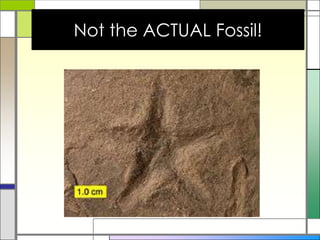
Fossils are the remains or traces of prehistoric life found in sedimentary rocks. The type of fossil formed depends on how and where the organism died and was buried. Fossils can be unaltered remains like teeth and shells, or altered remains that have changed over time through processes like petrification or carbonization. Trace fossils provide indirect evidence of prehistoric life through things like tracks, burrows, and coprolites. Fossils are important for interpreting ancient environments and changes over time.