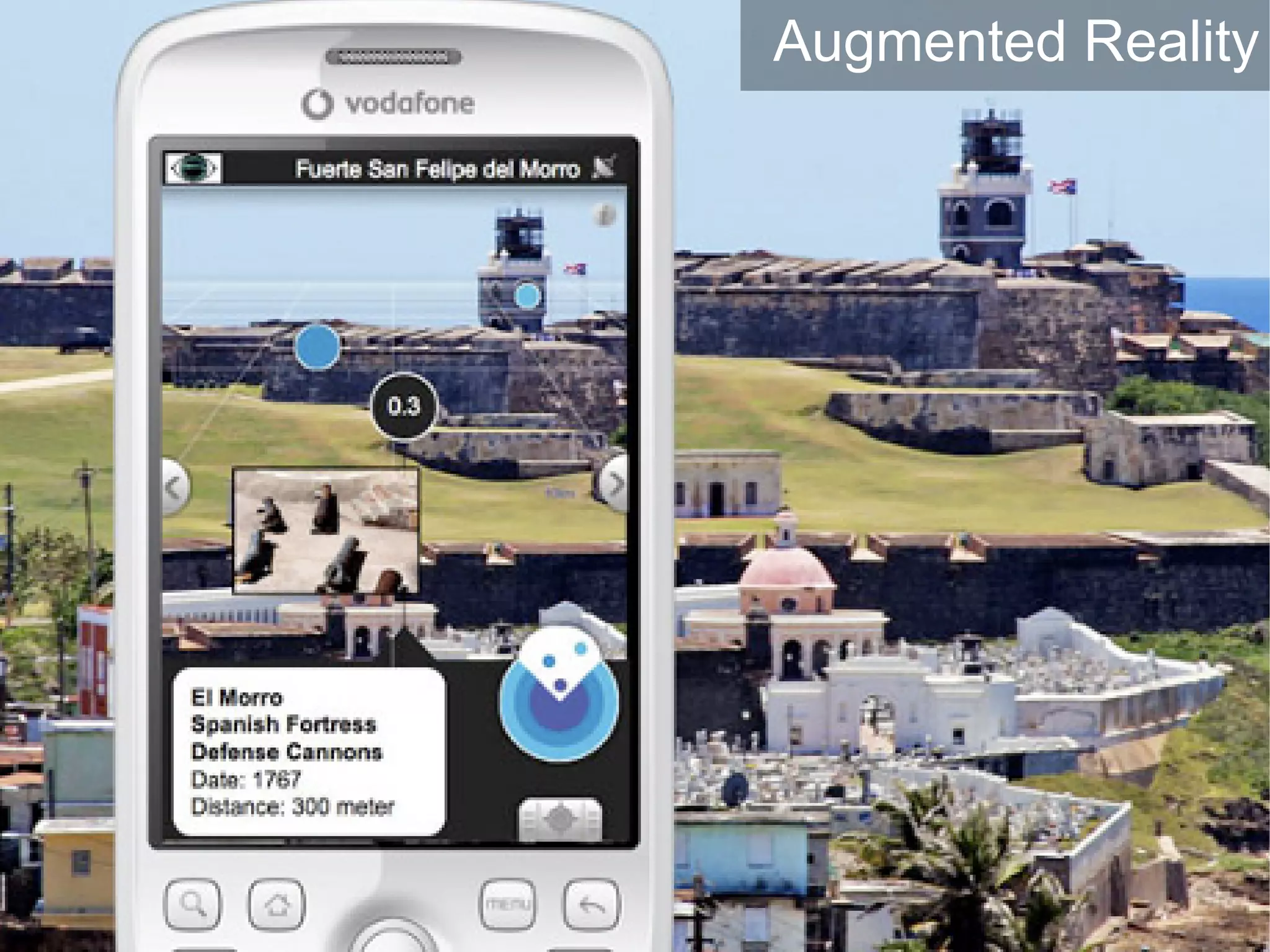
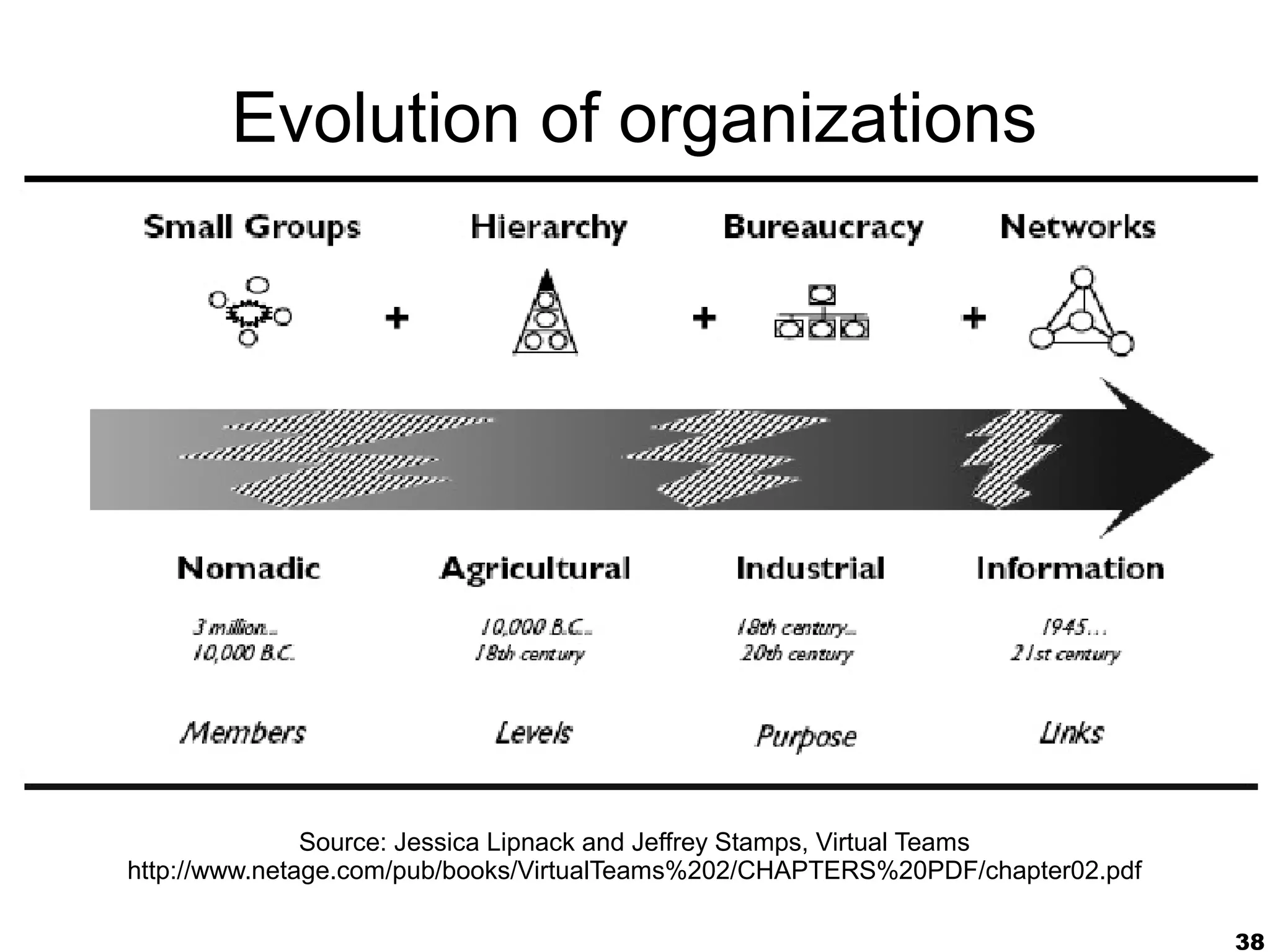
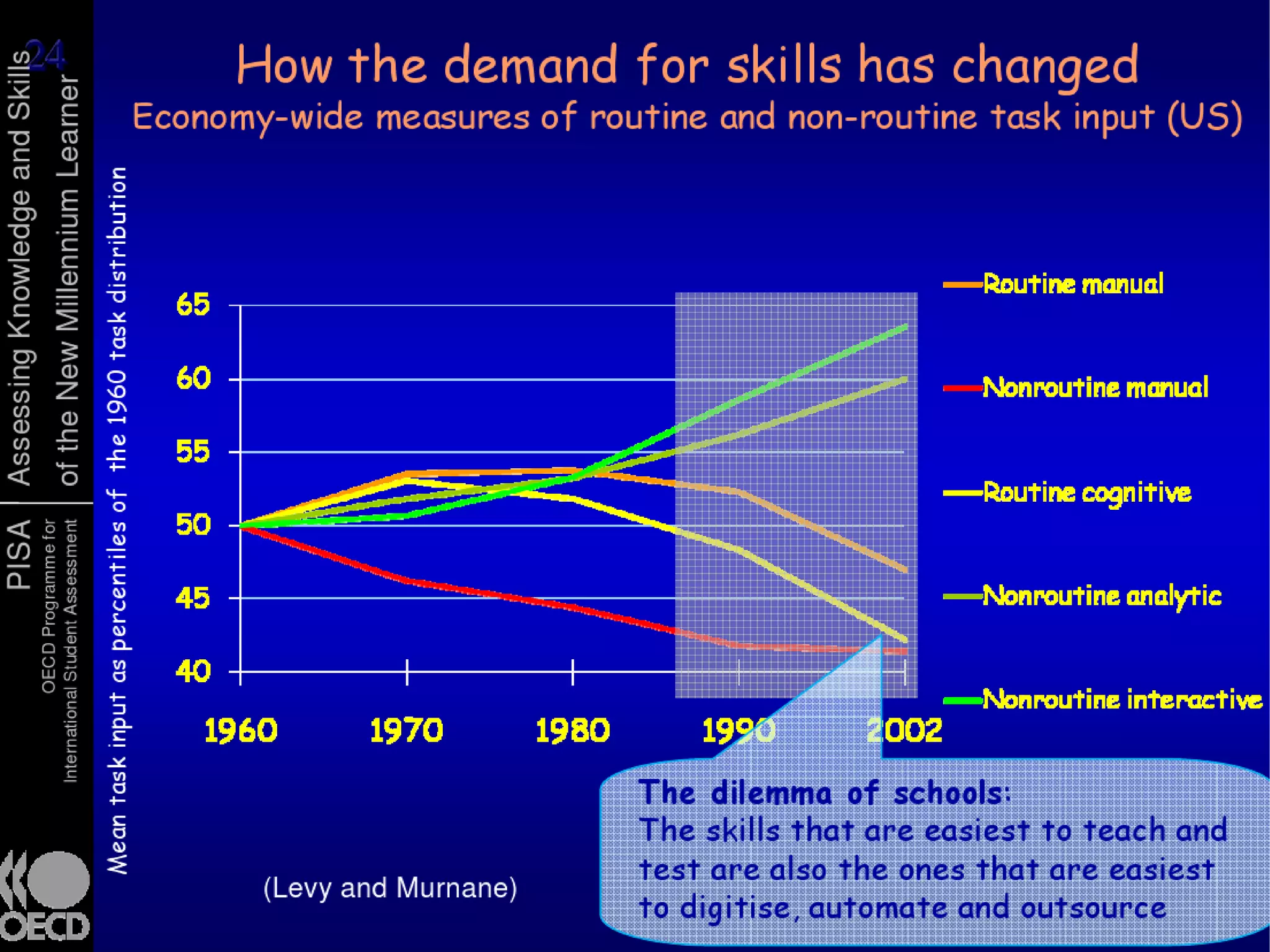
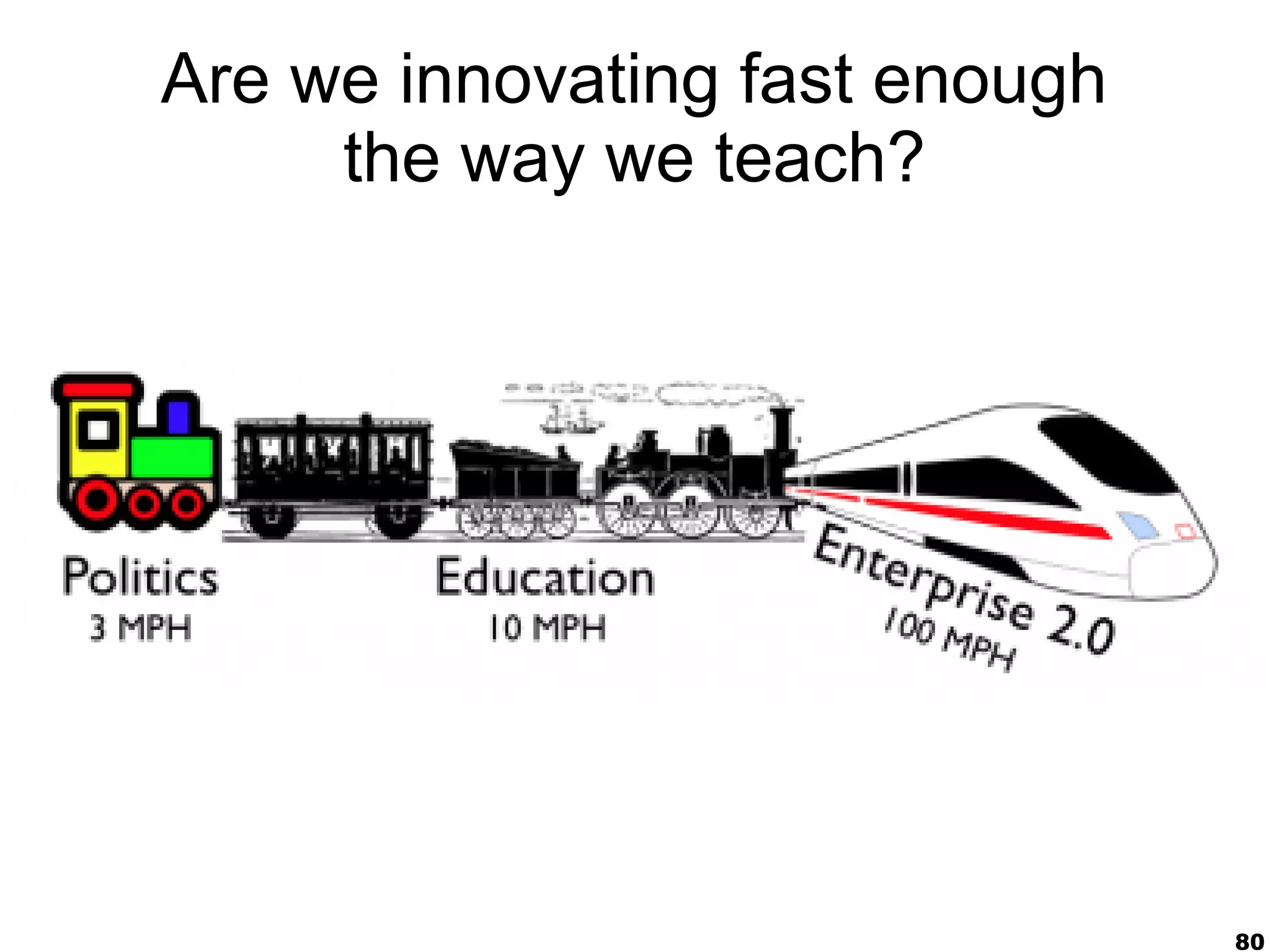
