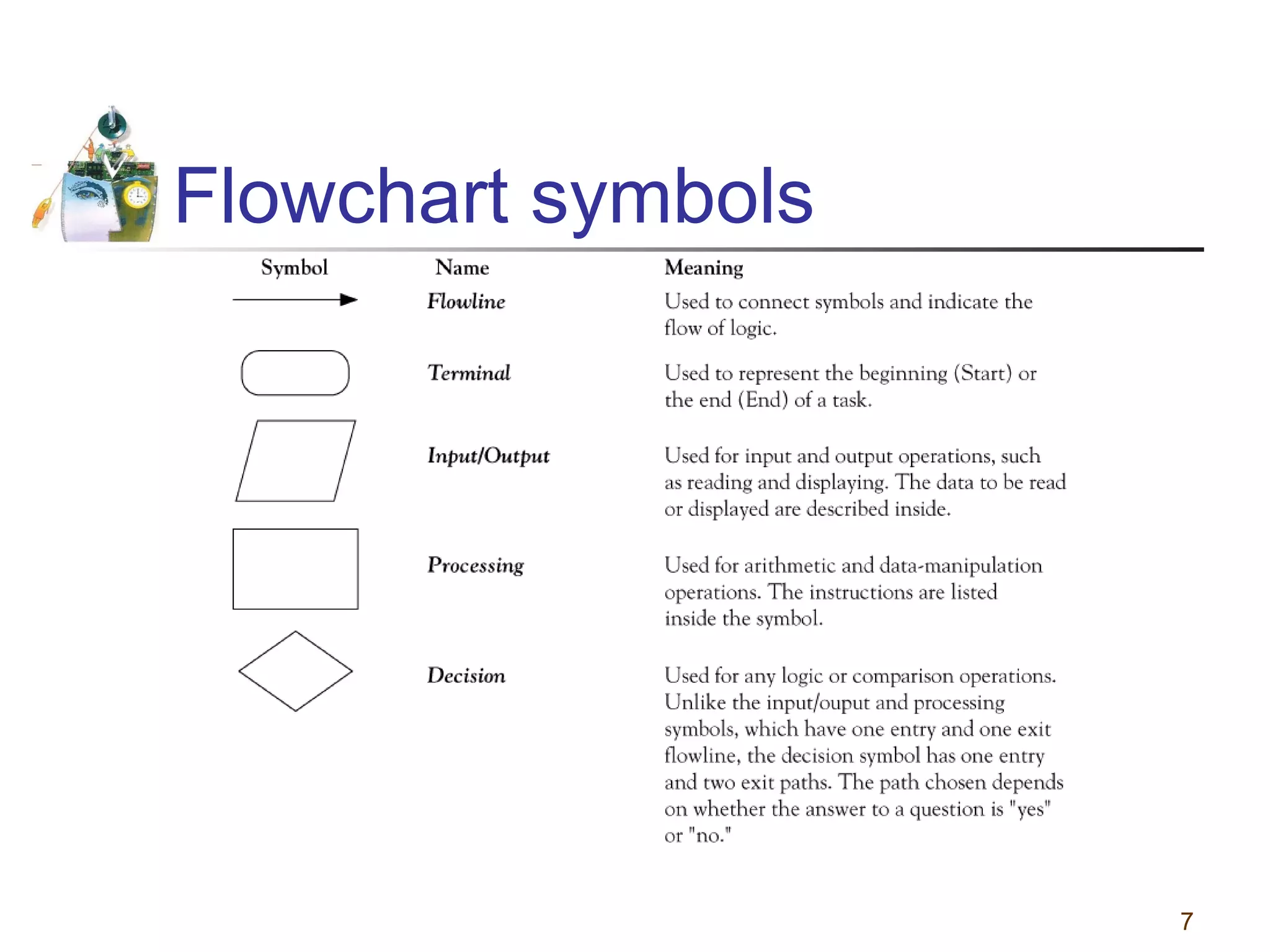
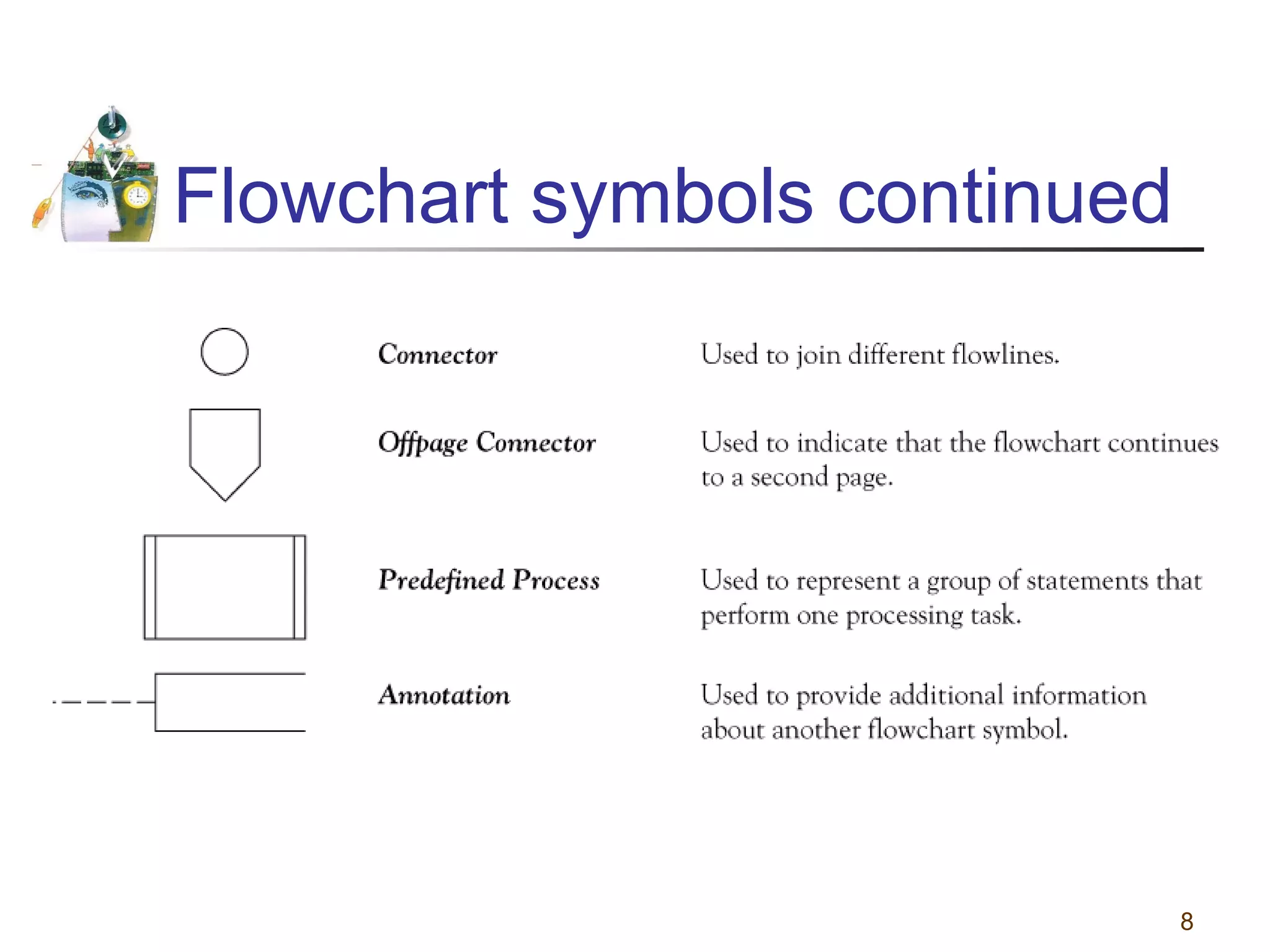
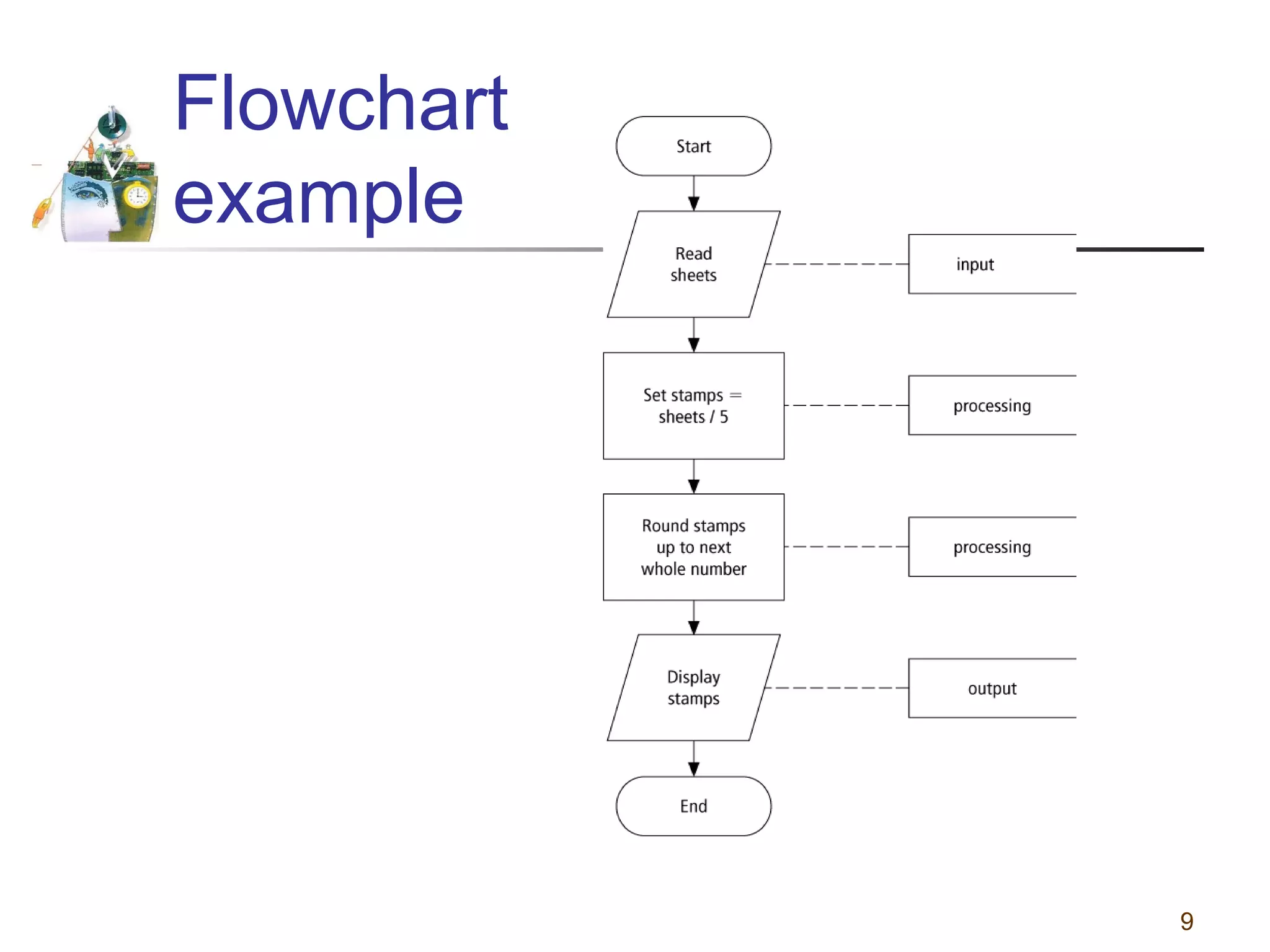
