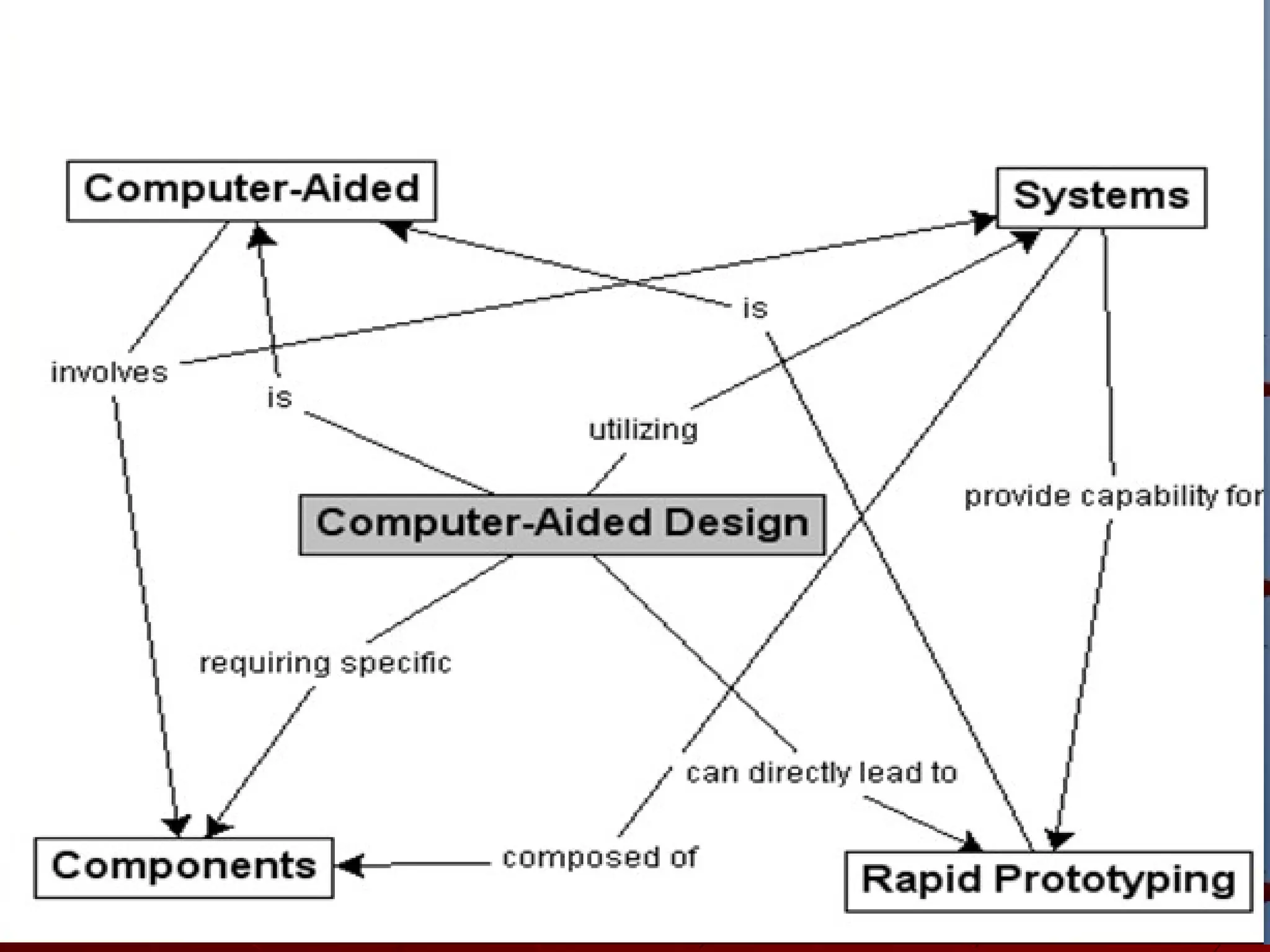
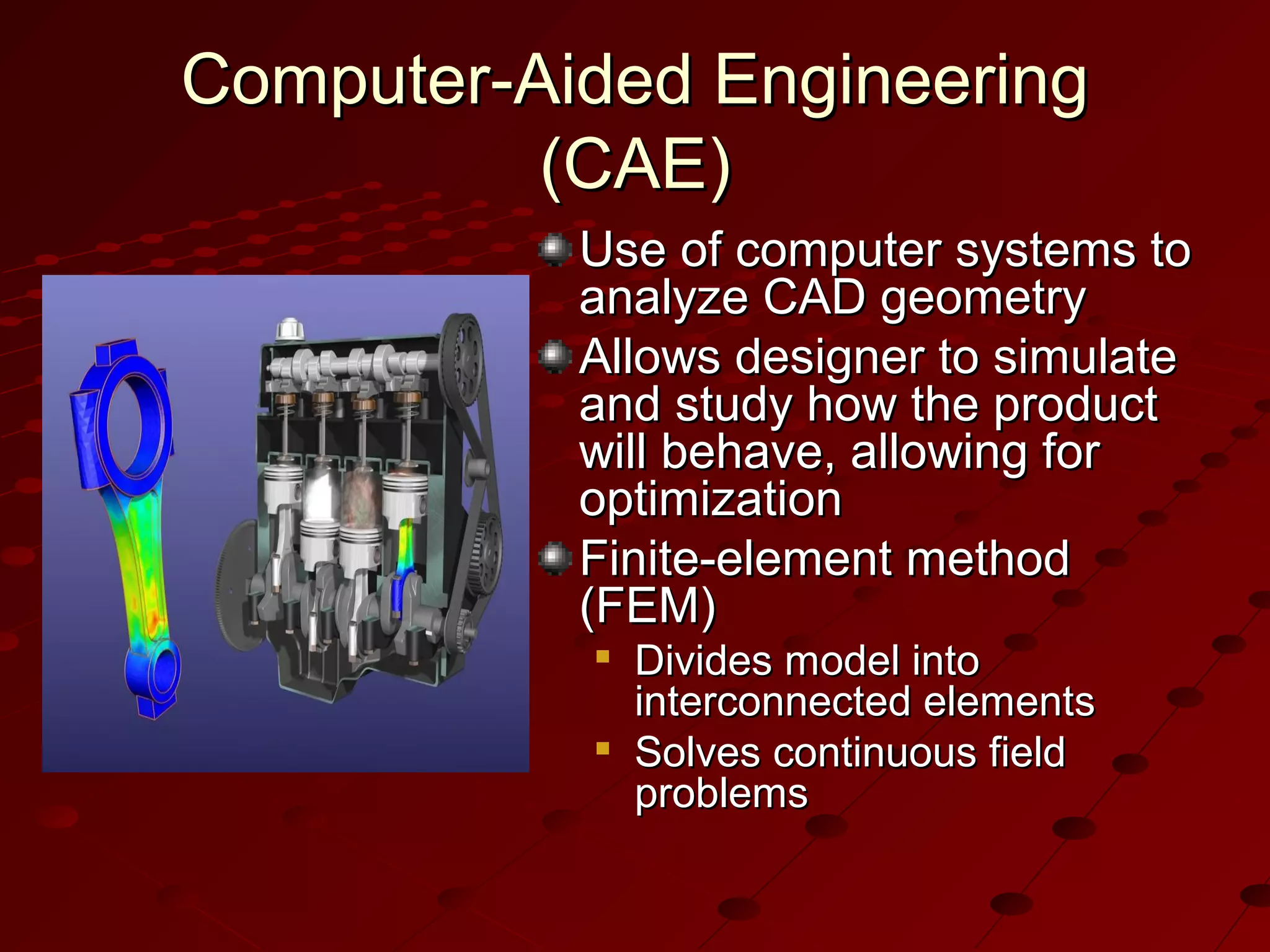
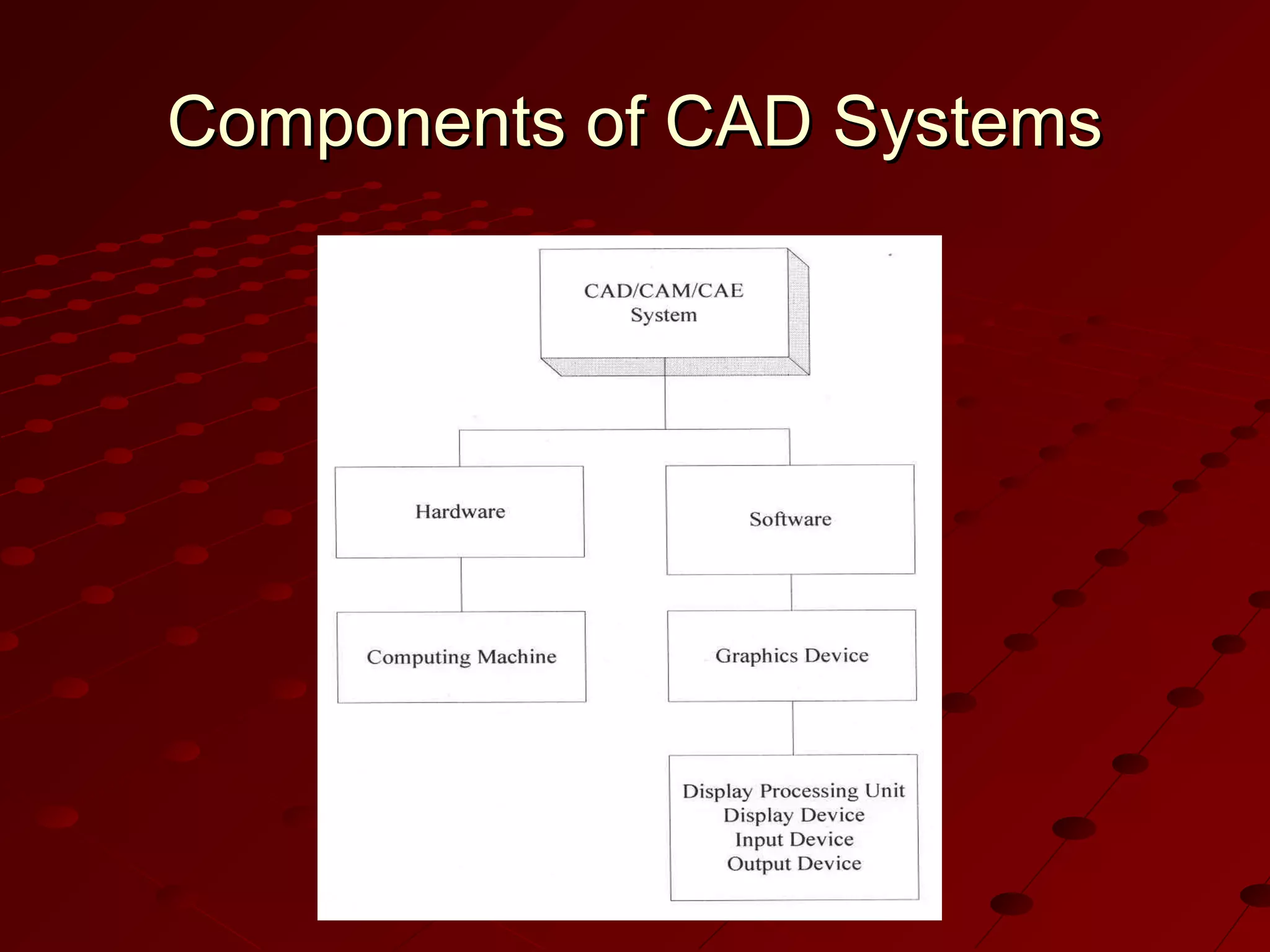
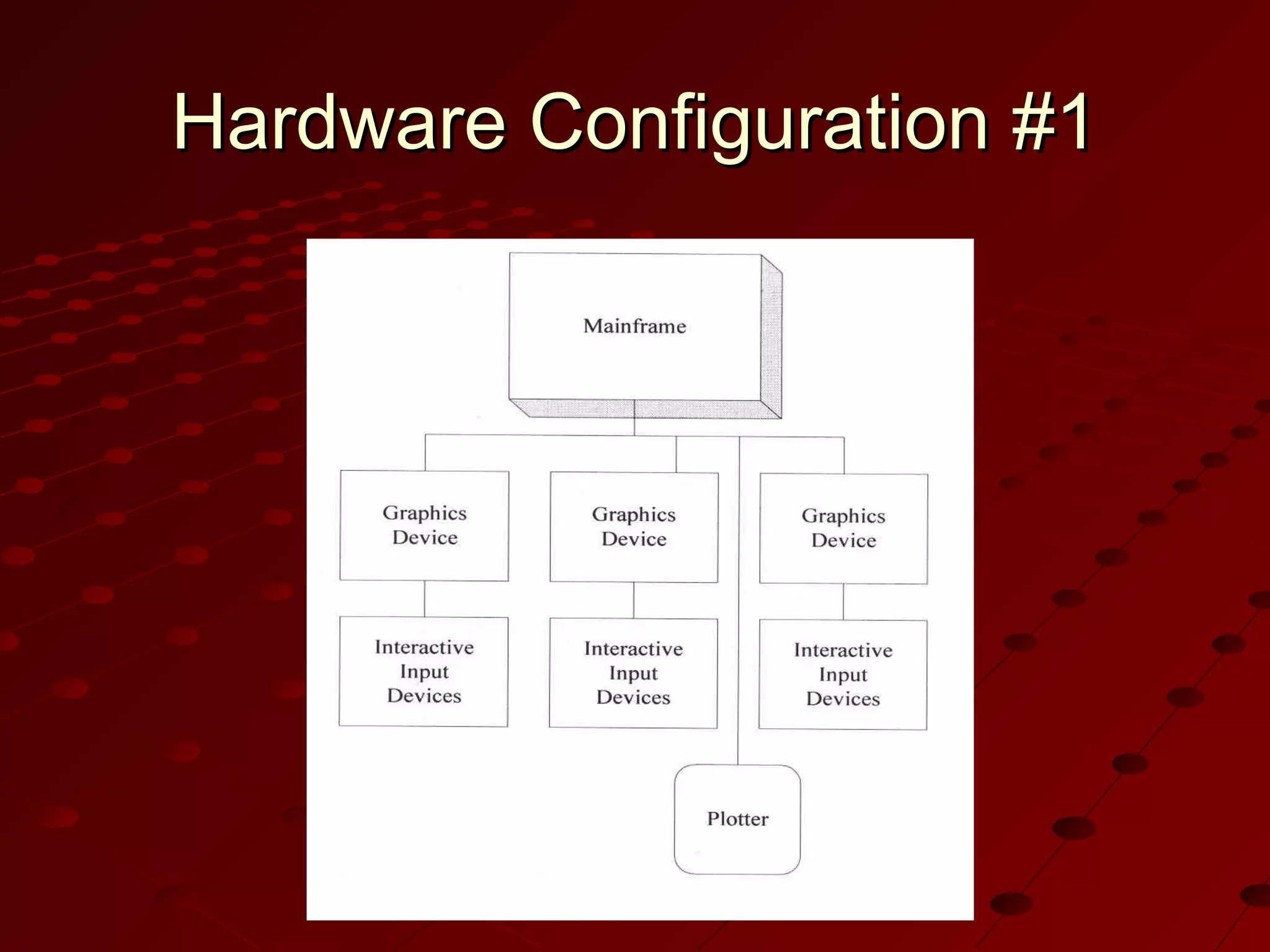
