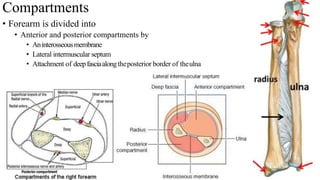
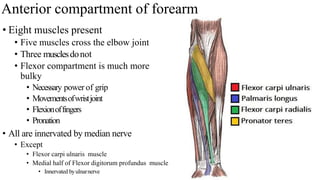
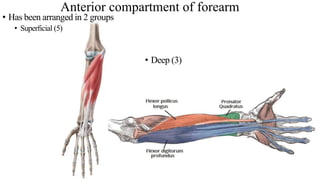
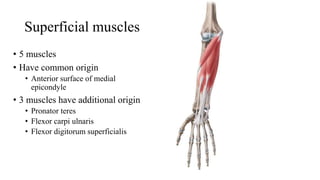
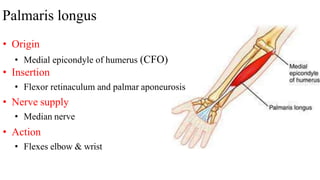
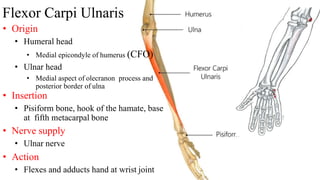
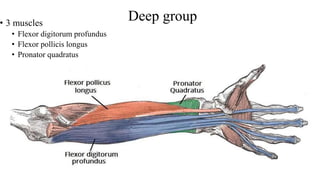
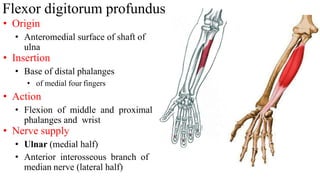
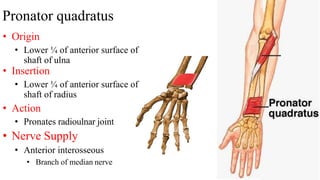
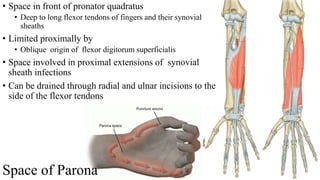
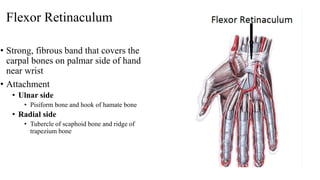
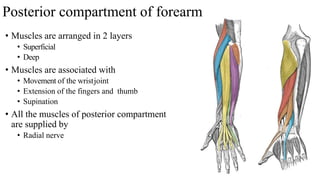
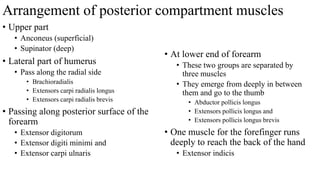
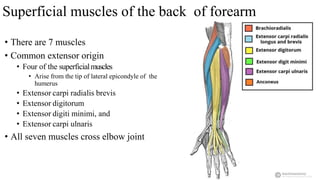
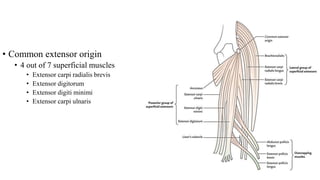
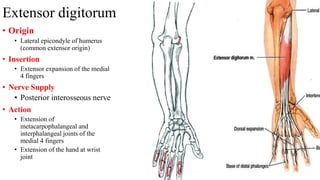
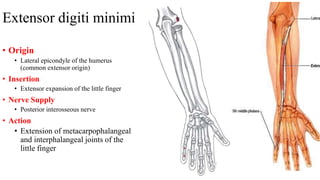
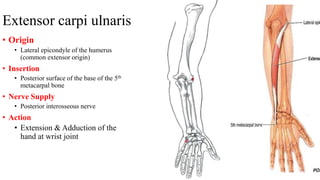
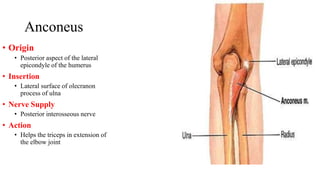
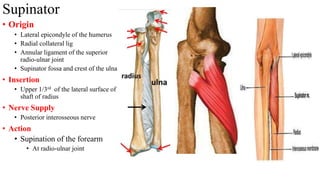
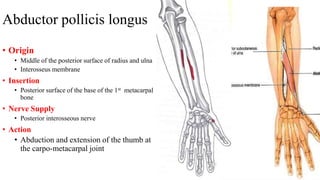
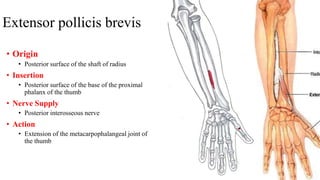
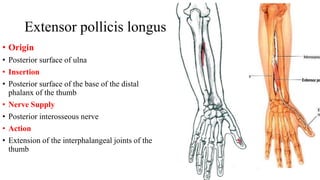