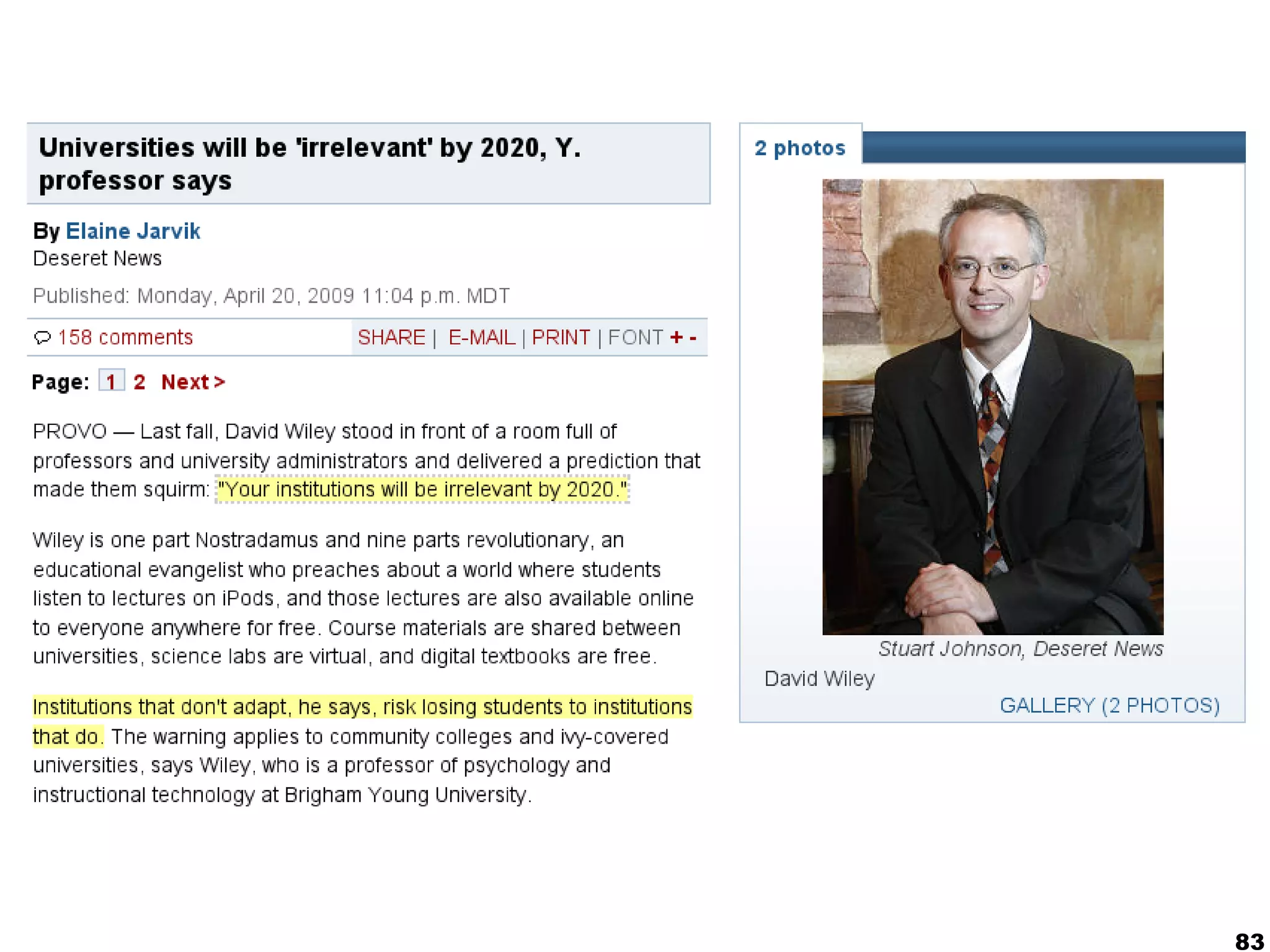
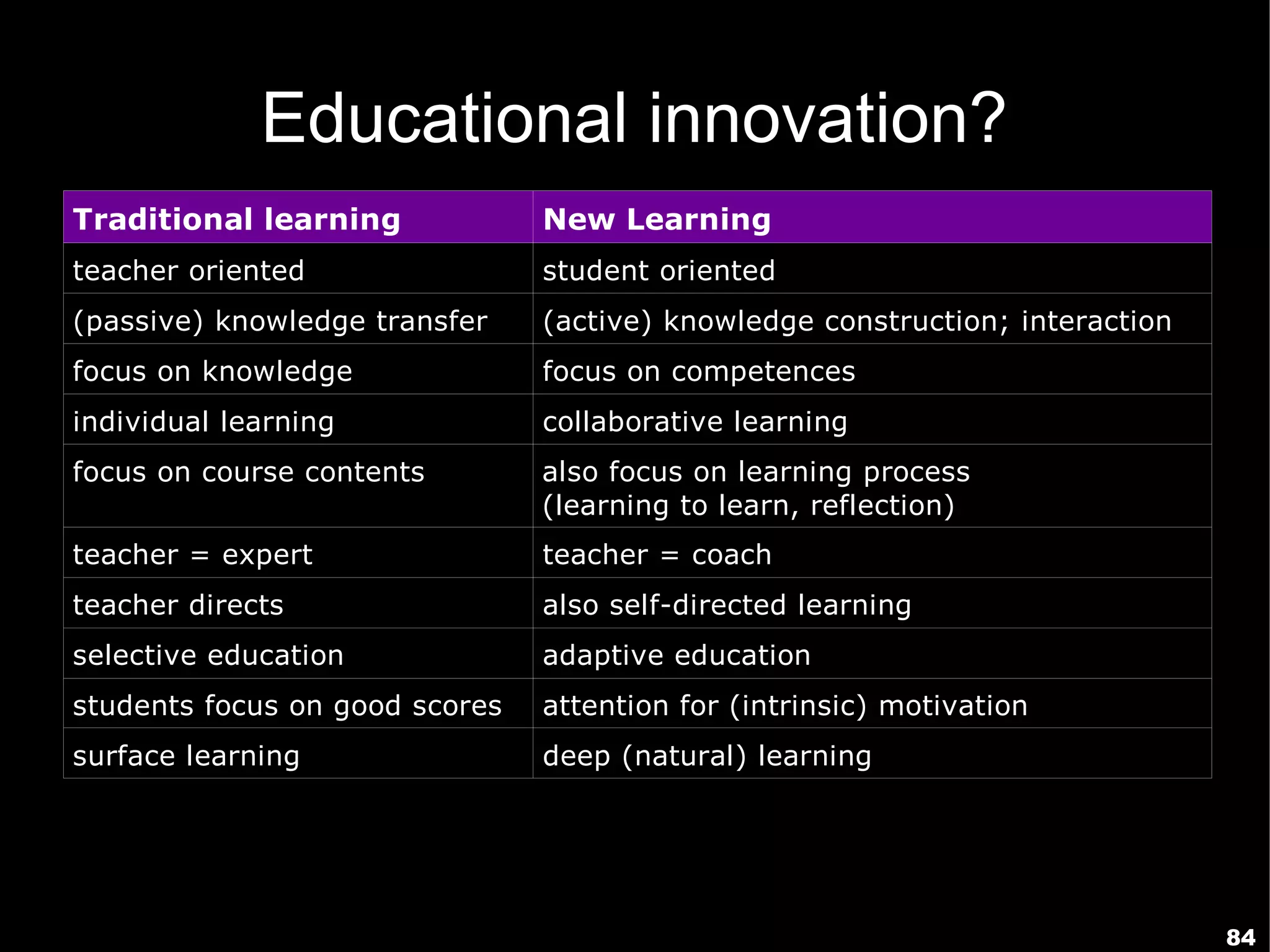
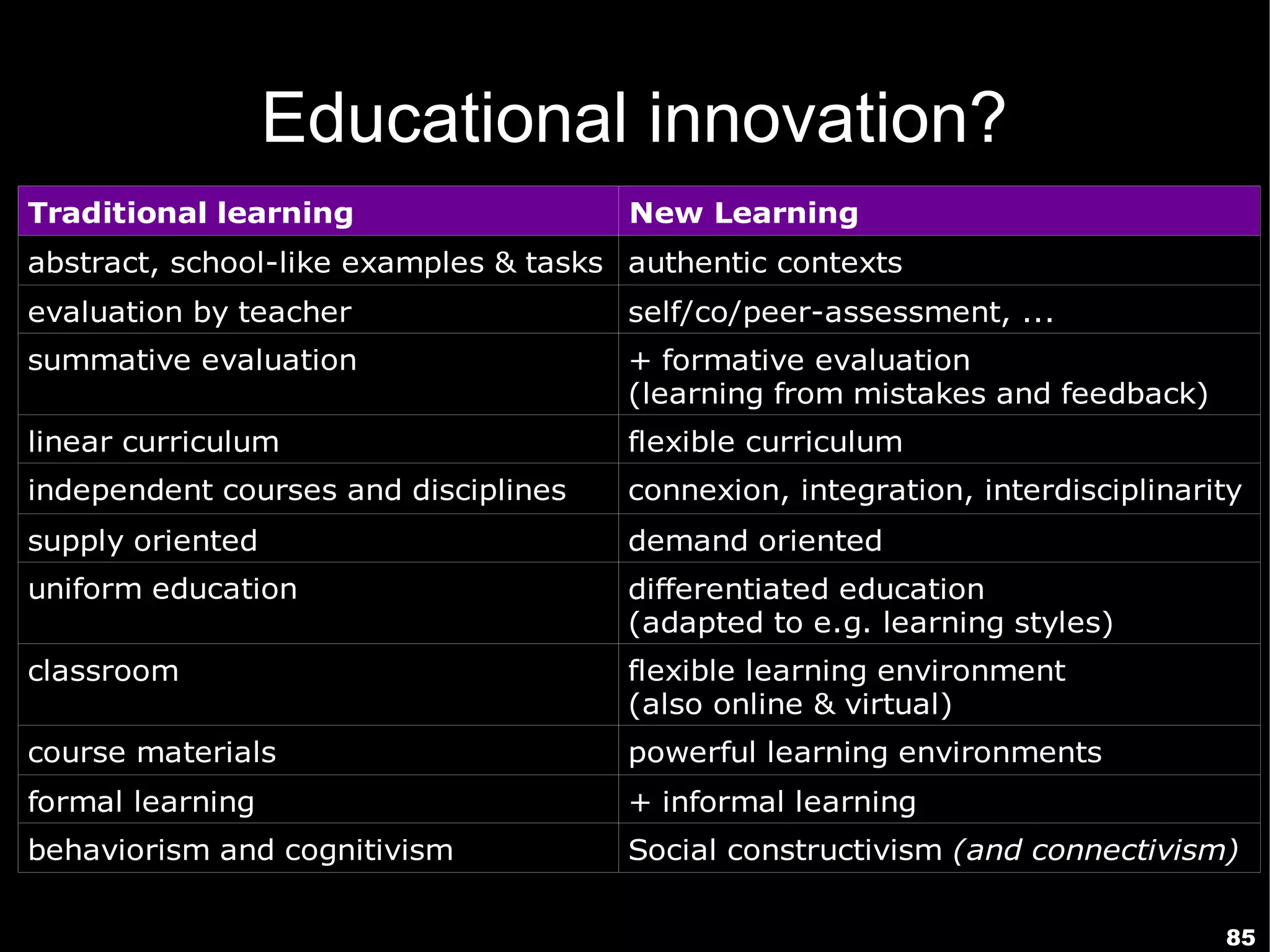
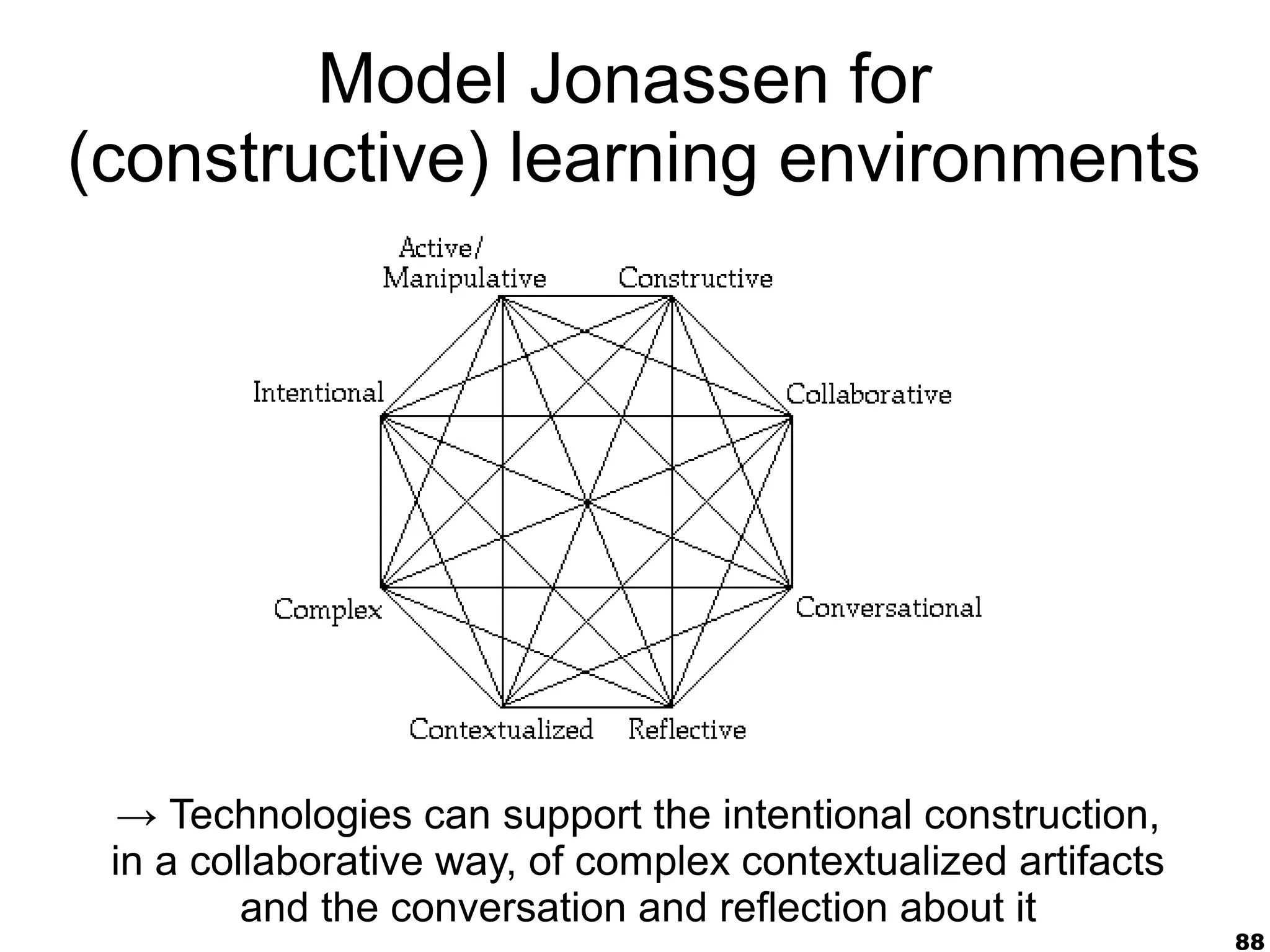
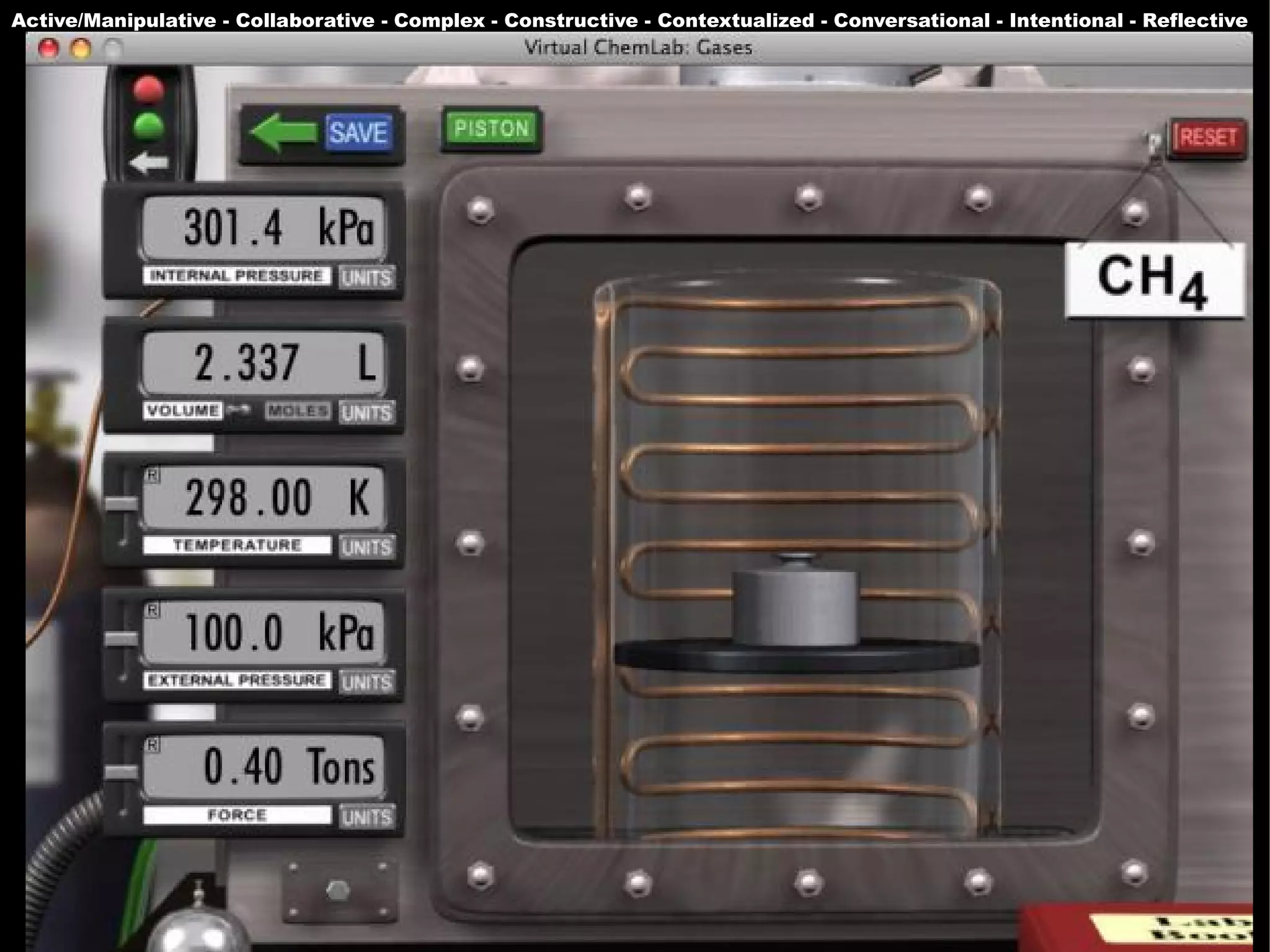