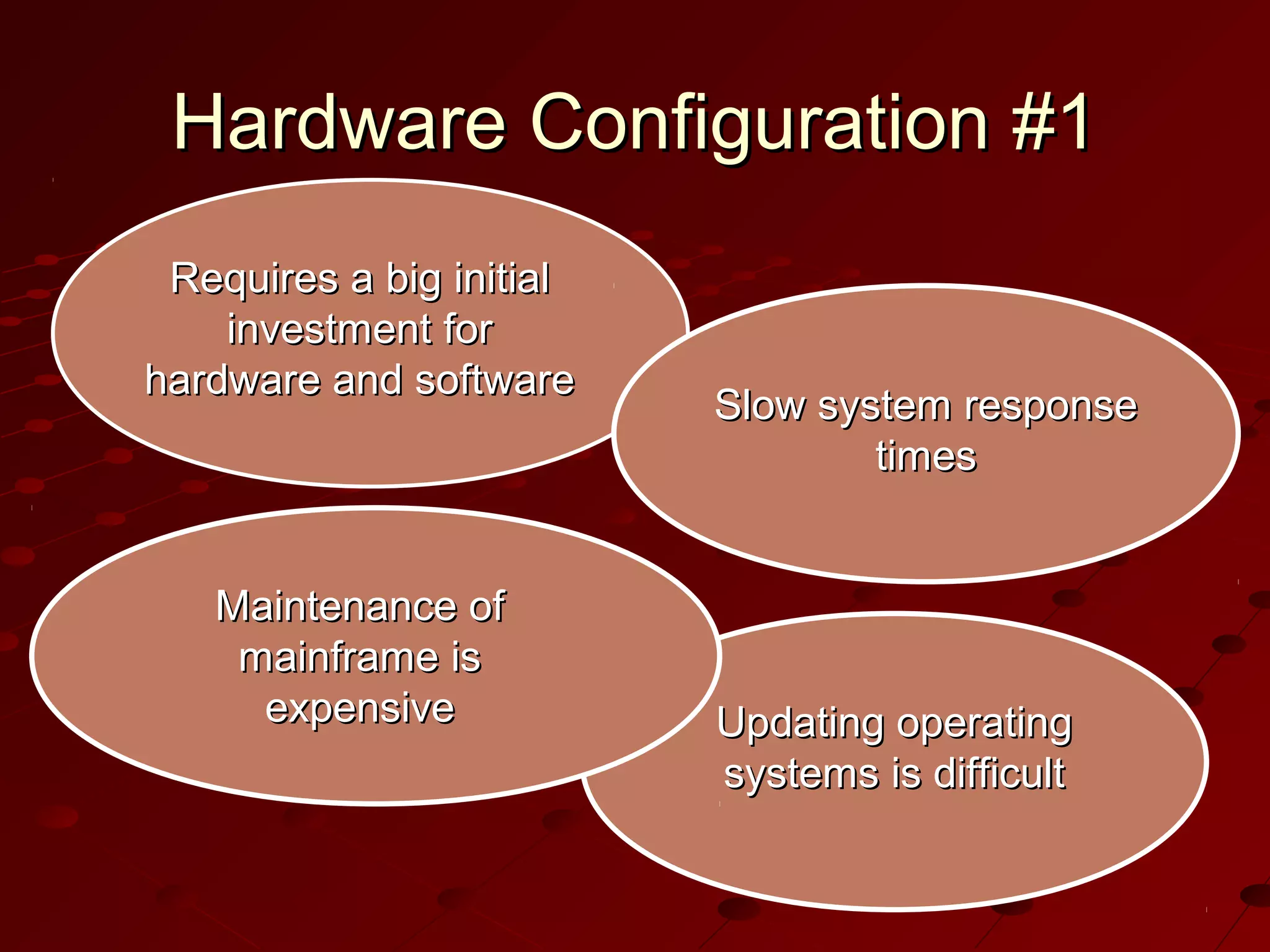
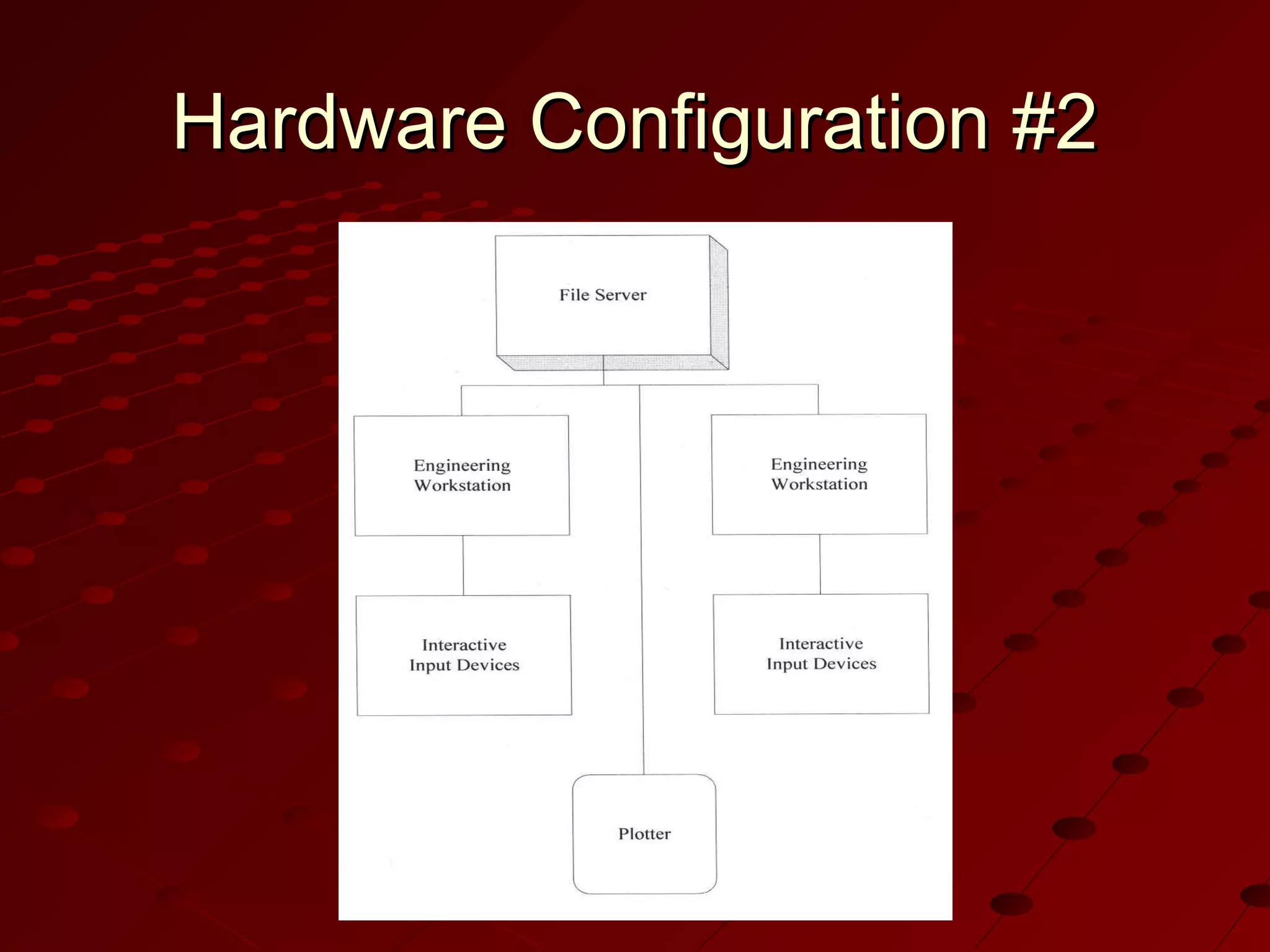
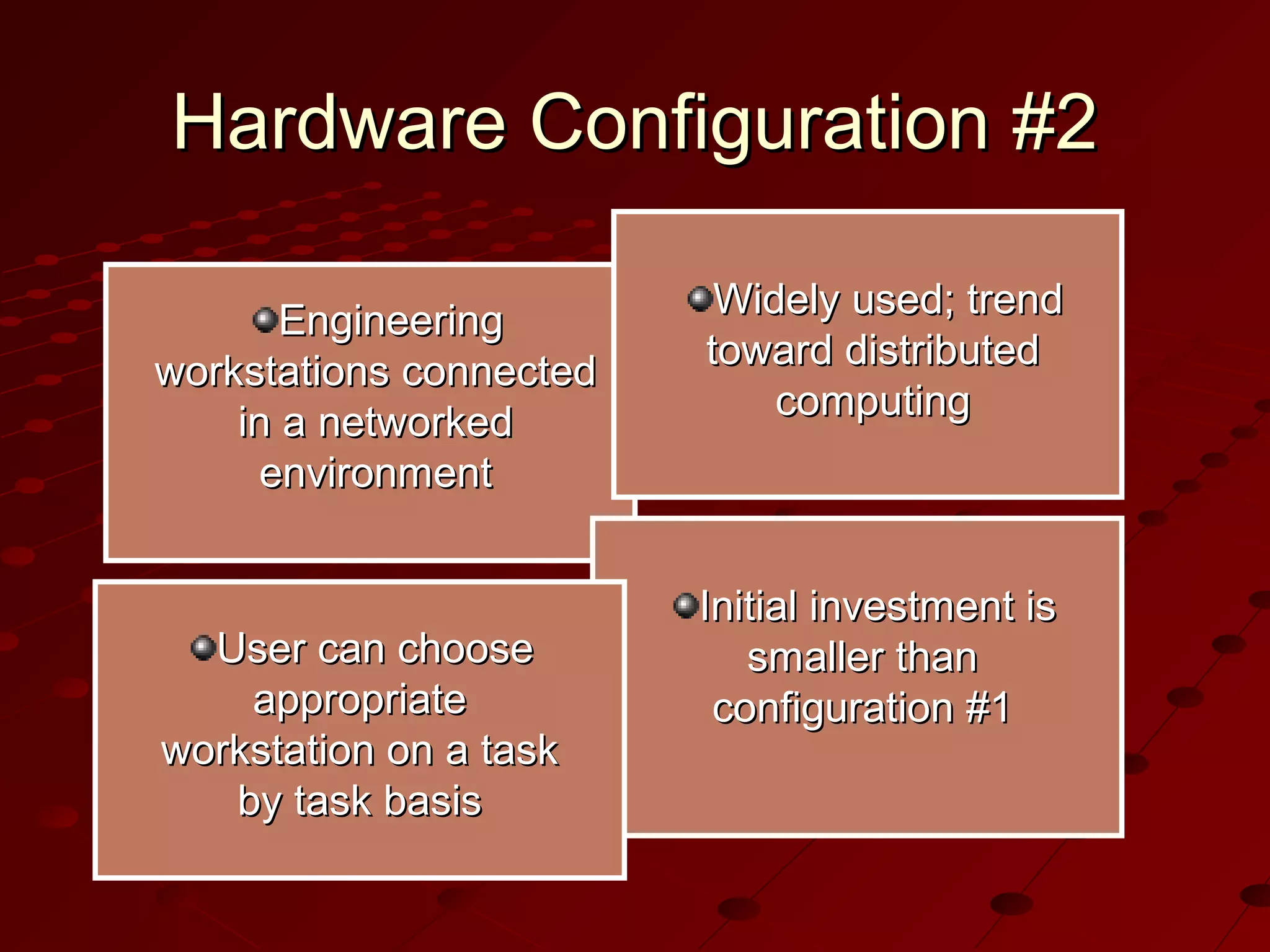
