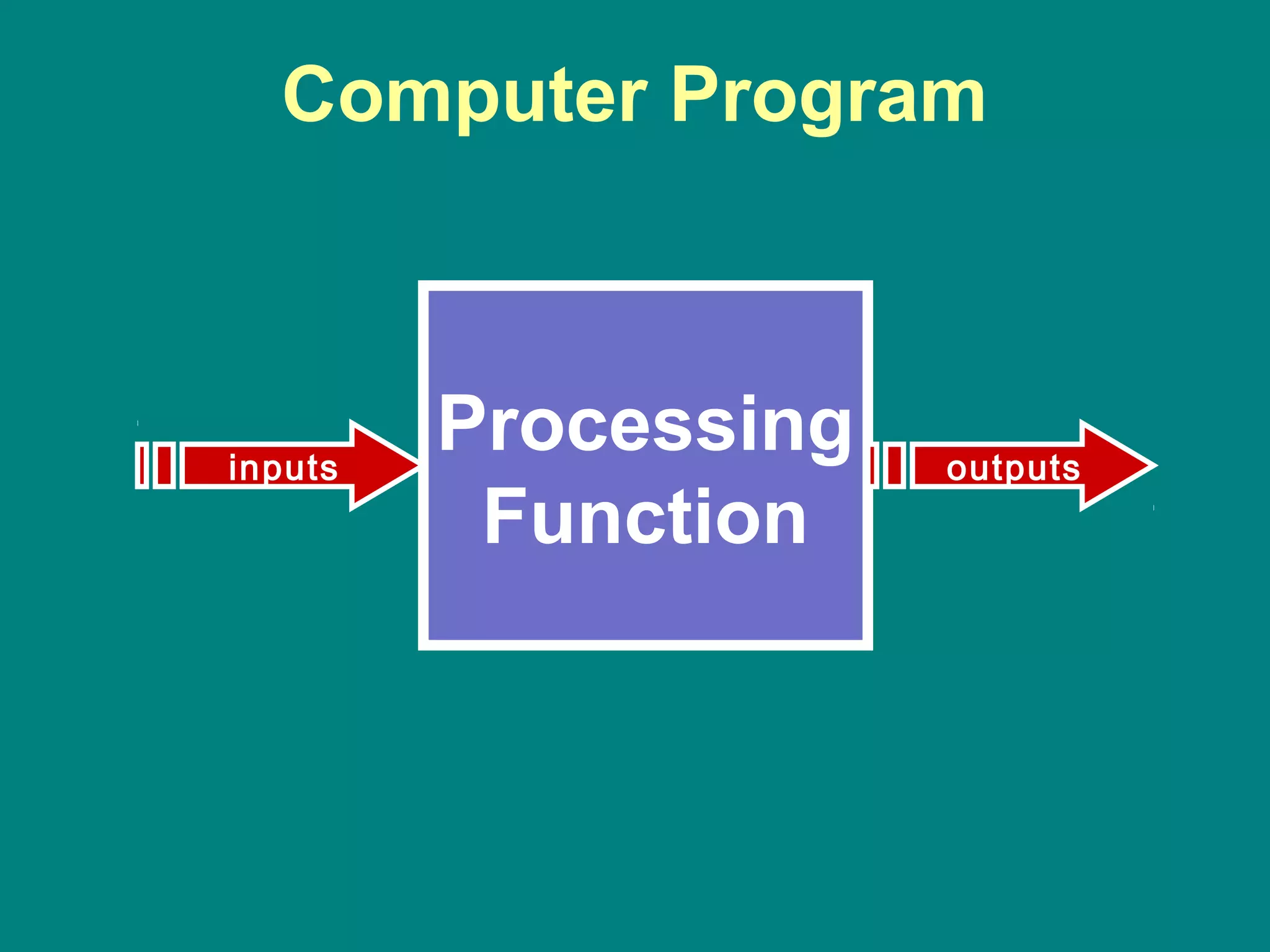
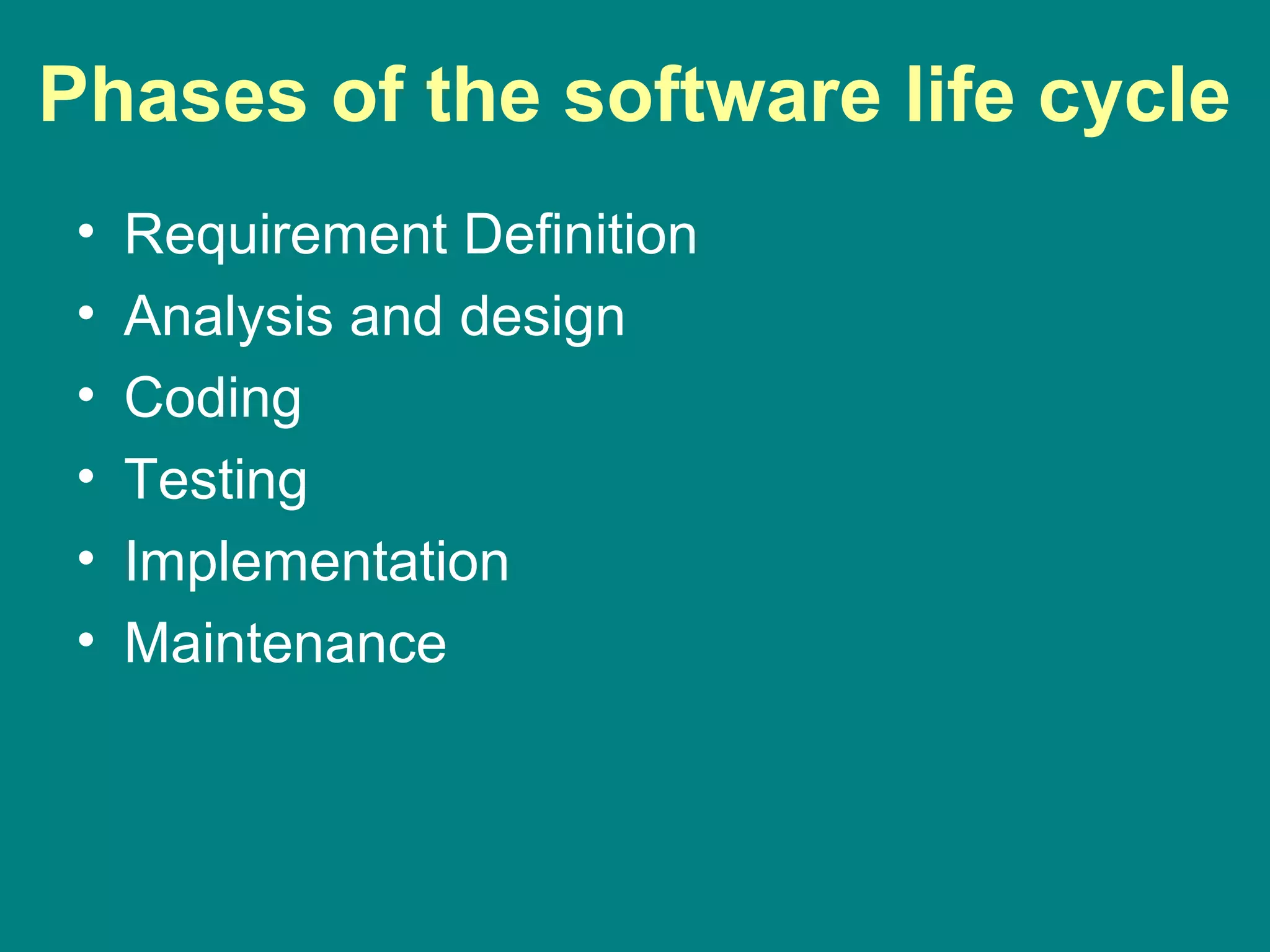
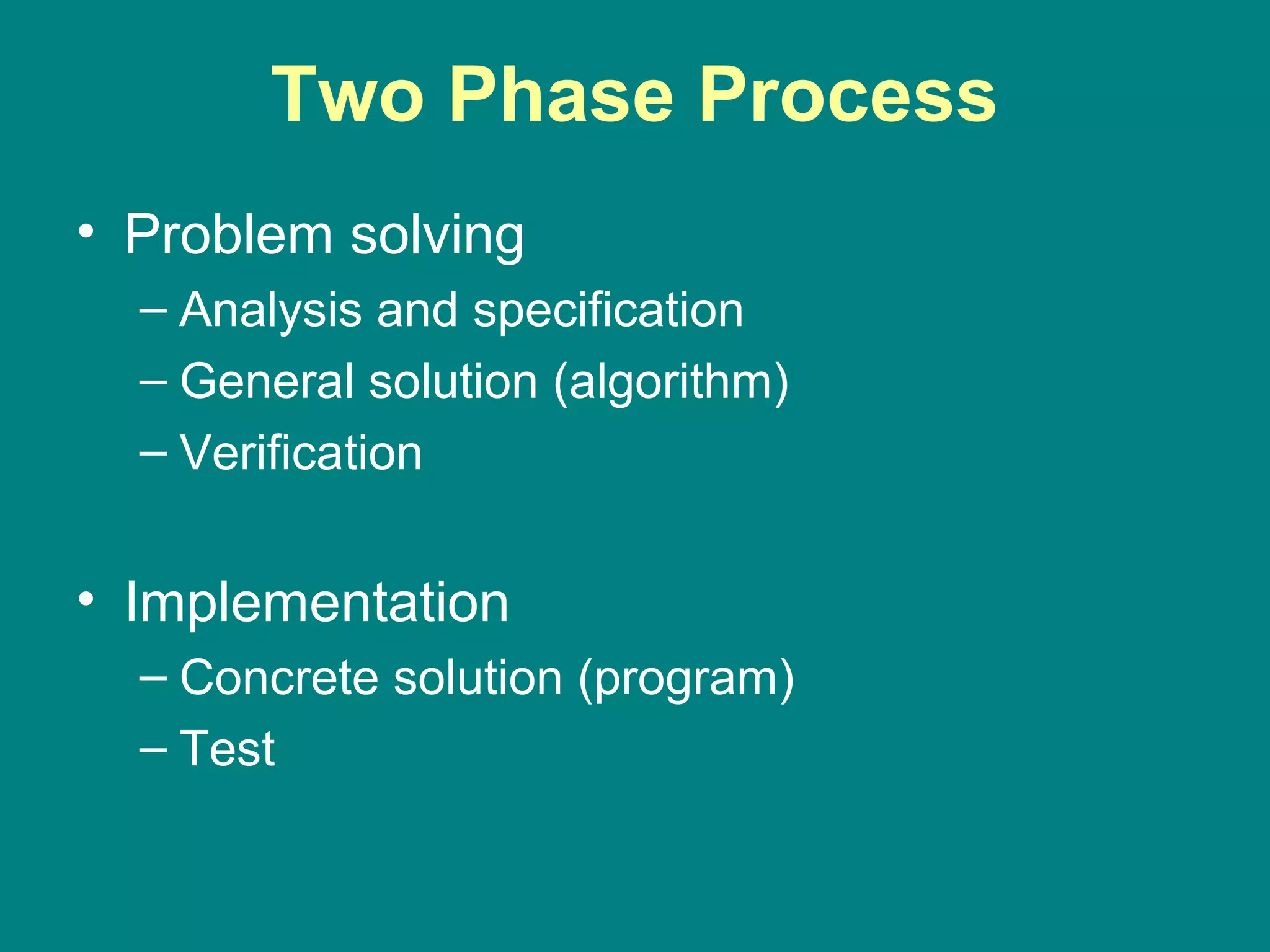
