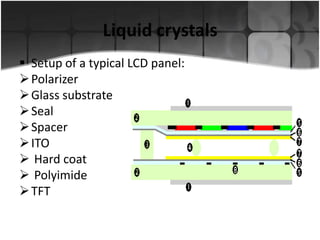
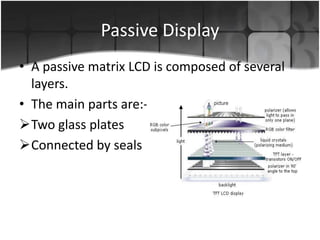
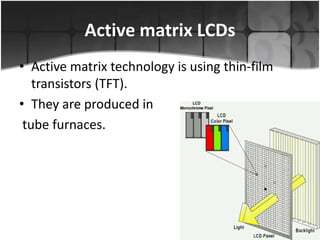
Flat panel displays are thin, lightweight electronic visual displays that use technologies like LCD, LED, OLED, and plasma. They have largely replaced bulkier CRT displays. There are two main types: volatile displays that require constant refreshing like LCDs, and static displays that maintain image without refreshing like some e-readers. Flat panels are used in devices like laptops, phones, TVs due to their thinness and portability compared to CRTs.