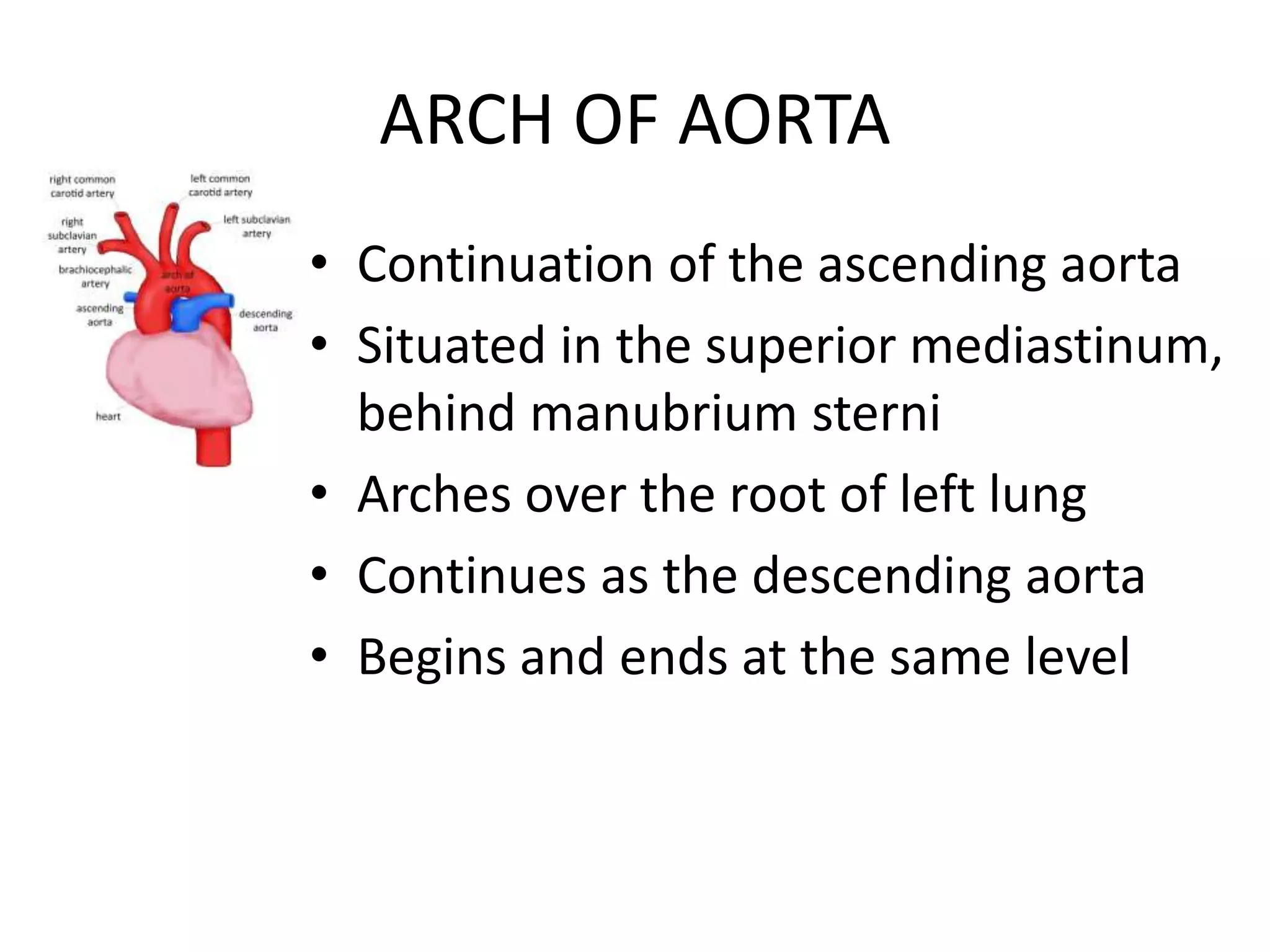
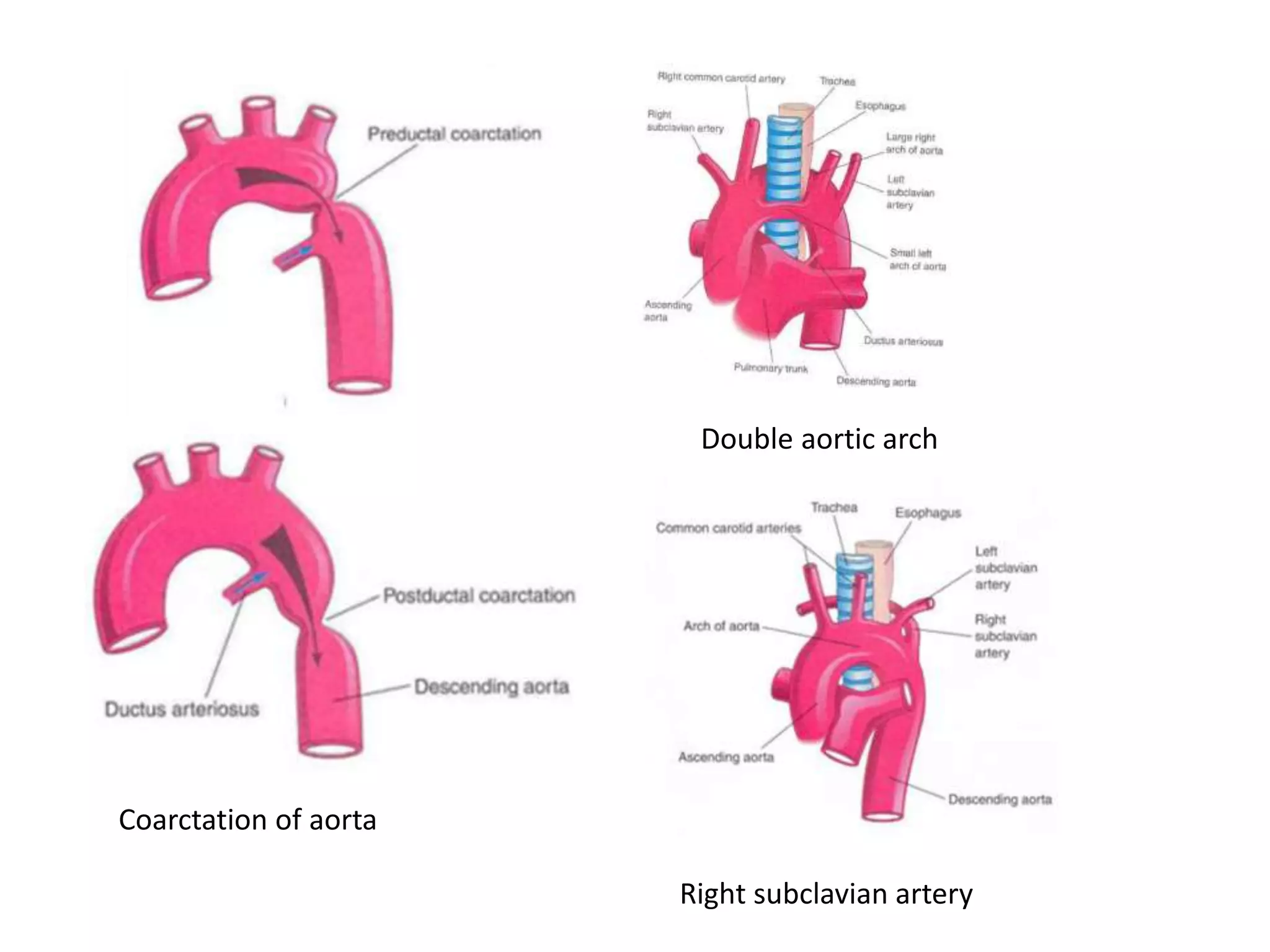
The arch of the aorta begins behind the upper border of the second right sternochondral joint and arches over the root of the left lung before ending at the lower border of the fourth thoracic vertebra. It has anterior relations including nerves and veins and posterior relations such as the trachea and esophagus. Its main branches are the brachiocephalic trunk, left common carotid artery, and left subclavian artery. Developmental anomalies of the arch of the aorta include right sided aortic arch, double aortic arch, abnormal origin of the right subclavian artery, and coarctation of the aorta.