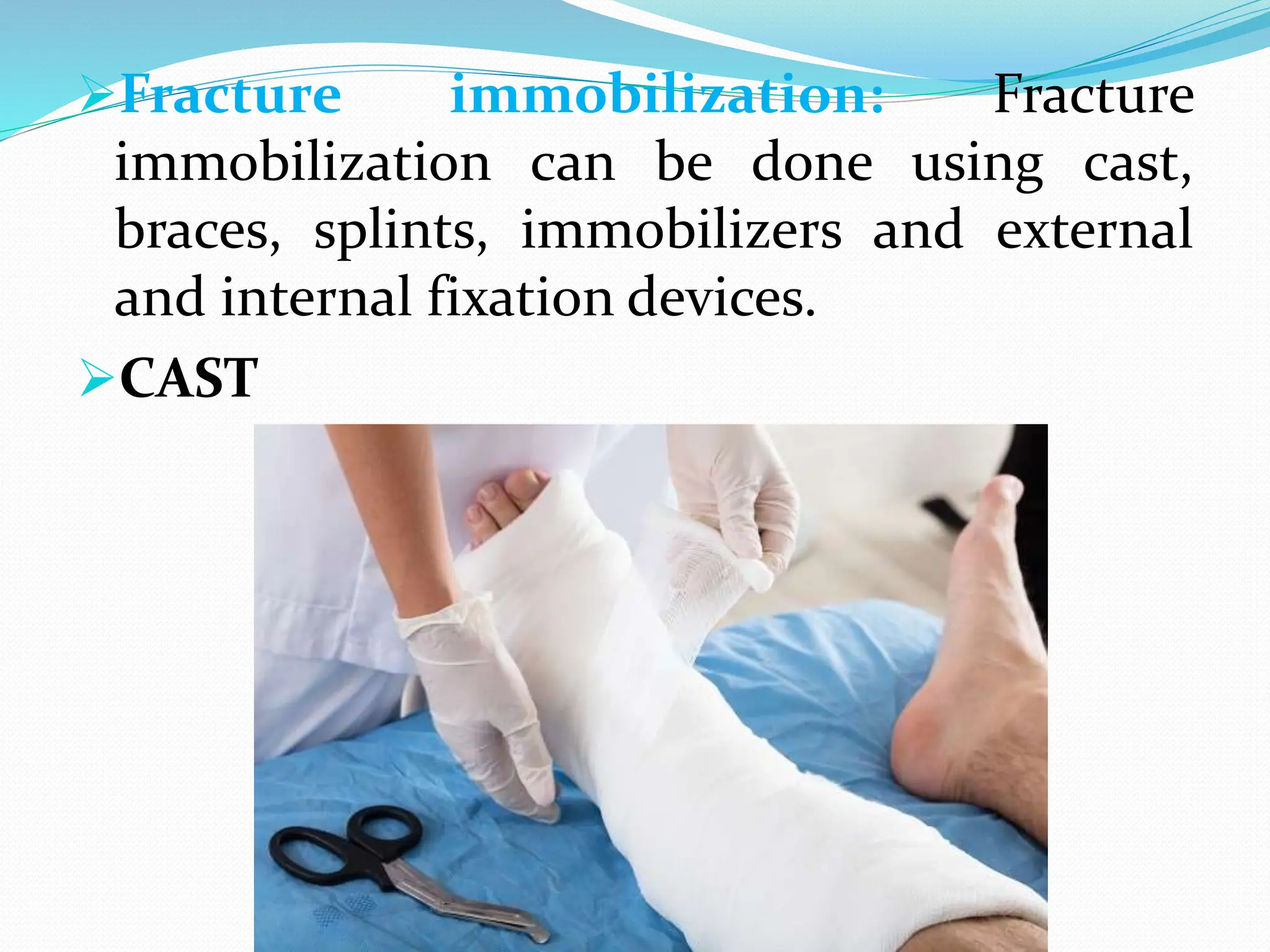
Fracture is a break in the bone caused by trauma or disease. The document discusses the different types of fractures such as closed versus open, displaced versus nondisplaced, and classifications based on the direction of the break. Symptoms include pain, deformity, loss of function. Diagnosis involves history, physical exam, and imaging tests like x-rays. Treatment involves reducing and immobilizing the fracture through methods like casting, bracing, traction, or surgery. Nursing care focuses on pain management, preventing complications like immobilization, and ensuring proper healing through diet, exercise, and patient education.