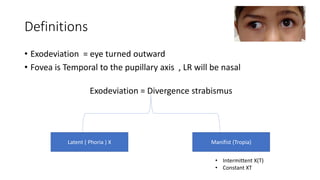
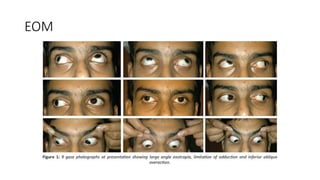
The document discusses exotropia, defined as an eye turning outward, describing types such as intermittent exotropia, which occurs occasionally, and constant exotropia. It covers evaluation and management of exotropia, including correcting refractive errors, orthoptic exercises, patching, prisms, and surgical options like recession of the lateral rectus muscle. The document provides details on differentiating and classifying types of exotropia based on clinical tests like the prism alternate cover test and monocular occlusion testing.