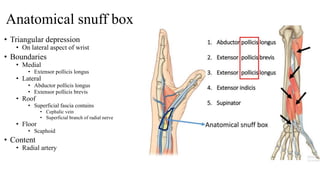
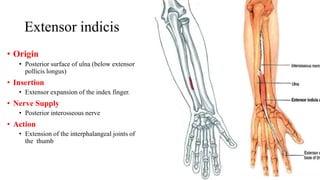
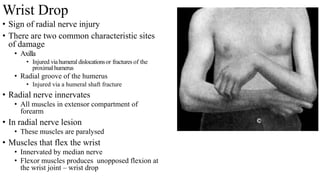
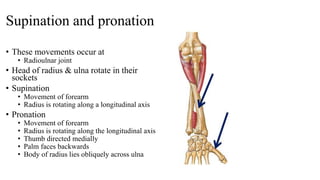
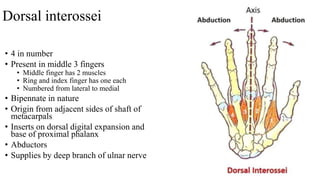
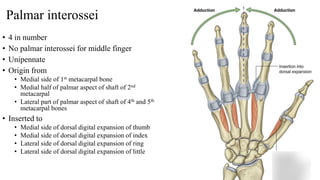
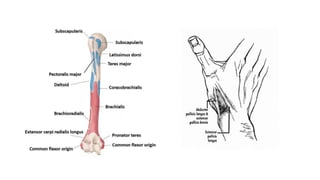
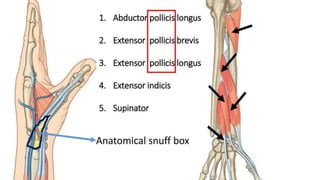
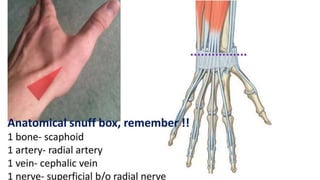
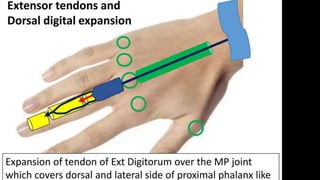
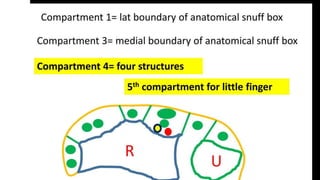
The forearm is divided into anterior and posterior compartments by interosseous membrane and septum. The anterior compartment contains 8 muscles innervated by median nerve except for flexor carpi ulnaris and half of flexor digitorum profundus which are innervated by ulnar nerve. The posterior compartment contains muscles for wrist extension, finger extension and supination, all innervated by radial nerve. The interossei muscles are located between metacarpal bones and control finger abduction/adduction.