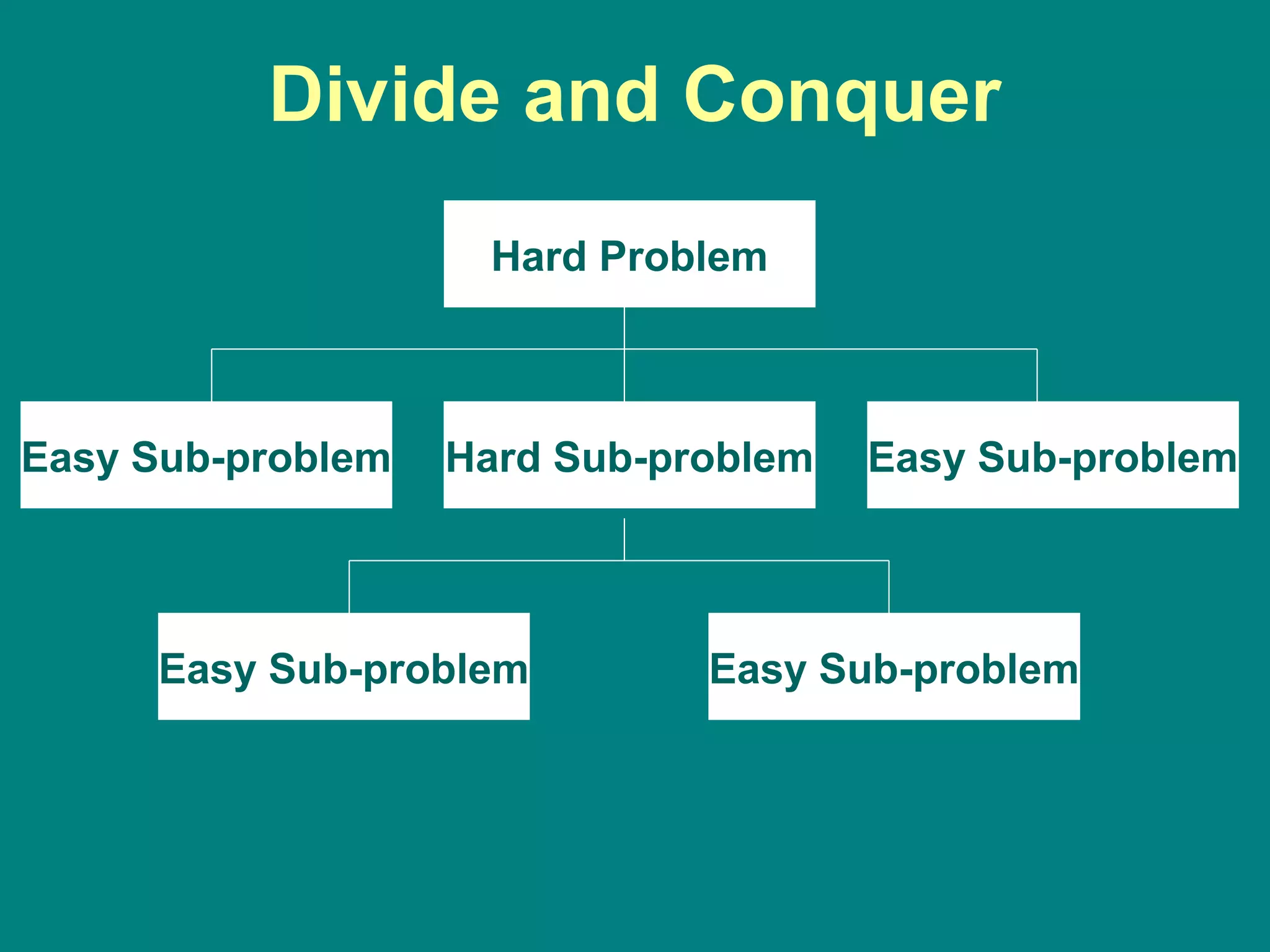
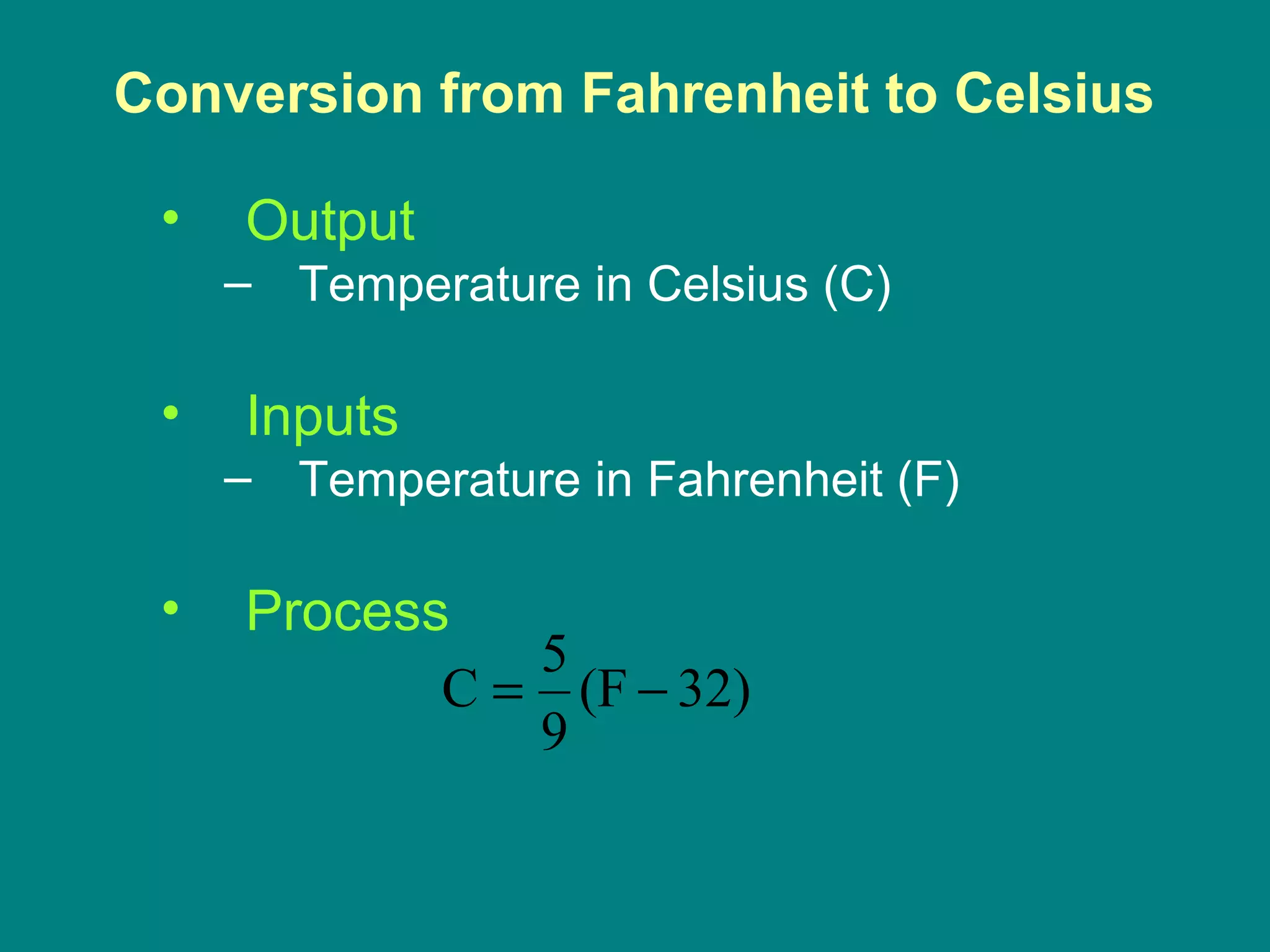