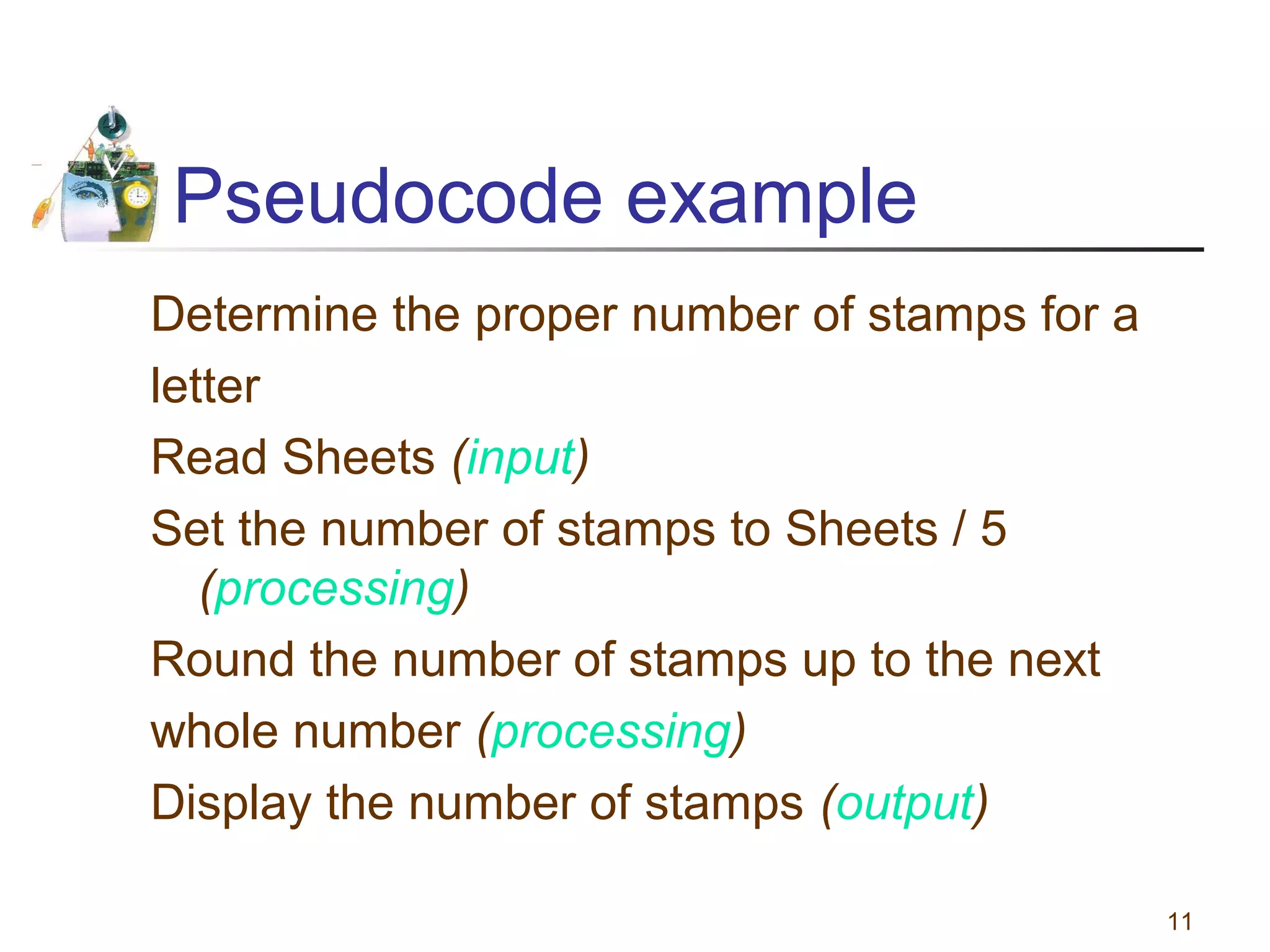
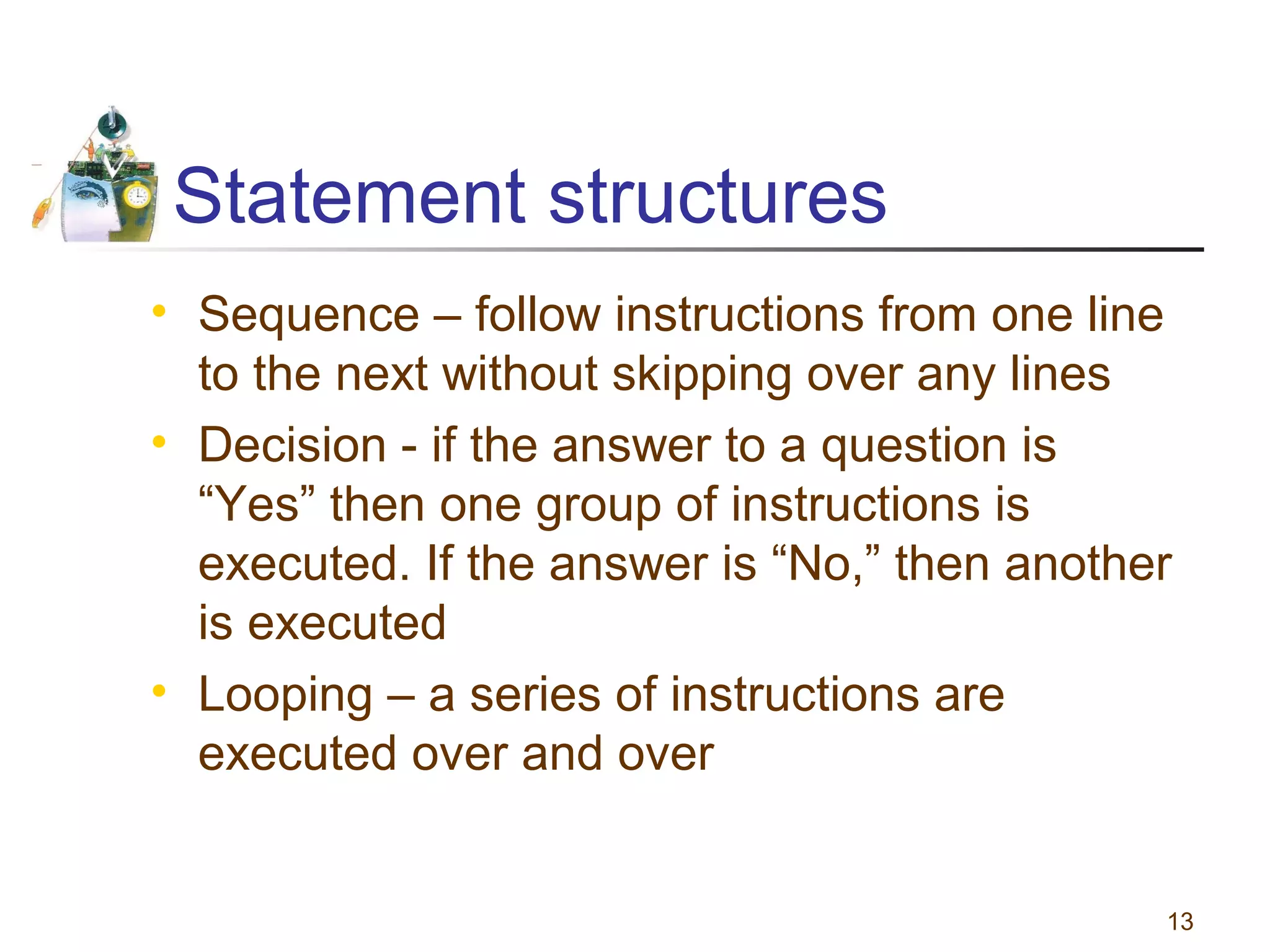
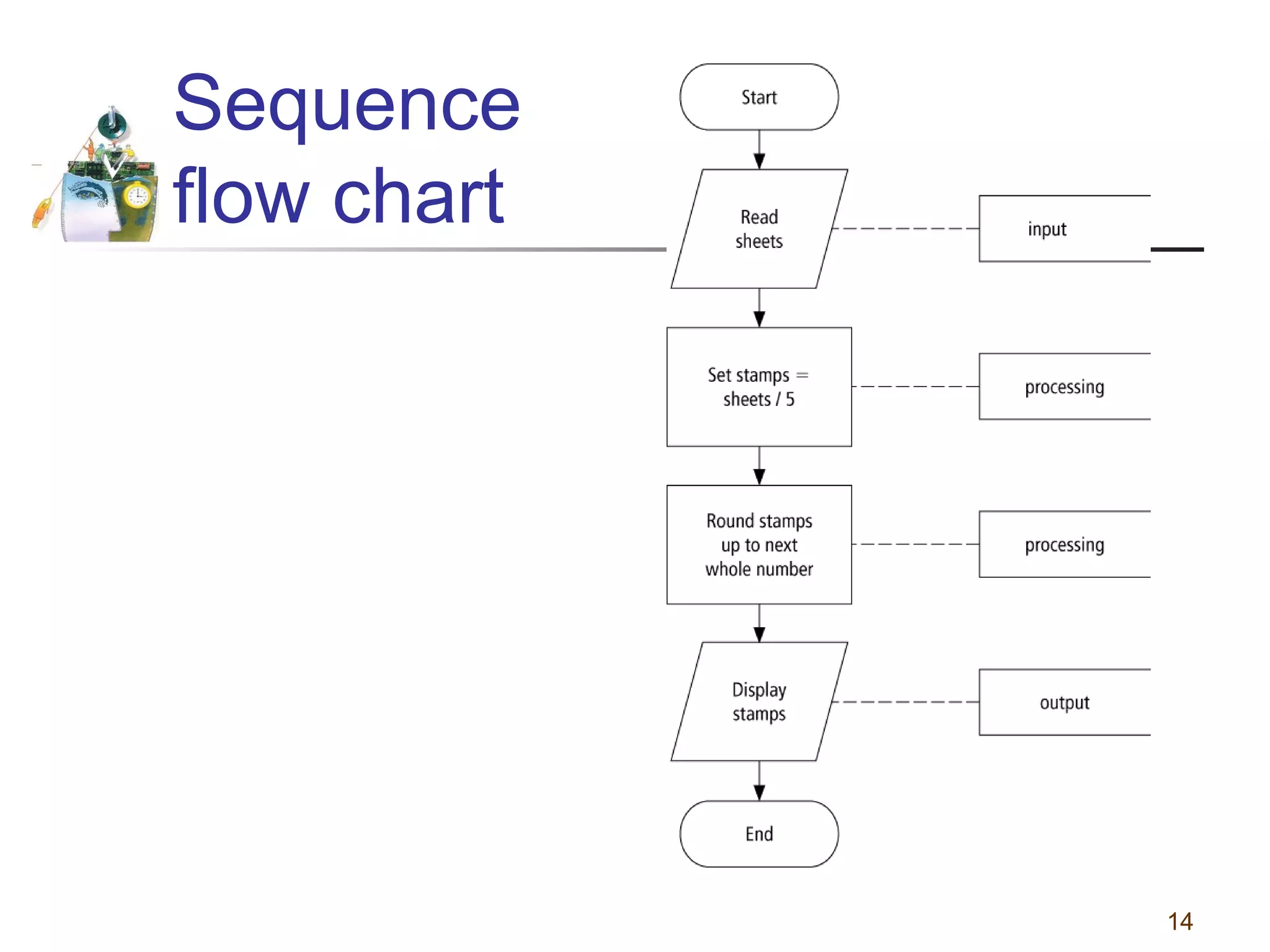
