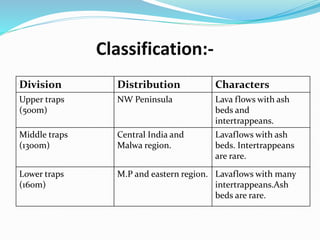
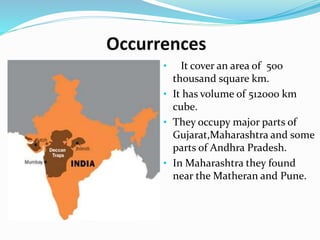
The document summarizes key information about the Deccan Traps volcanic formation in India. It describes the Deccan Traps as the largest volcanic formation in the Indian subcontinent, located between latitudes 17-24 degrees and longitudes 73-74 degrees. The document further classifies the Deccan Traps into upper, middle, and lower divisions based on their thickness and characteristics. It notes that the Deccan Traps cover an area of 500,000 square kilometers and have an estimated volume of 512,000 cubic kilometers.