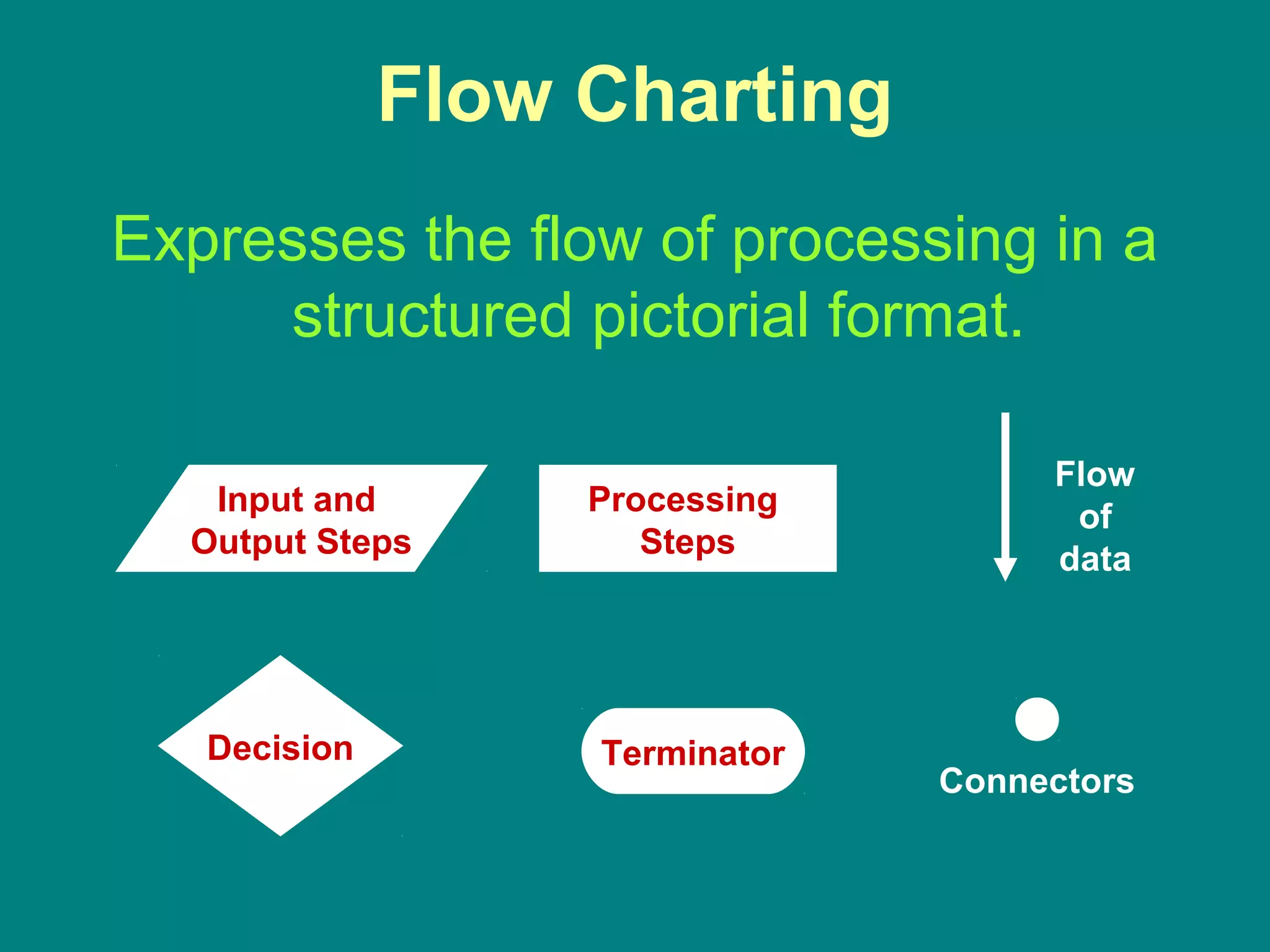
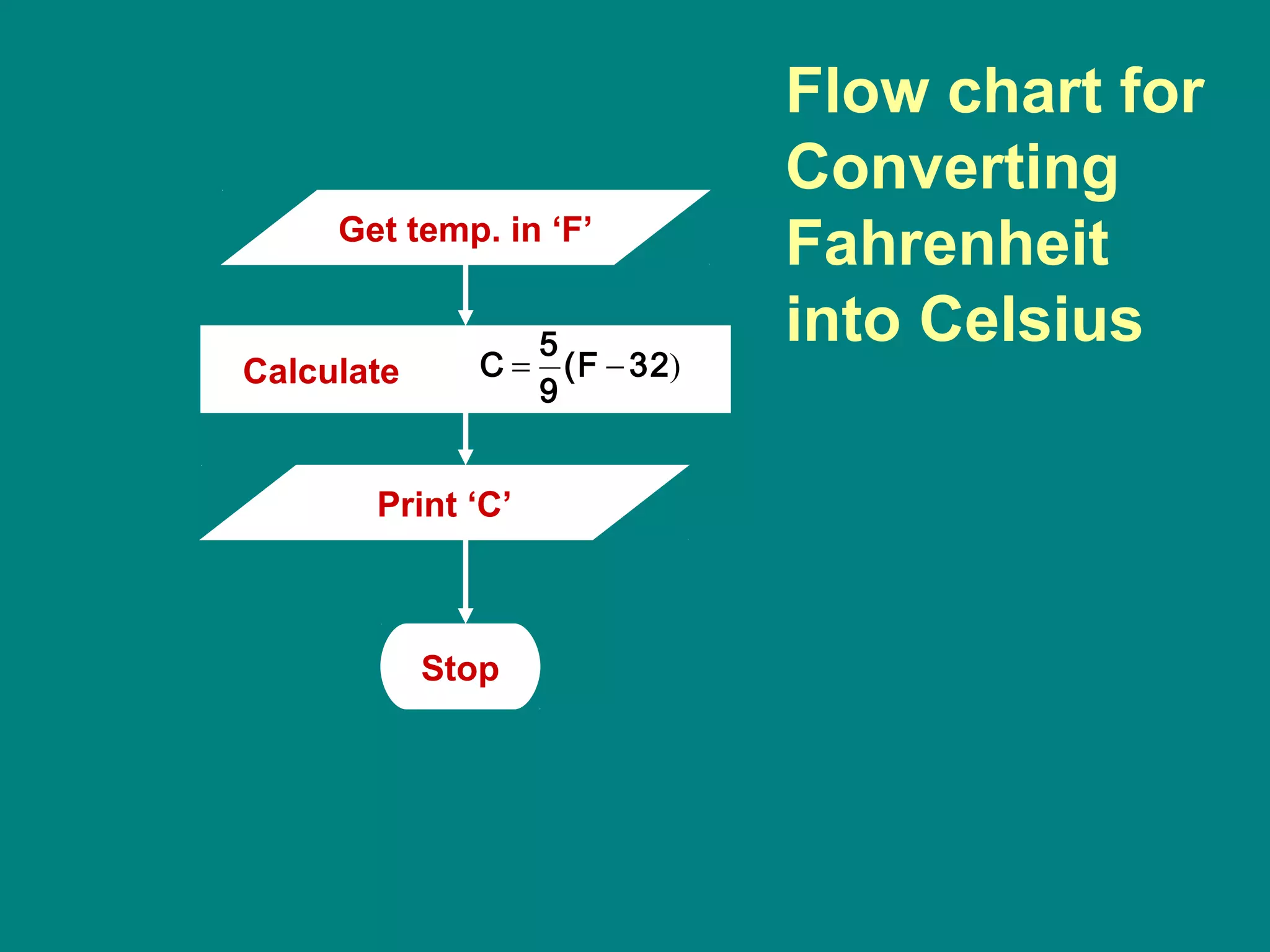
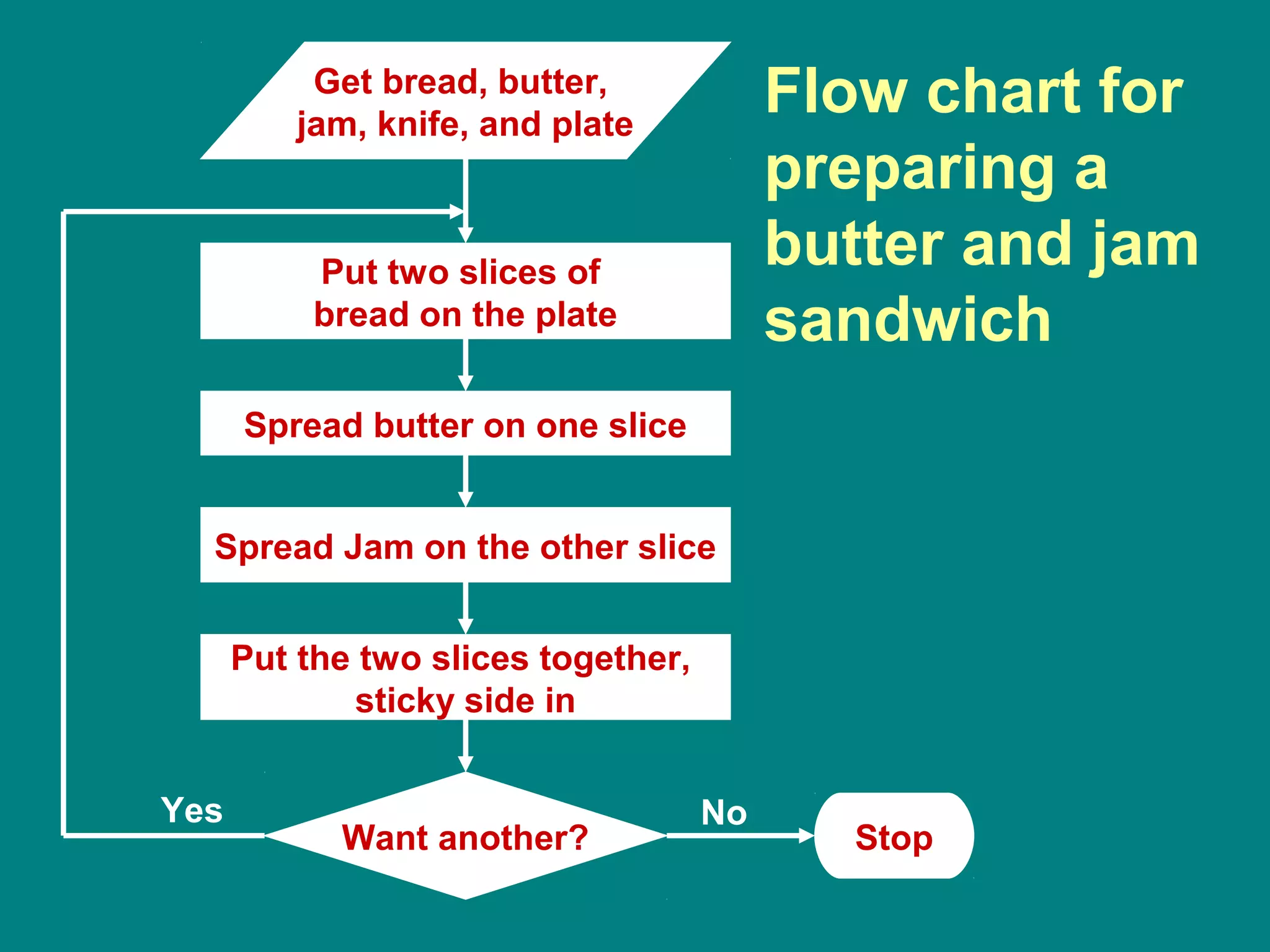