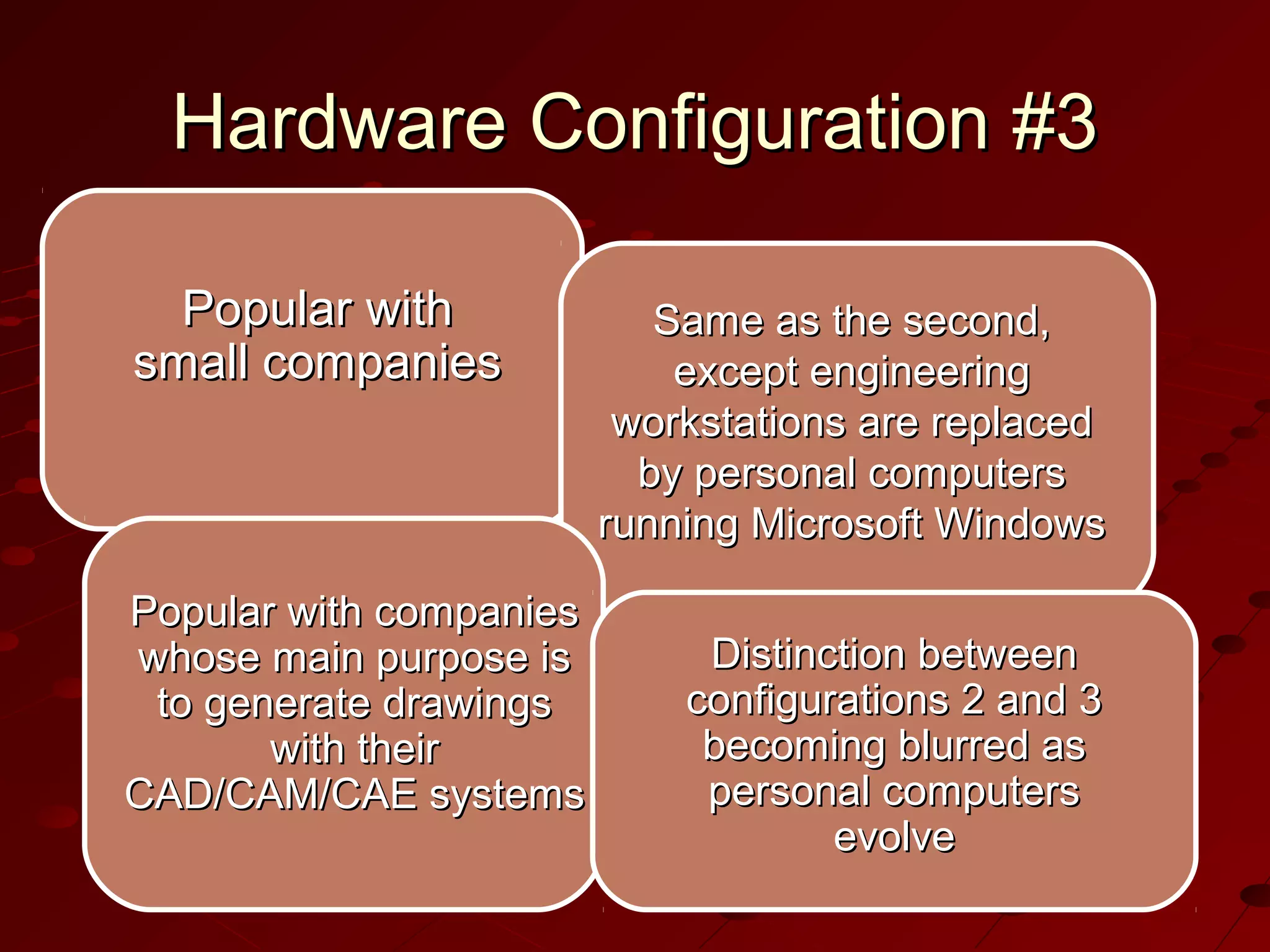
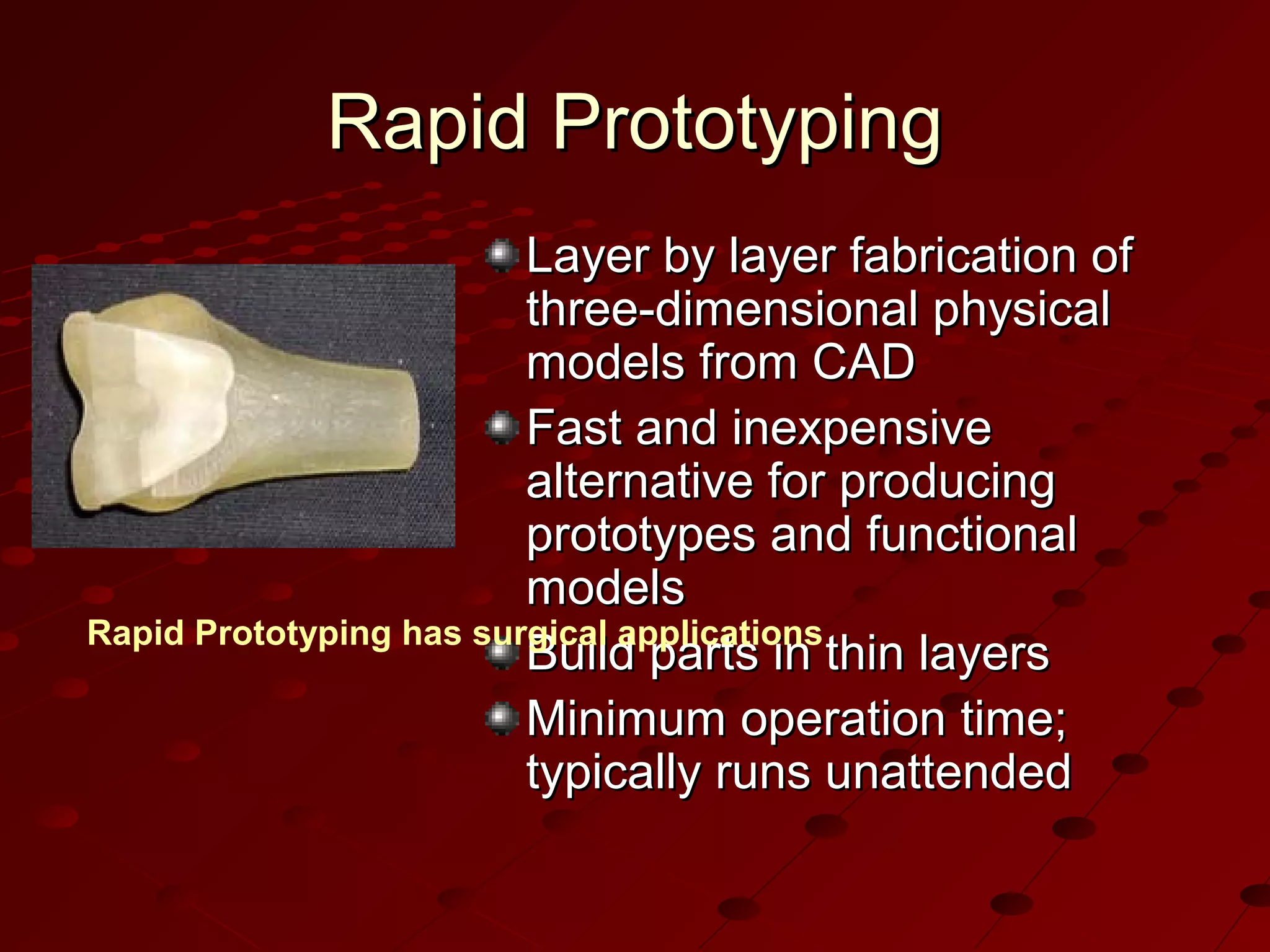
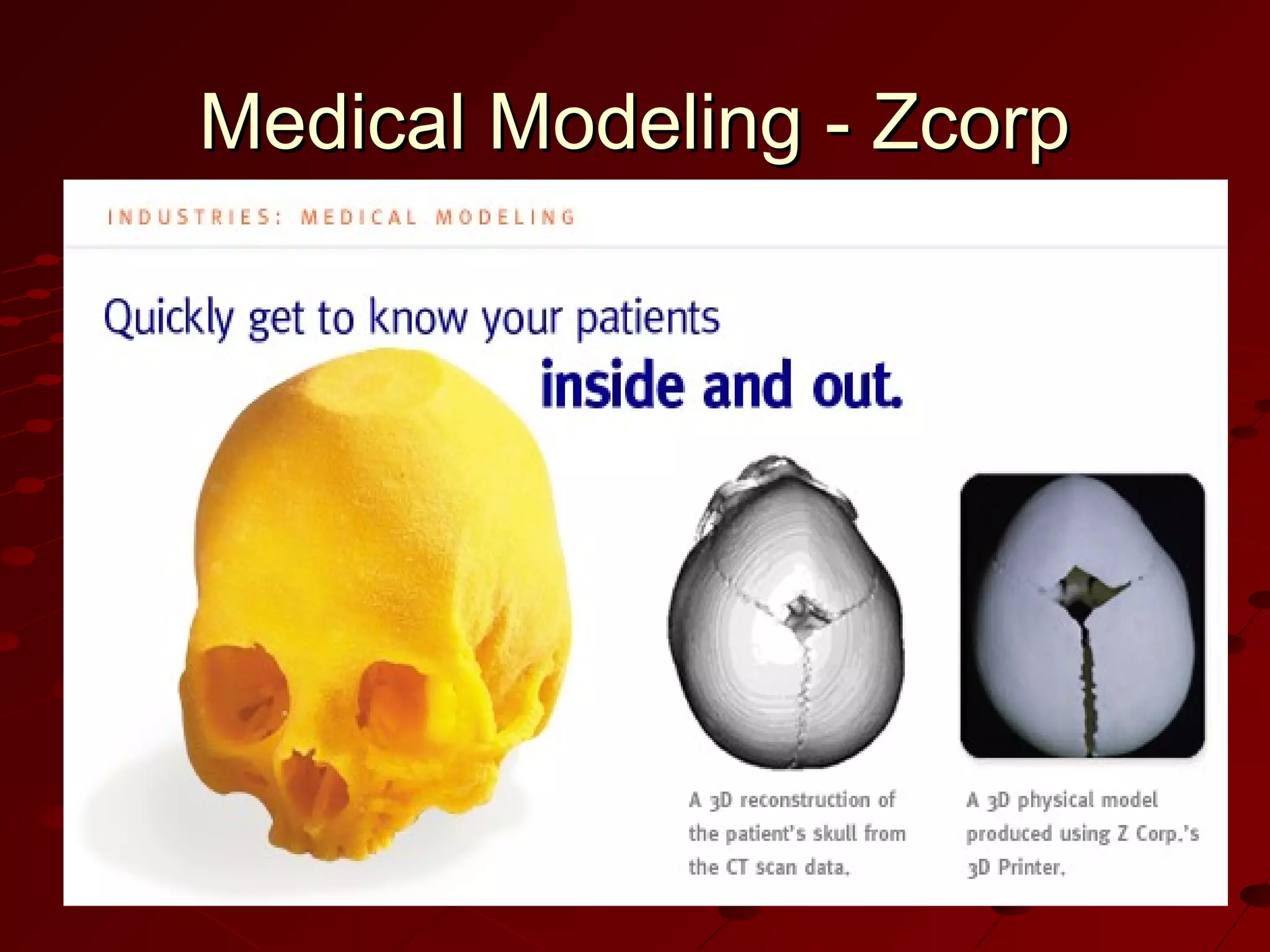
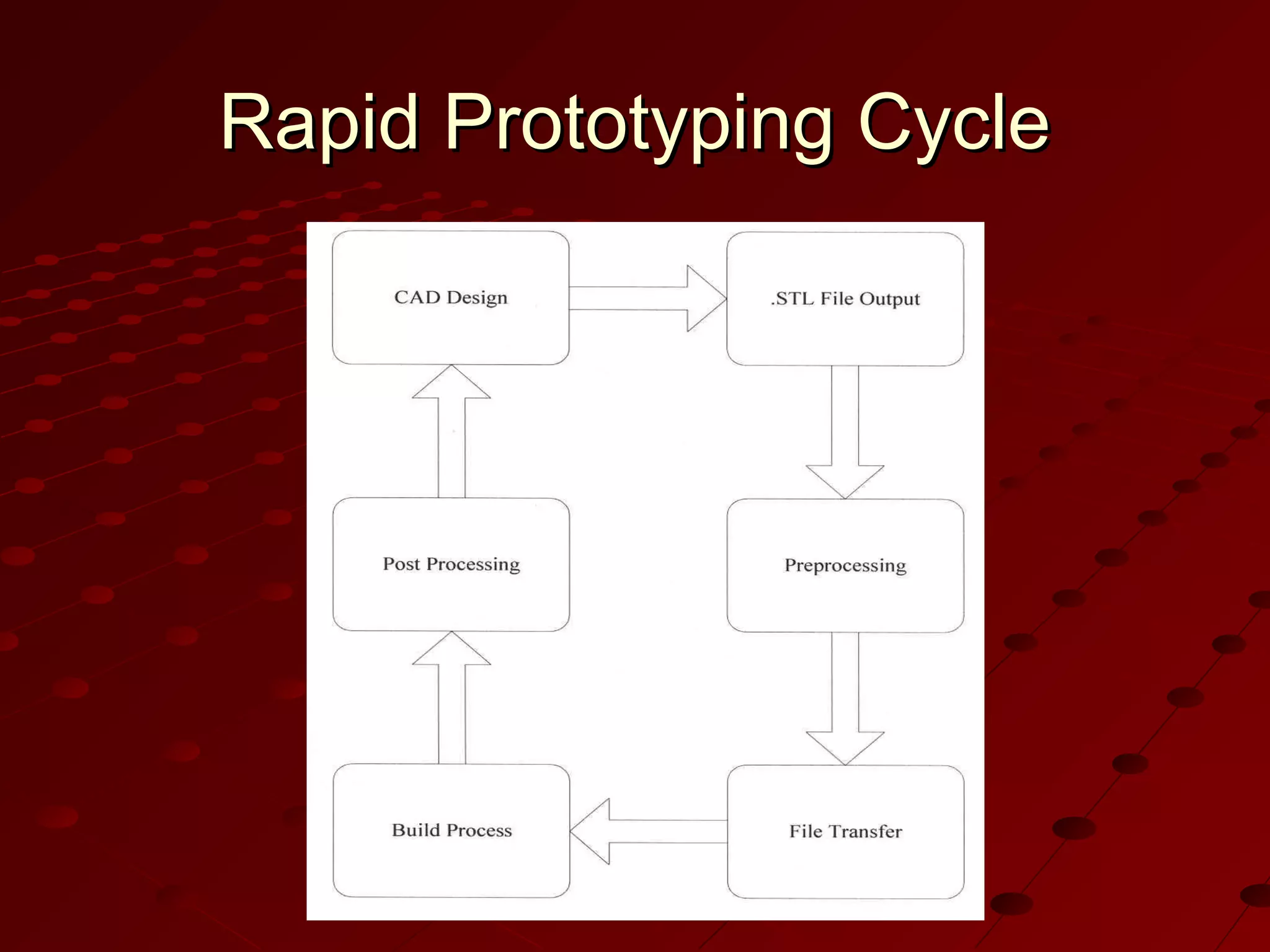