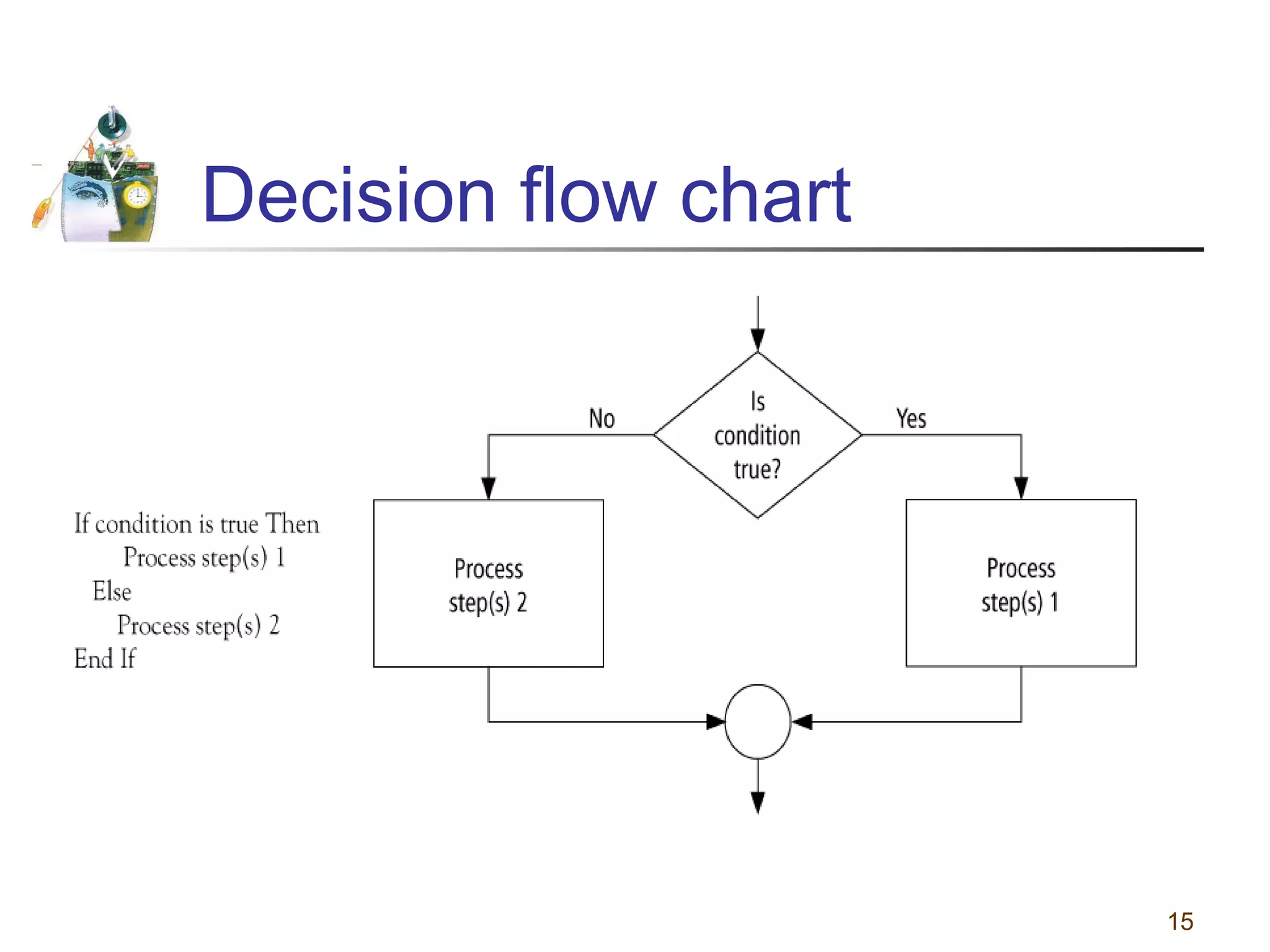
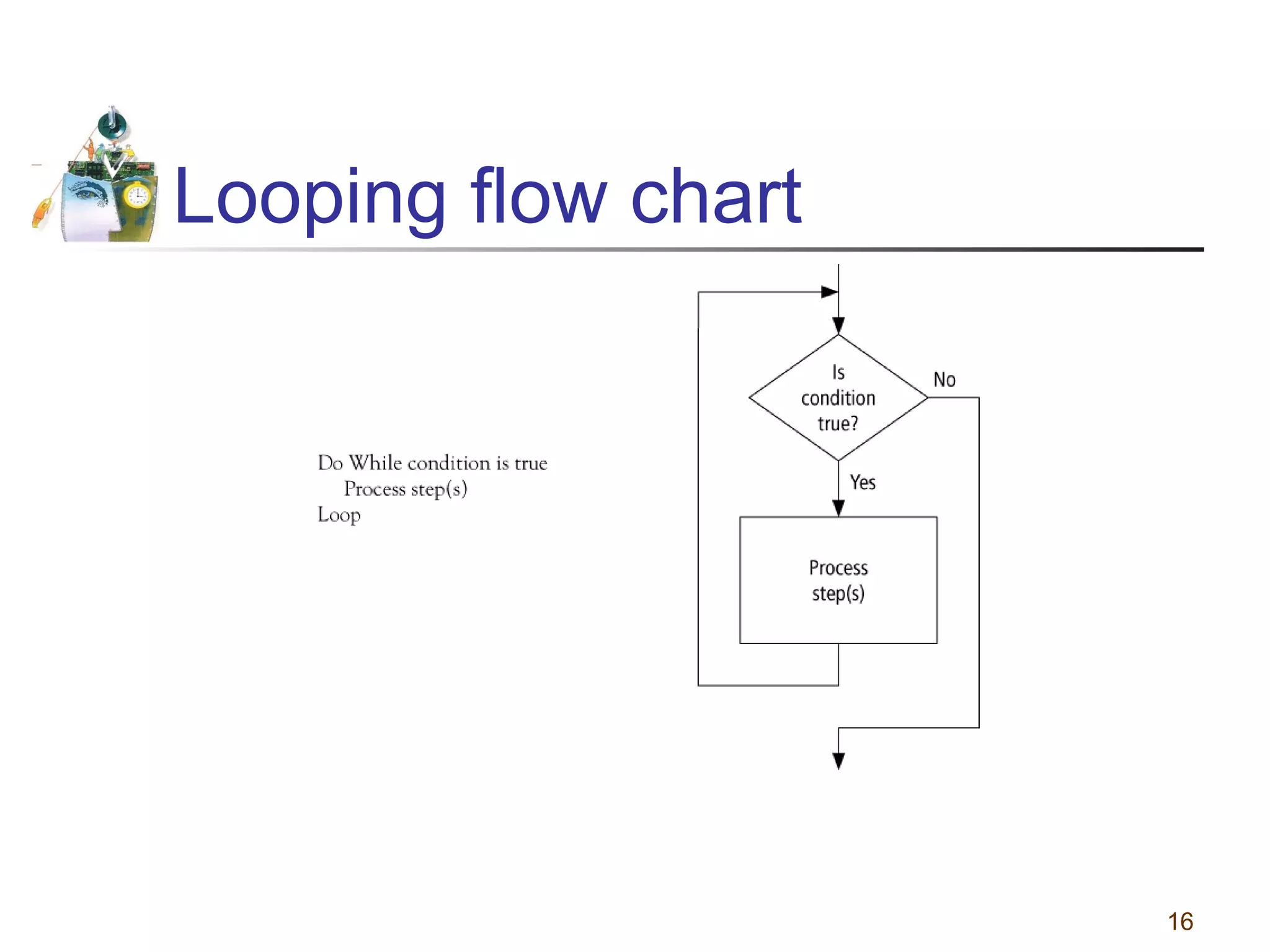
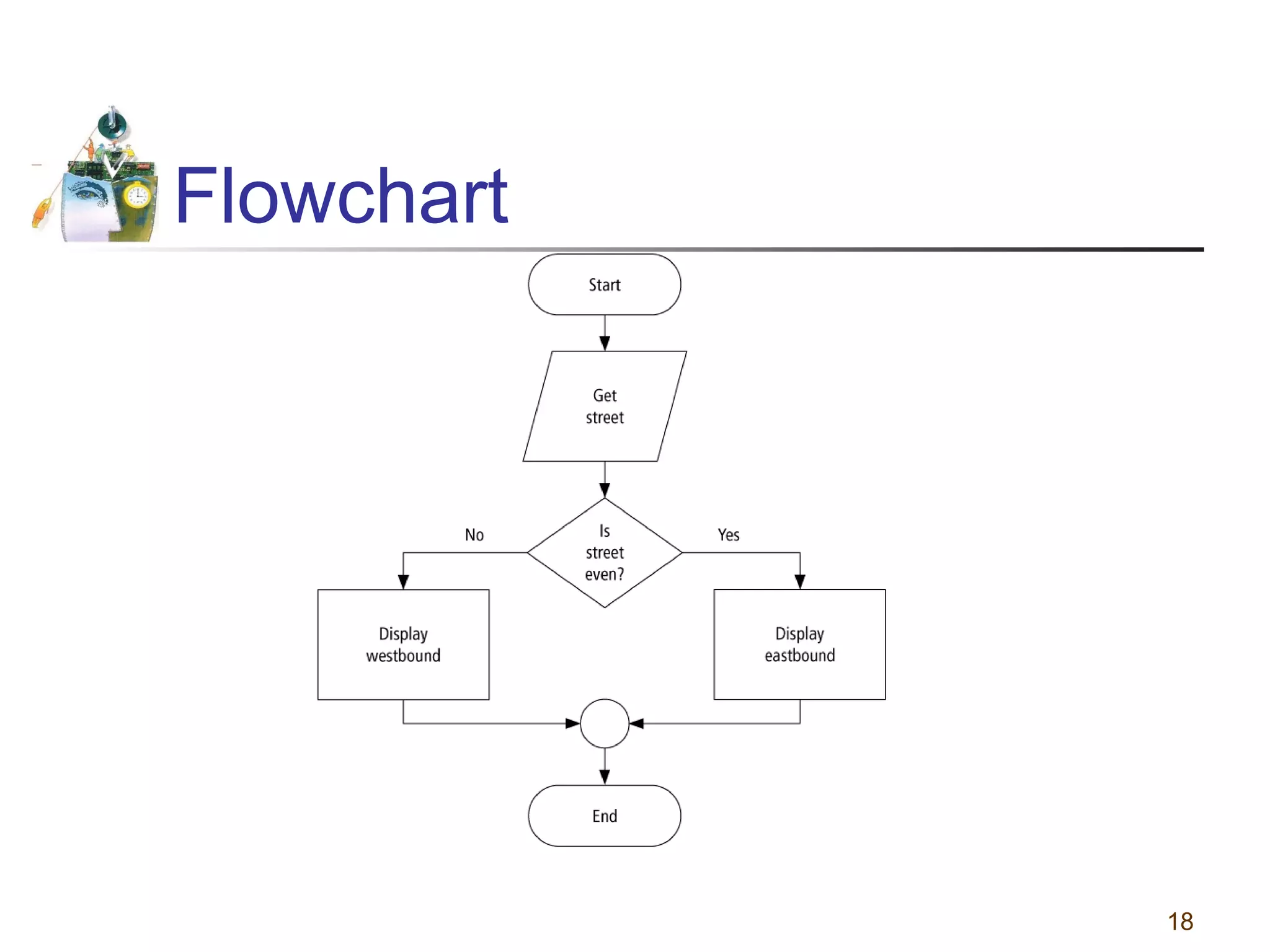