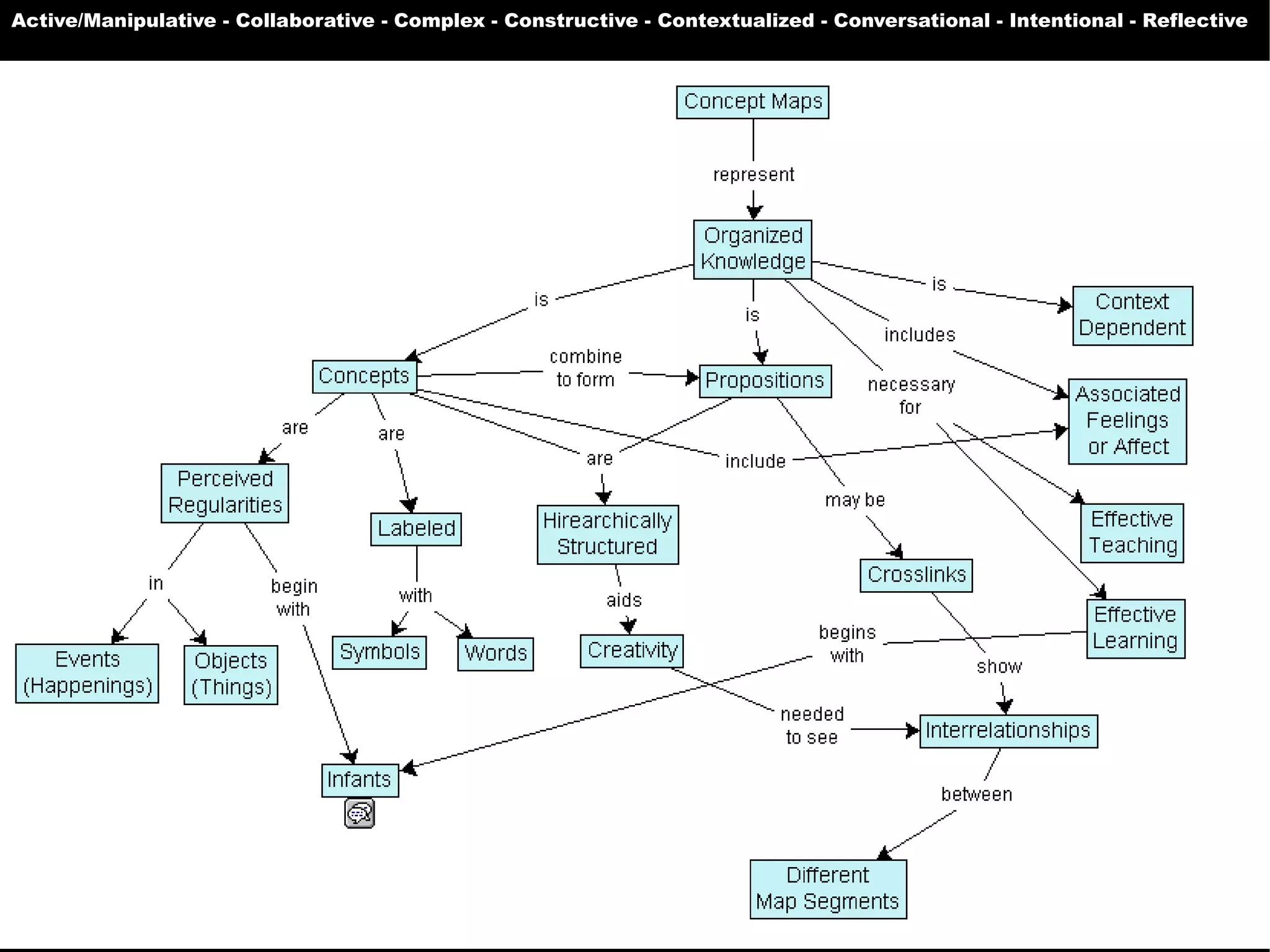
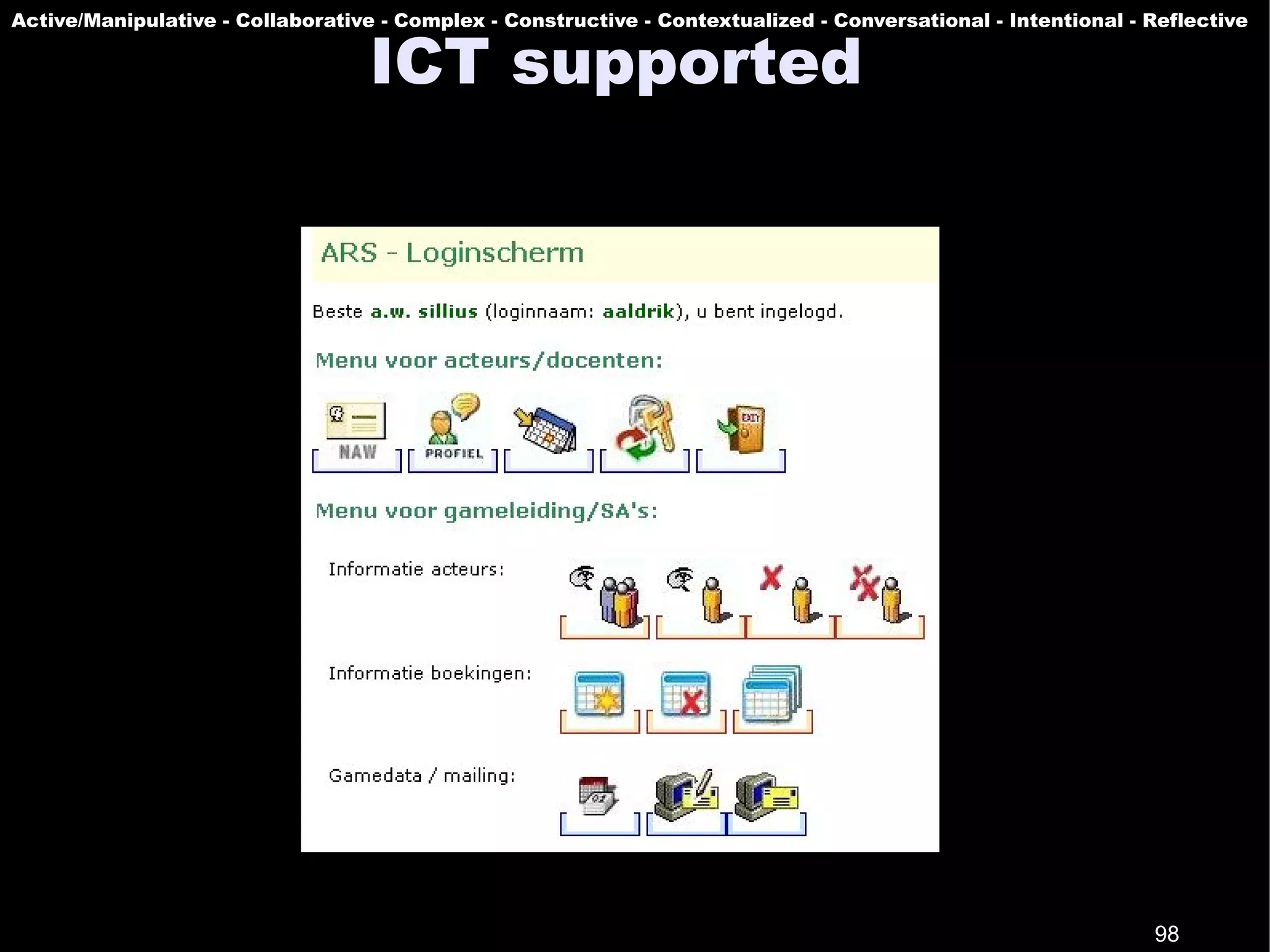
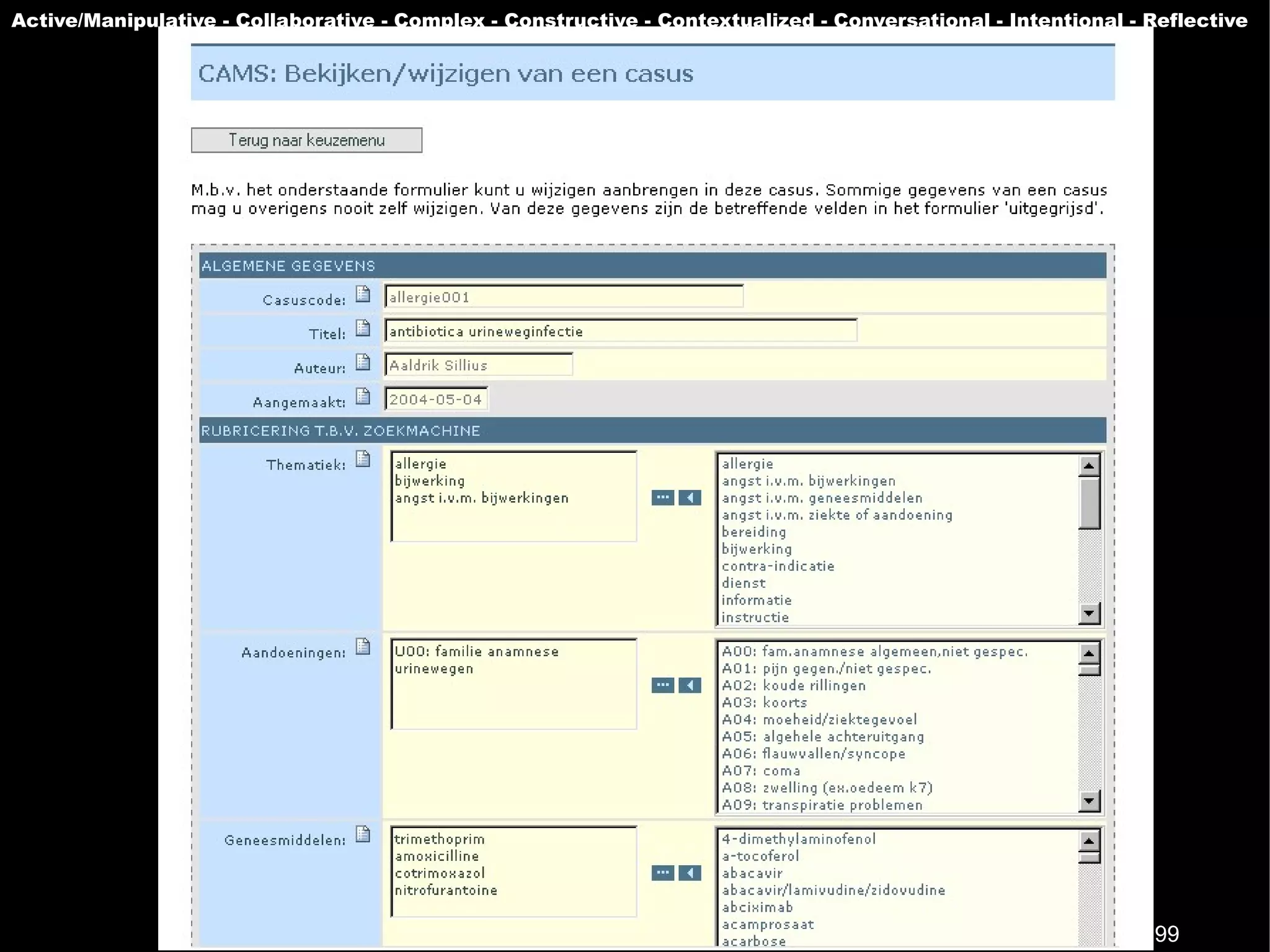
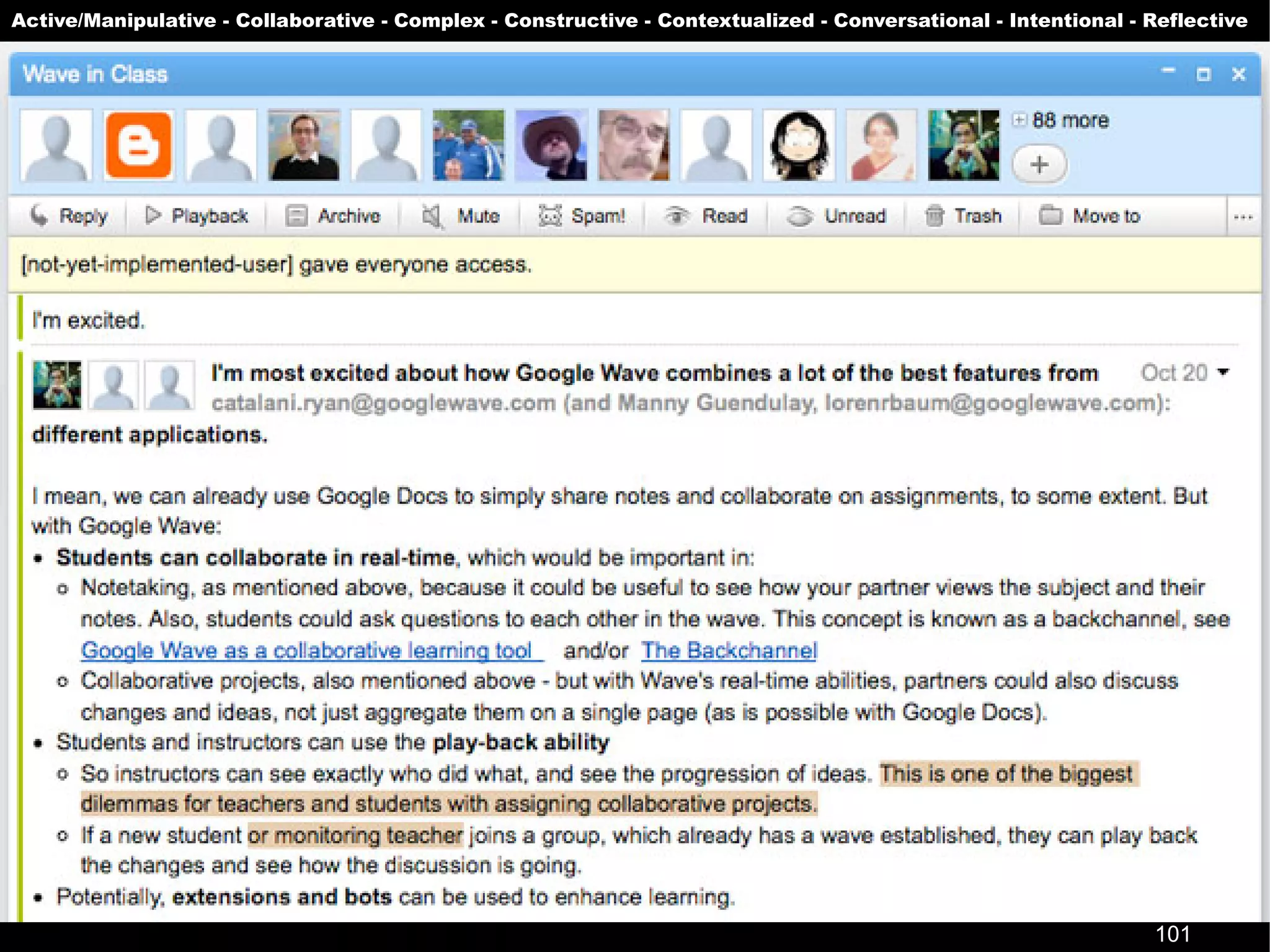
