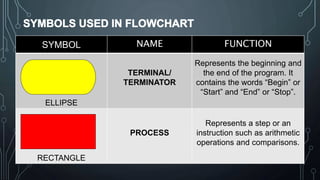
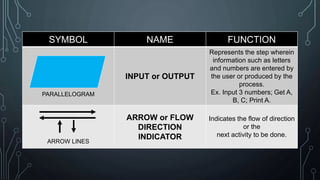
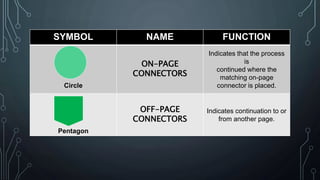
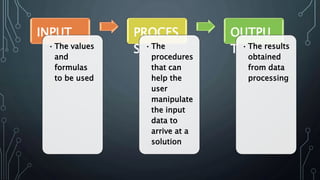
The document discusses programming as the process of creating instructions for computers, emphasizing the use of flowcharts as a tool for representing algorithms and logic visually. It describes various flowchart symbols along with their functions, and highlights best practices for creating effective flowcharts. Additionally, several problem-solving examples demonstrate how to generate flowcharts for specific programming tasks.