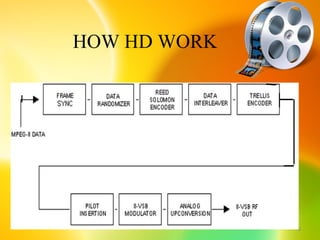
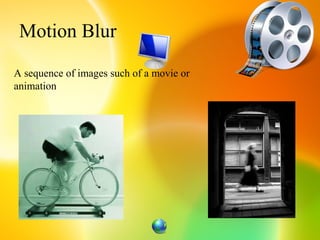
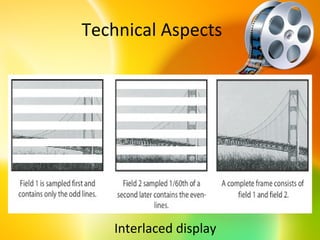
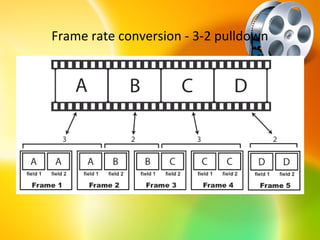
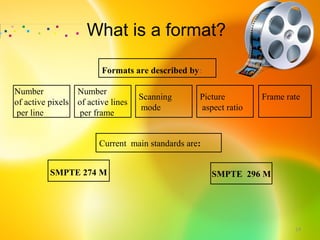
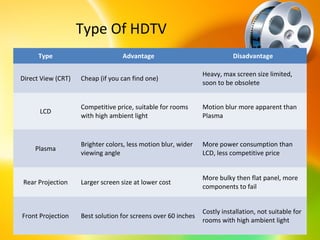
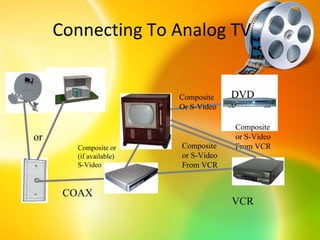
HDTV provides higher quality digital video broadcasts compared to analog television. It offers improved resolution, reduced noise and ghosting, and additional audio/data services. HDTV transitioned from analog to digital broadcasts and its adoption is growing. Key aspects include higher pixel counts, different display technologies like plasma and DLP, and higher frame rates that reduce motion blur compared to standard definition. HDTV connectivity requires components that support digital signals and higher resolutions. Its impact includes increased spending on equipment and production quality.