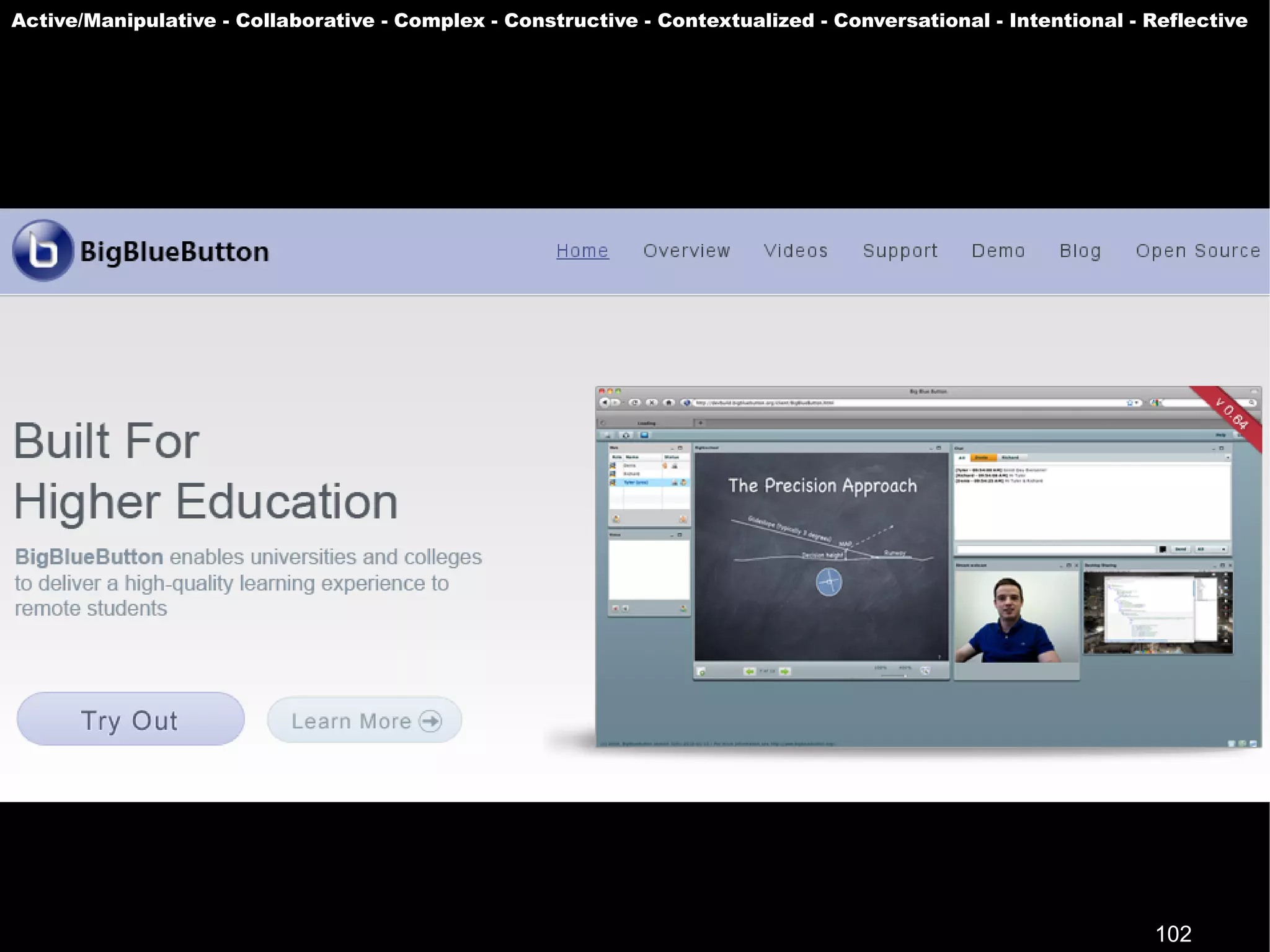
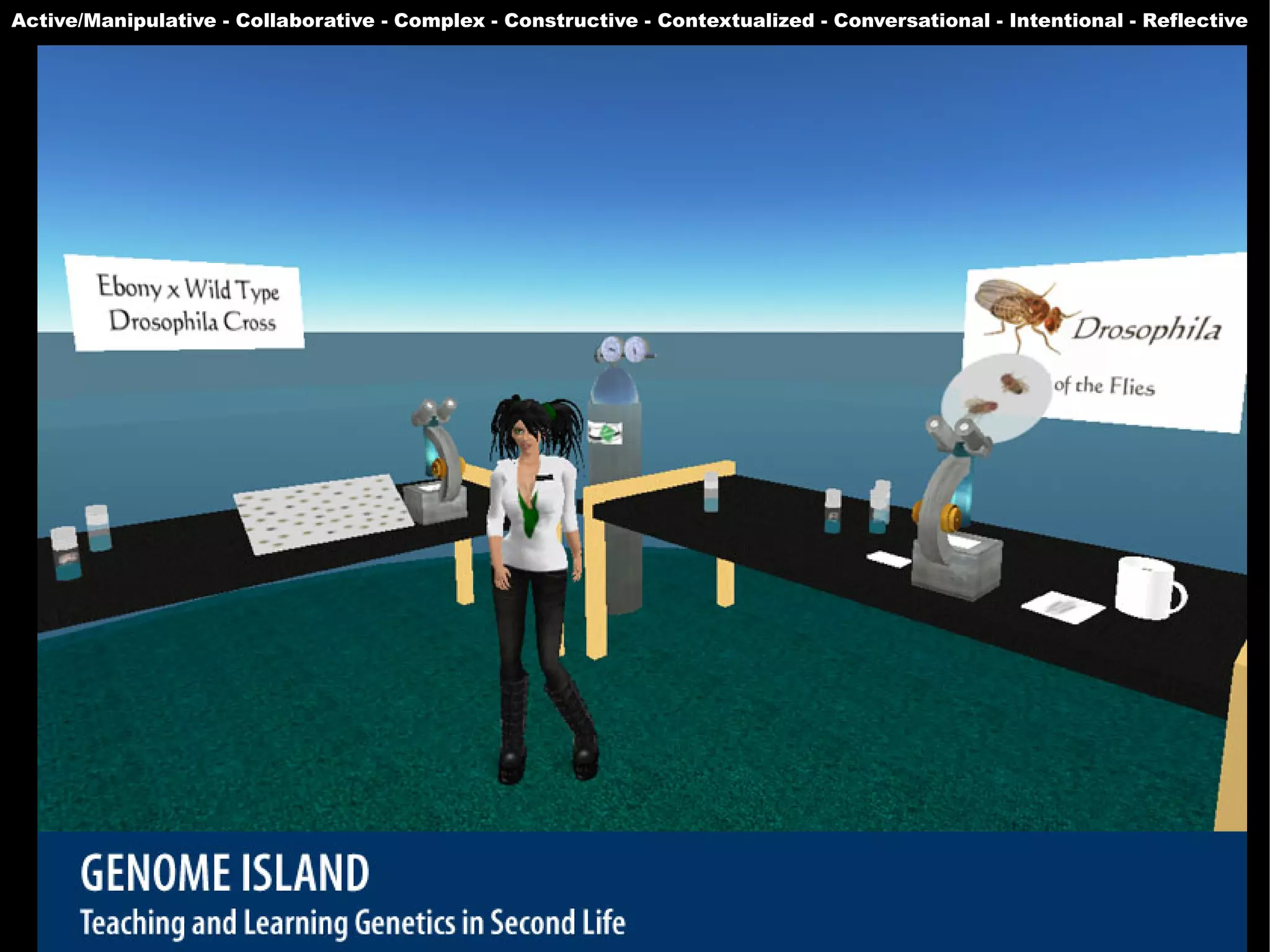
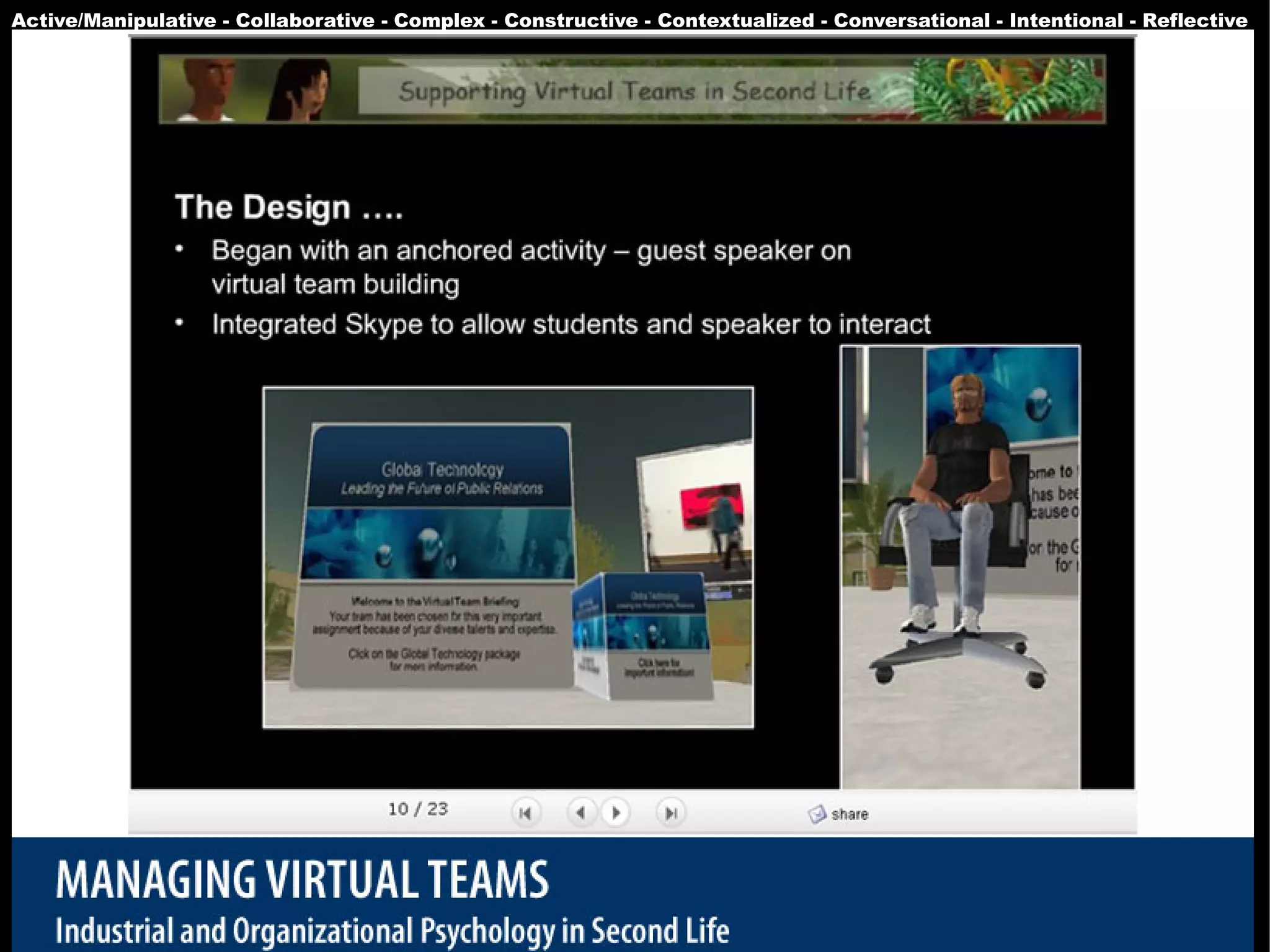
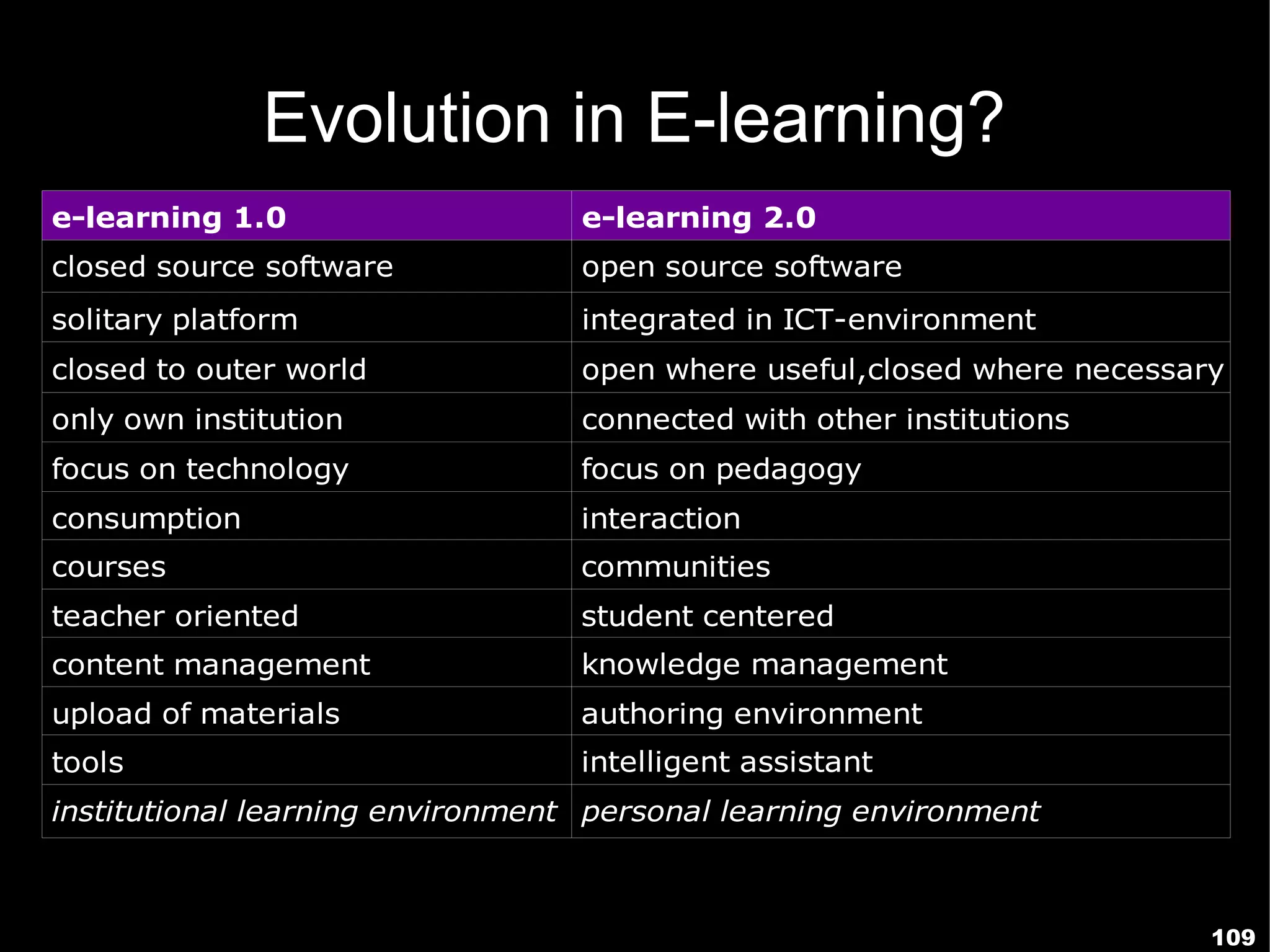
