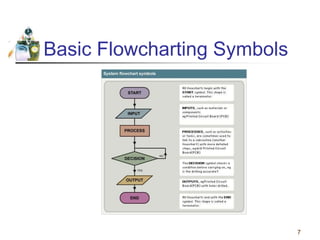
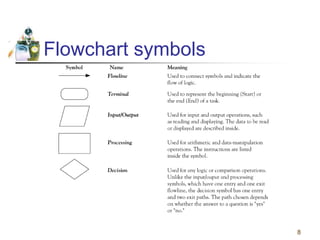
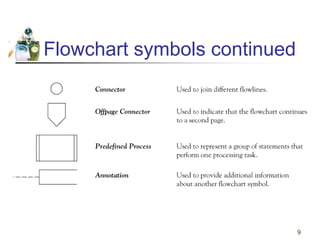
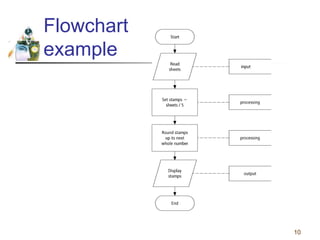
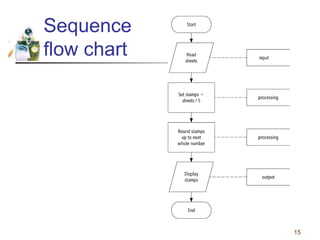
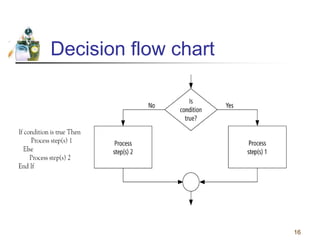
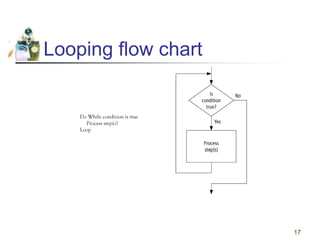
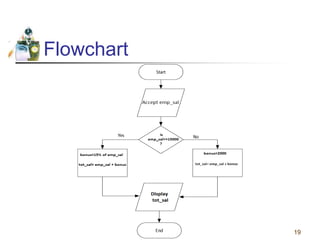
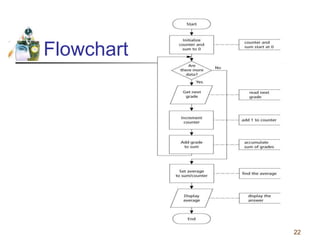
This document discusses flowcharts and pseudocode as tools for problem solving and programming. It provides examples of how to represent algorithms using flowcharts and pseudocode. Flowcharts graphically show the logical steps and relationships between steps to solve a problem. Pseudocode uses English-like phrases to outline the steps. The document gives examples of flowcharts and pseudocode for problems like calculating postage for letters and finding a class average grade. It also discusses basic flowchart symbols and programming structures like sequence, decision, and looping.