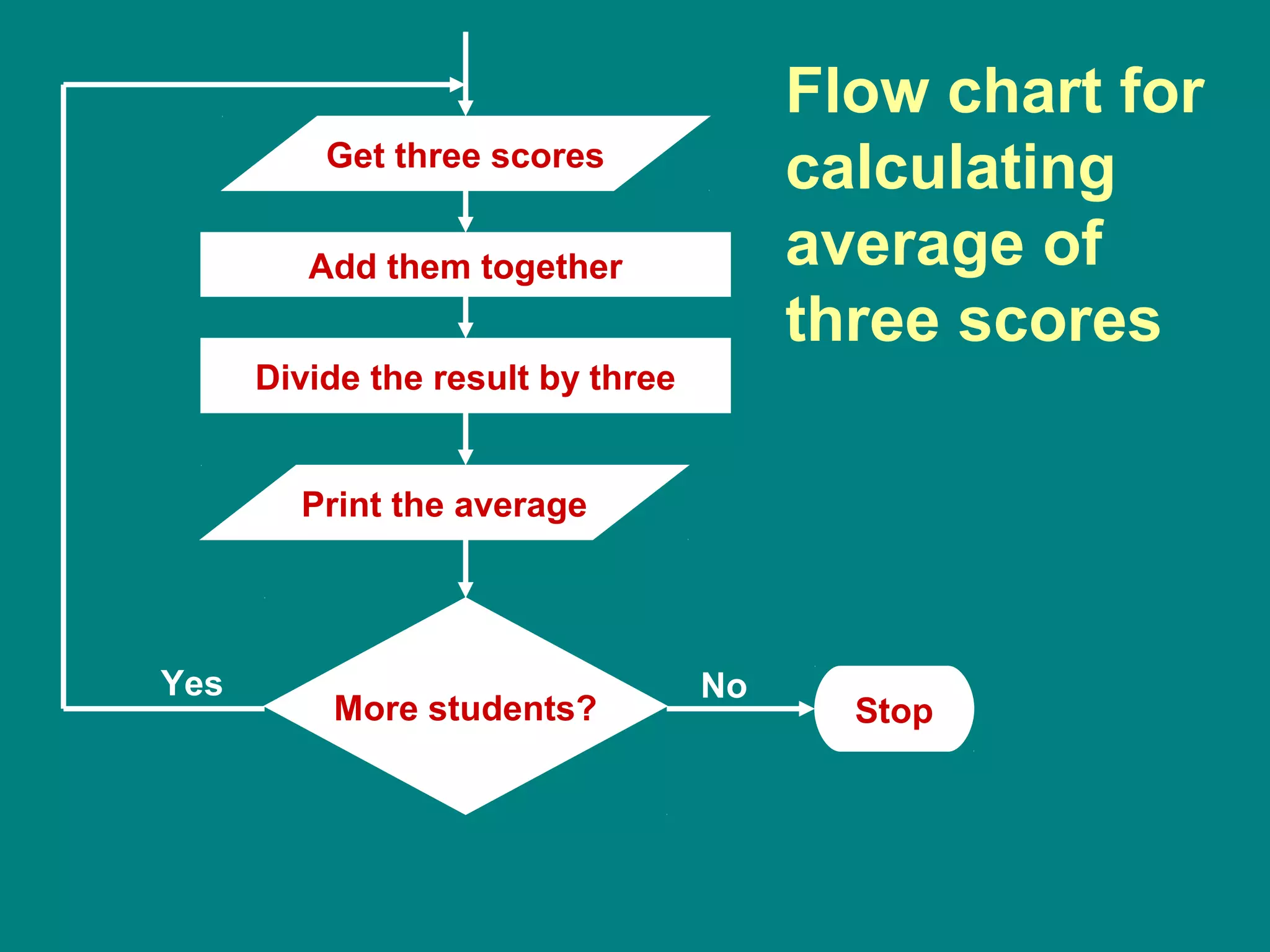
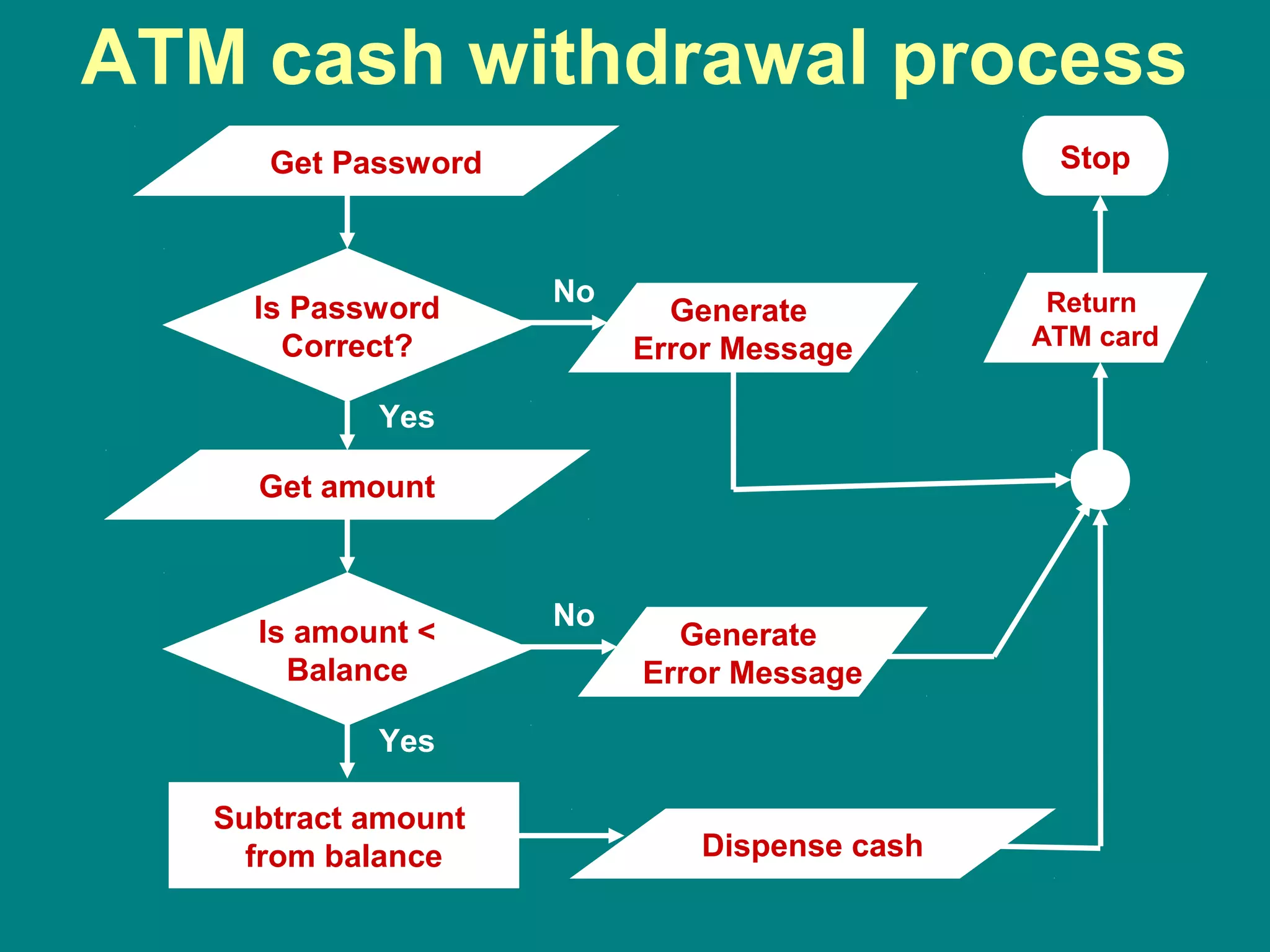
Computer programming involves planning a sequence of instructions for a computer to follow to solve a problem. It is a multi-step process that includes analyzing the problem, developing algorithmic instructions, and communicating the program to the computer. Common problem solving techniques used in programming include asking questions, looking for similarities, divide-and-conquer, and merging solutions. Programs allow computers to quickly and consistently repeat solutions.