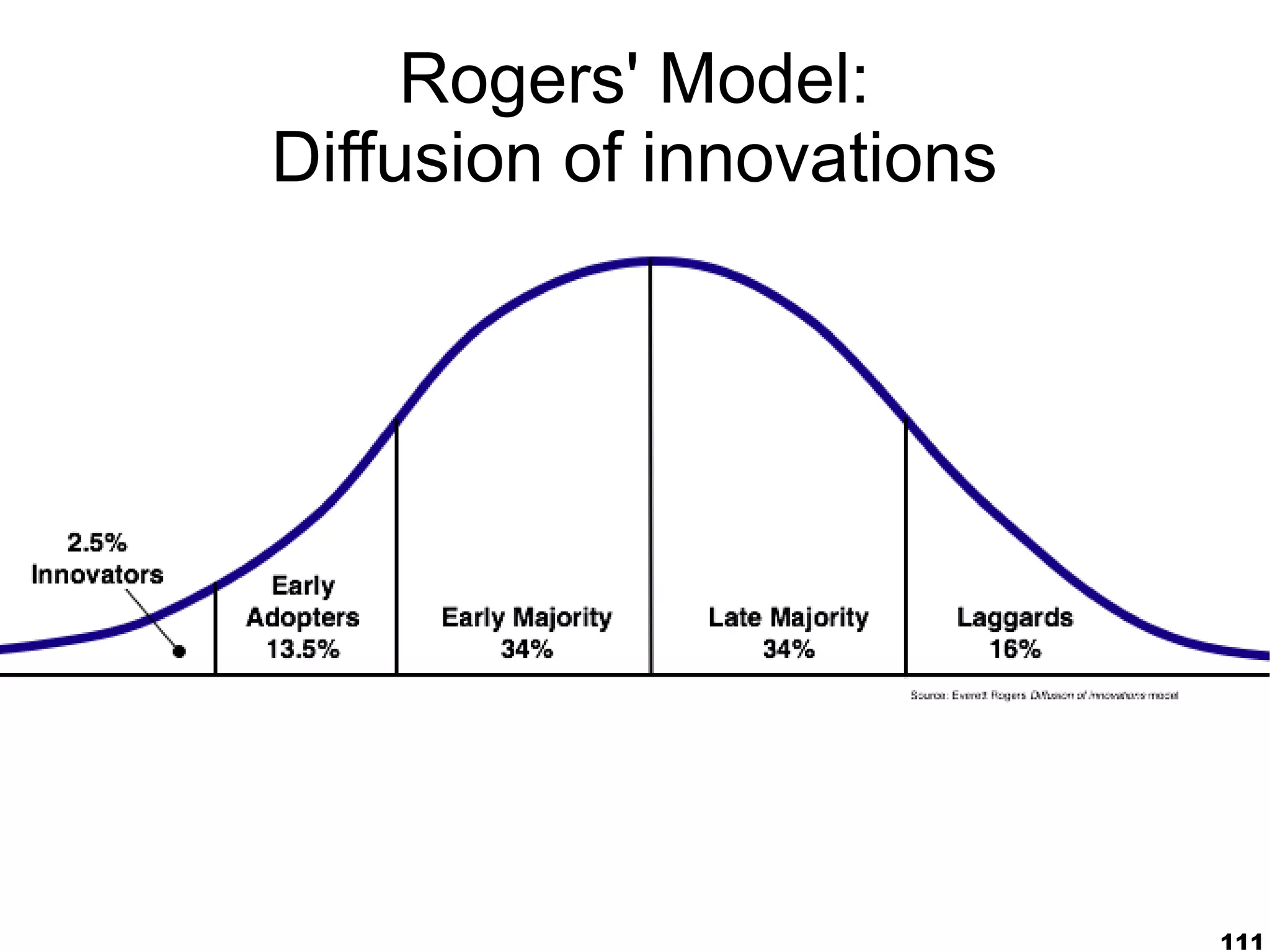
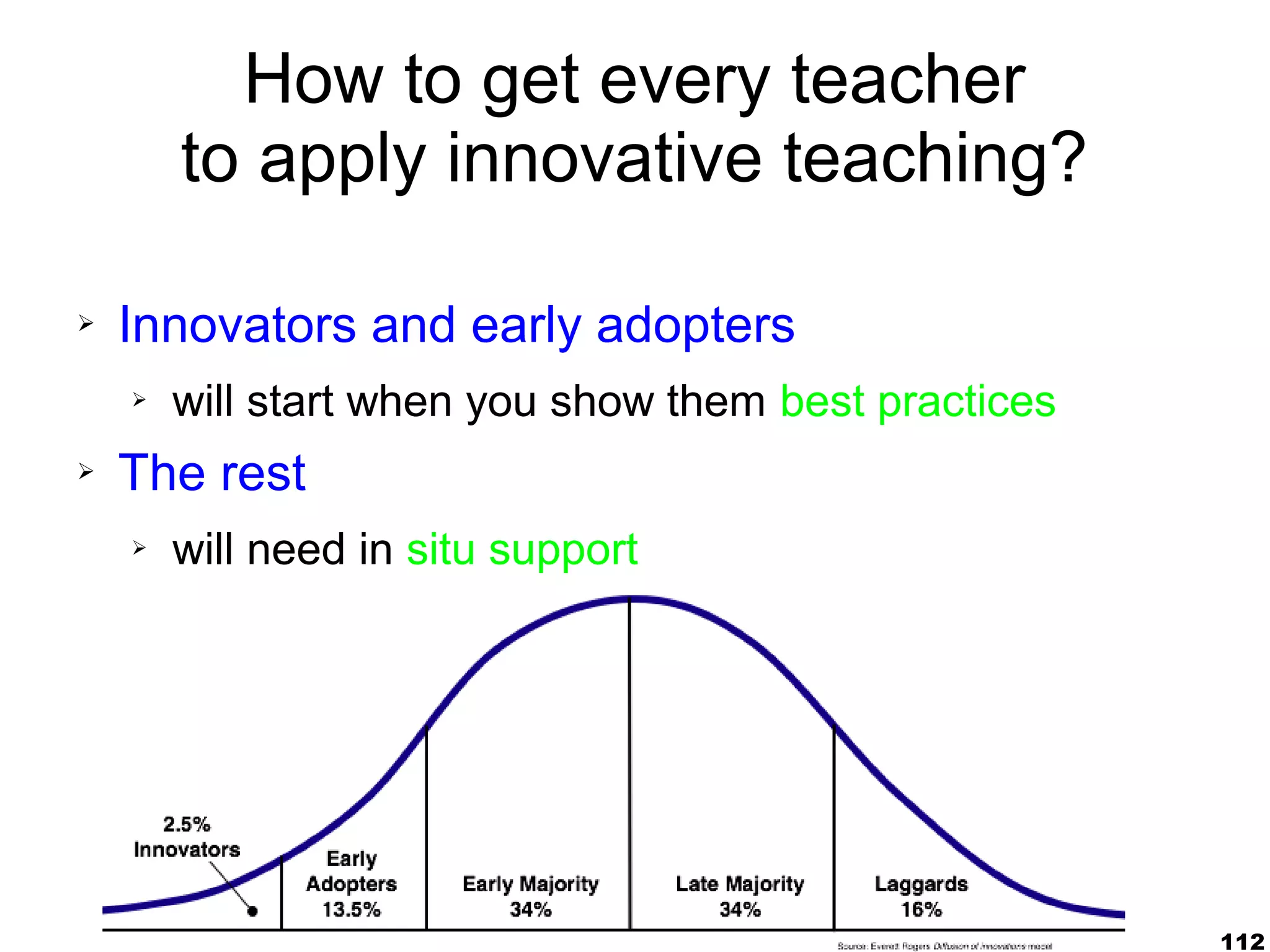
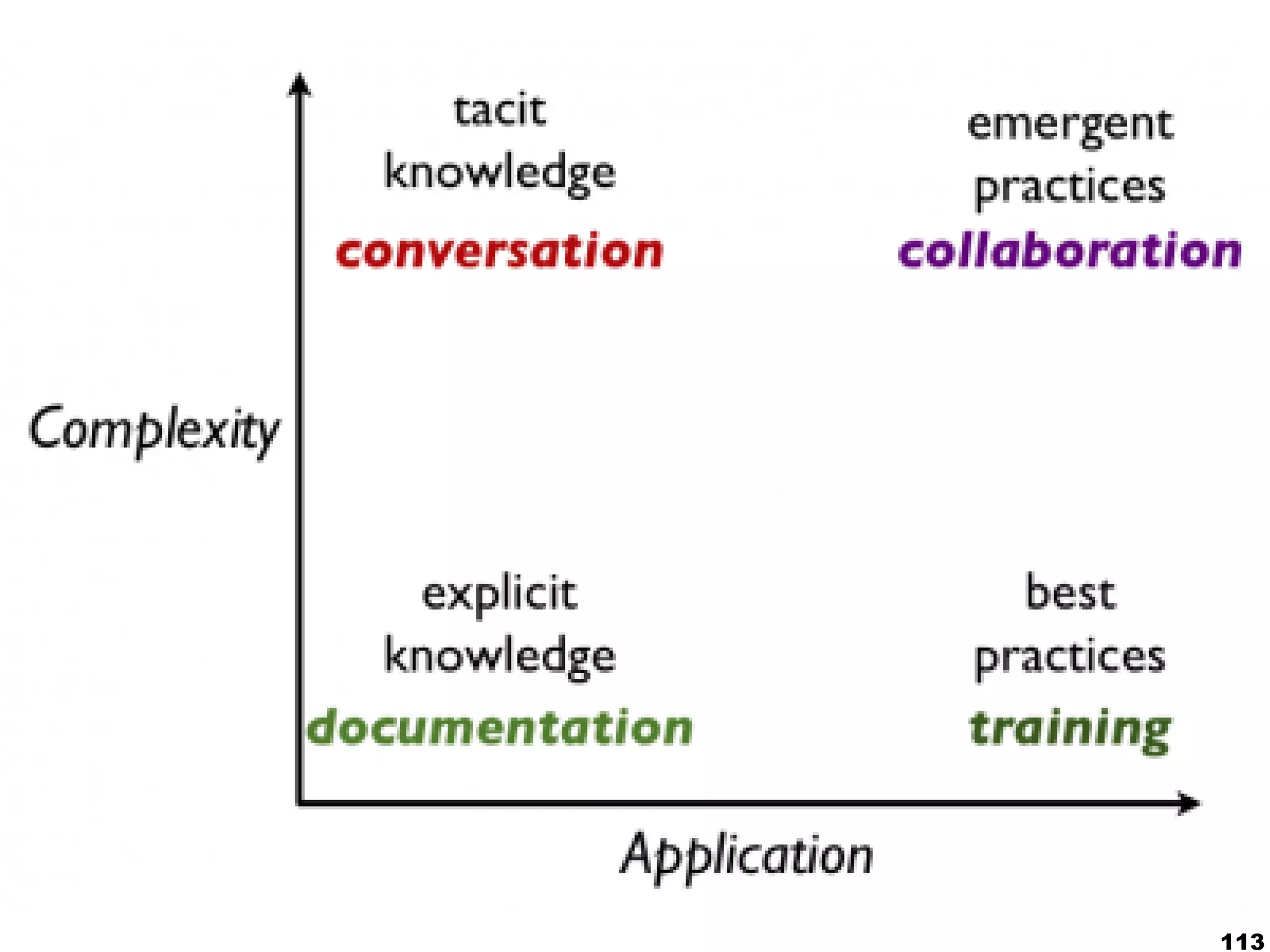
The document presents a guest lecture by Prof. Dr. Frederik Questier exploring the integration of digital technologies in education, emphasizing the importance of adapting teaching methods to leverage Information and Communication Technologies (ICT). It discusses the evolution of learning theories and skills necessary for future educators, while advocating for innovative approaches to enhance student engagement and collaborative learning. Additionally, the document outlines strategies for fostering academic innovation and the need for ongoing teacher training in this digital age.