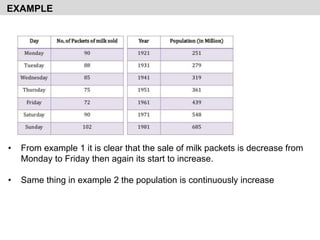
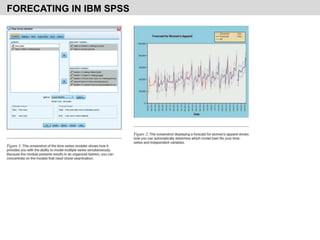
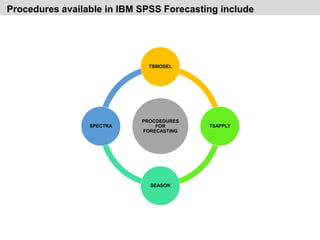
This document discusses forecasting techniques and time series analysis. It defines forecasting as the estimation or prediction of future outcomes, trends, or behavior through the use of statistics. The document outlines several key points:
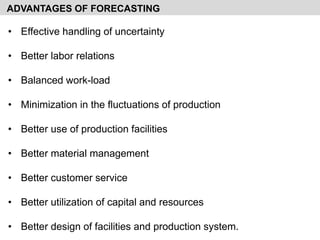
- It describes the meaning, definition, features, process, importance, advantages, and limitations of forecasting.
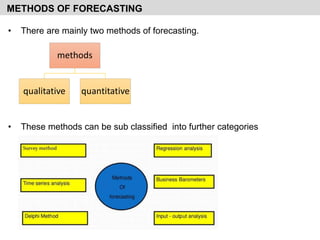
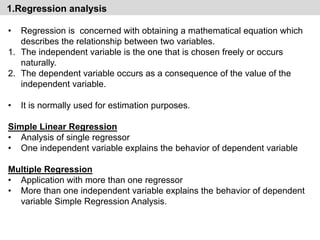
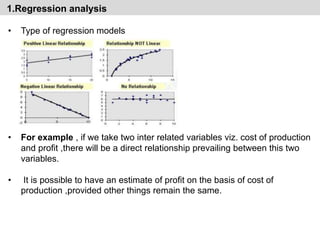
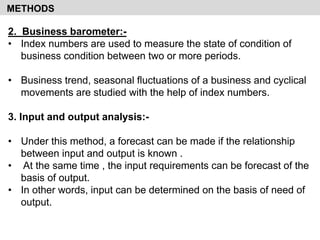
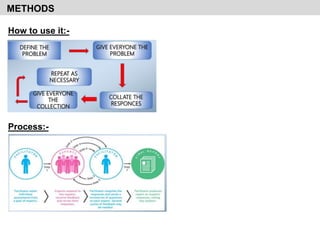
- It discusses various qualitative and quantitative forecasting methods including regression analysis, business barometers, input/output analysis, surveys, and time series analysis.
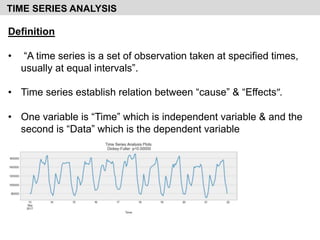
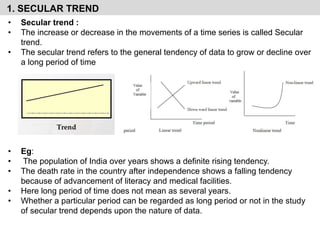
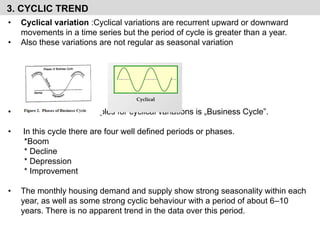
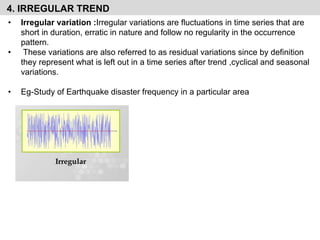
- It explains the components of time series analysis including secular trends, seasonal variations, cyclical variations, and irregular variations.
- It provides examples of each type of variation and discusses their importance for time series forecasting.