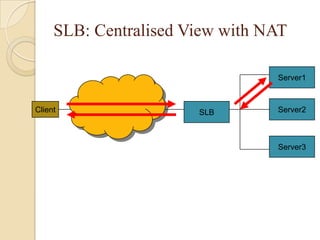
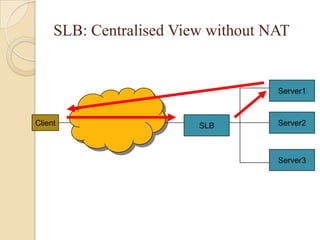
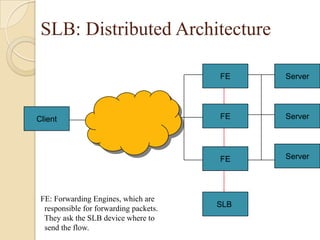
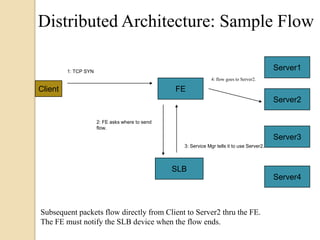
This document discusses load balancing, which is a technique for distributing work across multiple computing resources like CPUs, disk drives, and network links. The goals of load balancing are to maximize resource utilization, throughput, and response time while avoiding overloads and crashes. Static load balancing involves preset mappings, while dynamic load balancing distributes workload in real-time. Common load balancing algorithms are round robin, least connections, and response time-based. Server load balancing distributes client requests to multiple backend servers and can operate in centralized or distributed architectures using network address translation or direct routing.