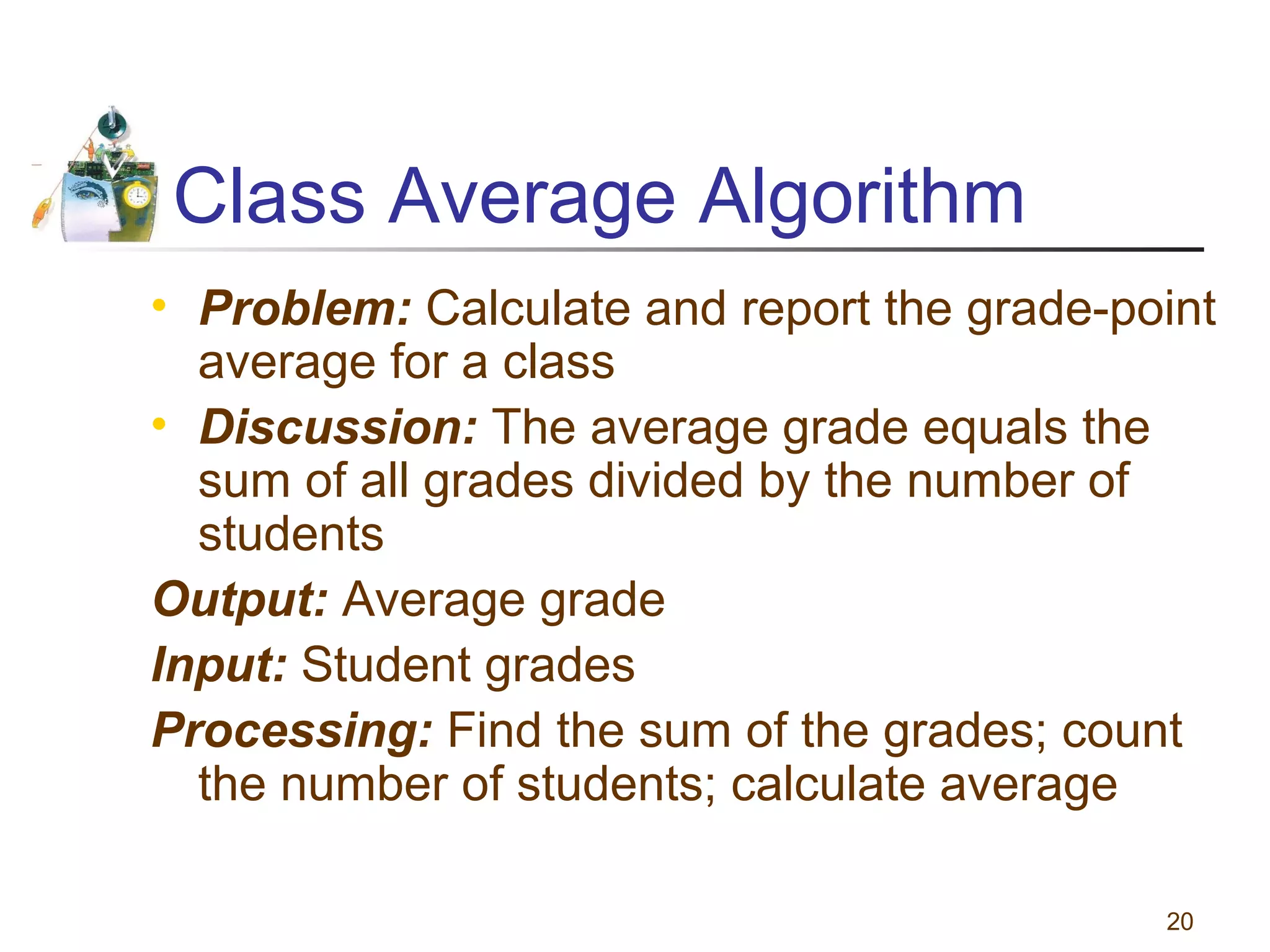
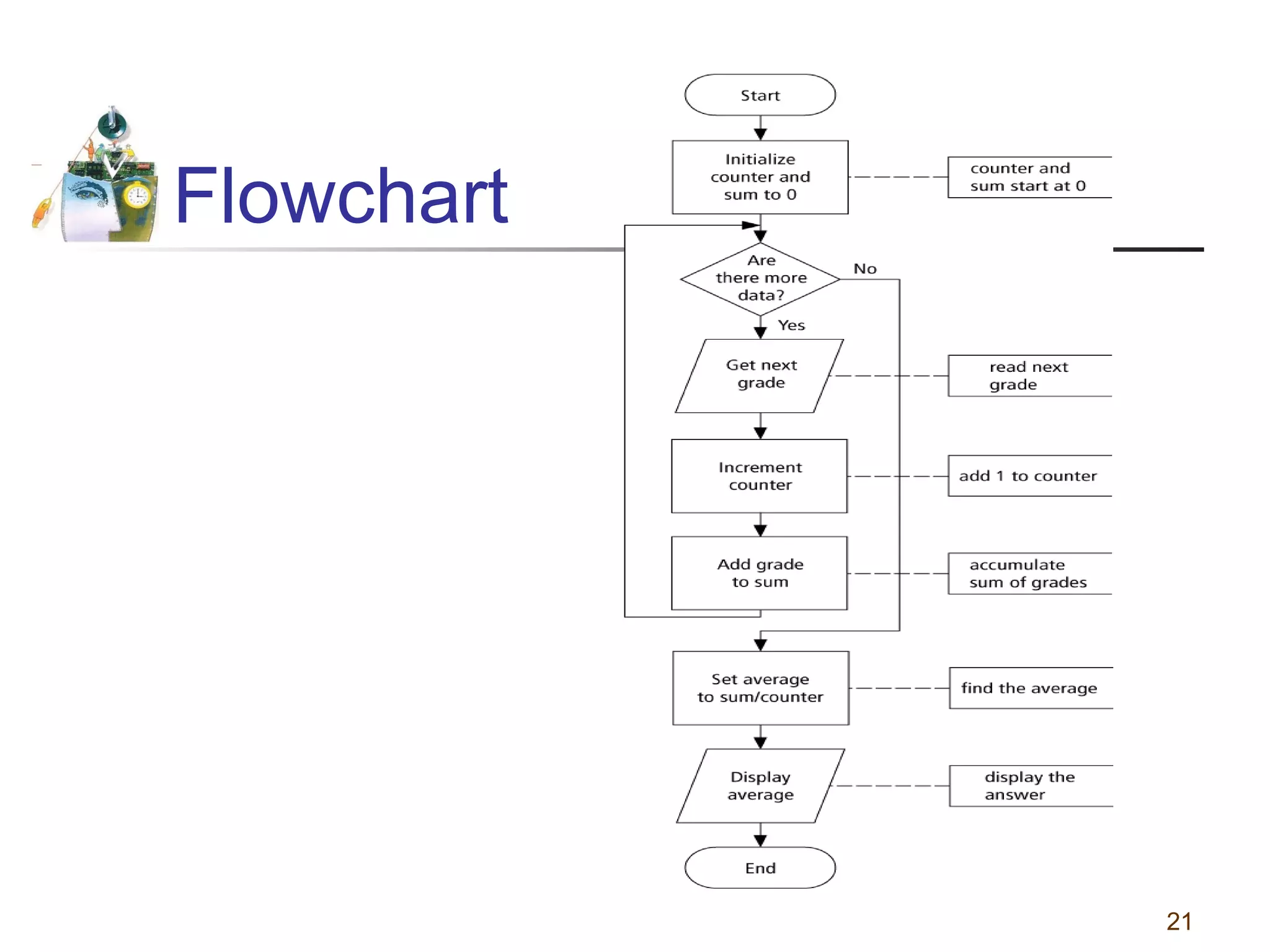
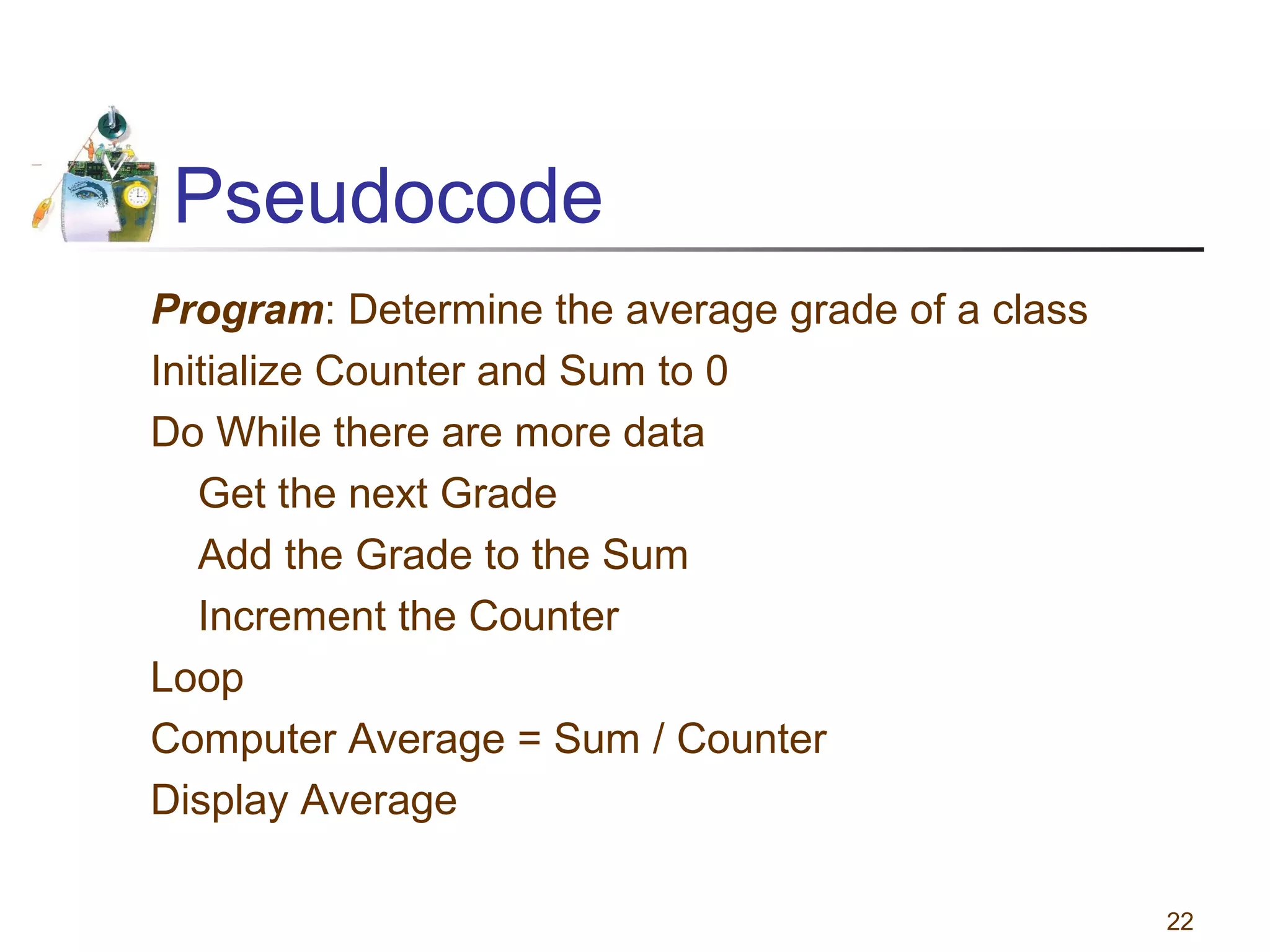
This document discusses various programming tools used to design algorithms, including flowcharts, pseudocode, and hierarchy charts. It provides examples of how to represent algorithms for calculating postage stamps needed and determining direction of NYC streets using flowcharts and pseudocode. Tips are given on flowcharts and pseudocode, such as that flowcharts clearly illustrate logic but are time-consuming, while pseudocode focuses on key tasks. Free online flowcharting software is also listed.