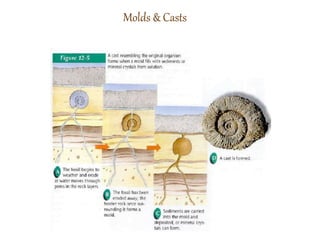
Fossils are preserved remains or traces of ancient life forms. They are most commonly found in sedimentary rock and form when organisms are buried and slowly replaced with minerals over time. The main types of fossils include petrified fossils where minerals replace the organism, molds and casts which preserve the shape of organisms, carbon films which leave thin carbon imprints, and trace fossils like footprints. Fossils provide evidence about past environments, climates, and how life has evolved and changed over millions of years as shown by the different organisms preserved in younger and older rock layers.