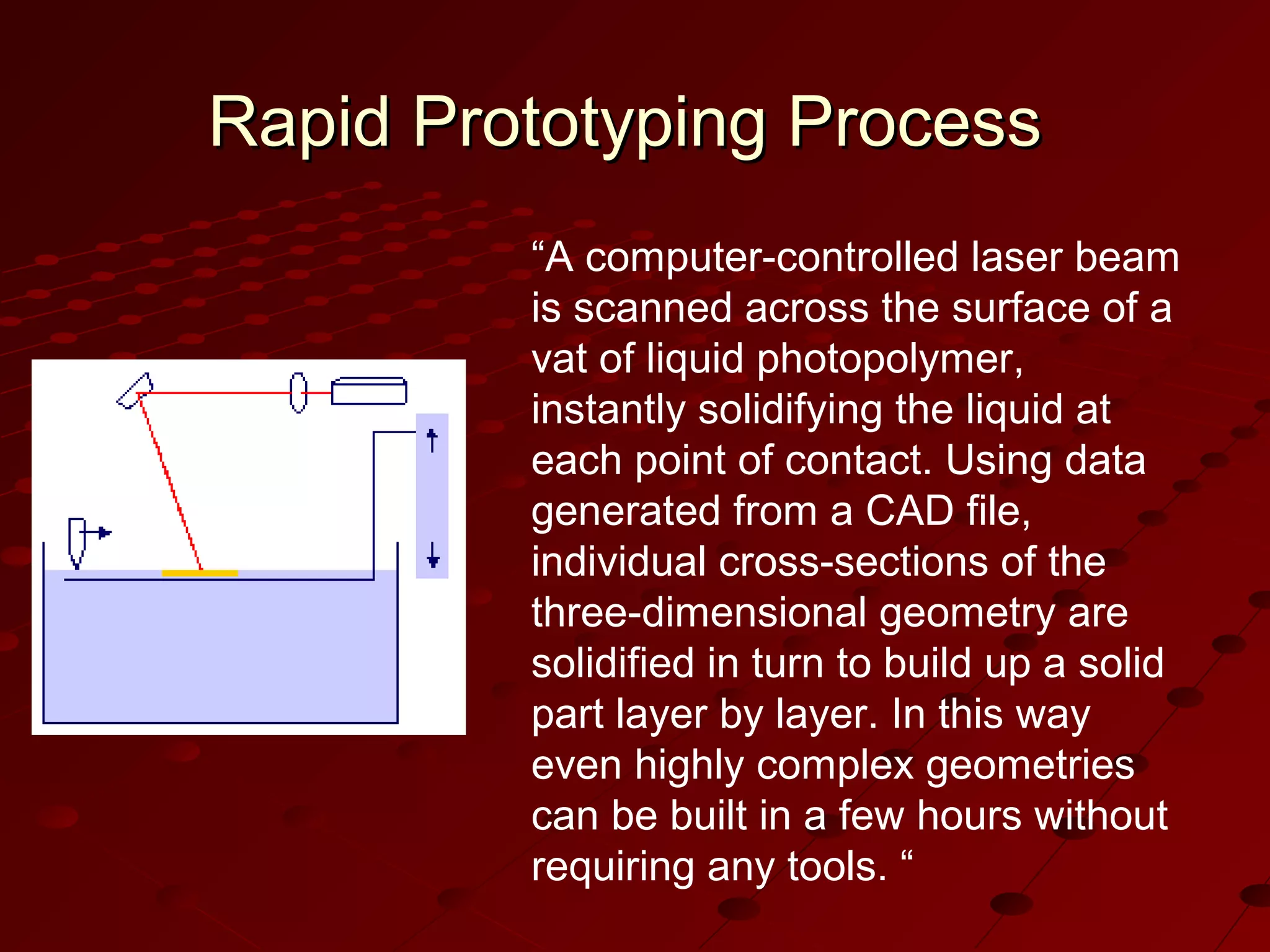
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) uses computer systems to assist in the creation, modification, analysis and optimization of designs. CAD defines the geometry of designs and performs tolerance analysis, mass property calculations and finite-element modeling. Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) uses computers to plan, manage and control manufacturing operations through direct or indirect interfaces with production resources like machine tools and robots. Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) analyzes CAD geometry through simulation to study how products will behave and allow for optimization using techniques like finite-element analysis.