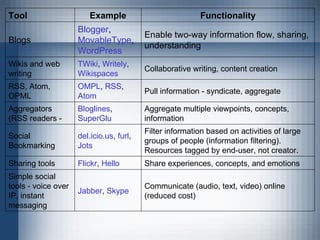
The document discusses challenges in distance learning and proposes a new collaborative open online learning (COOL) model using Web 2.0 technologies. It outlines issues with the current learning management system (LMS) model and publisher-driven content. The COOL model advocates for open access courses, learner-generated content, and leveraging social software to allow for collaboration, interaction and networking between faculty and students. Course development becomes an iterative process based on participant input and content is changed through ongoing edits by the learning community.