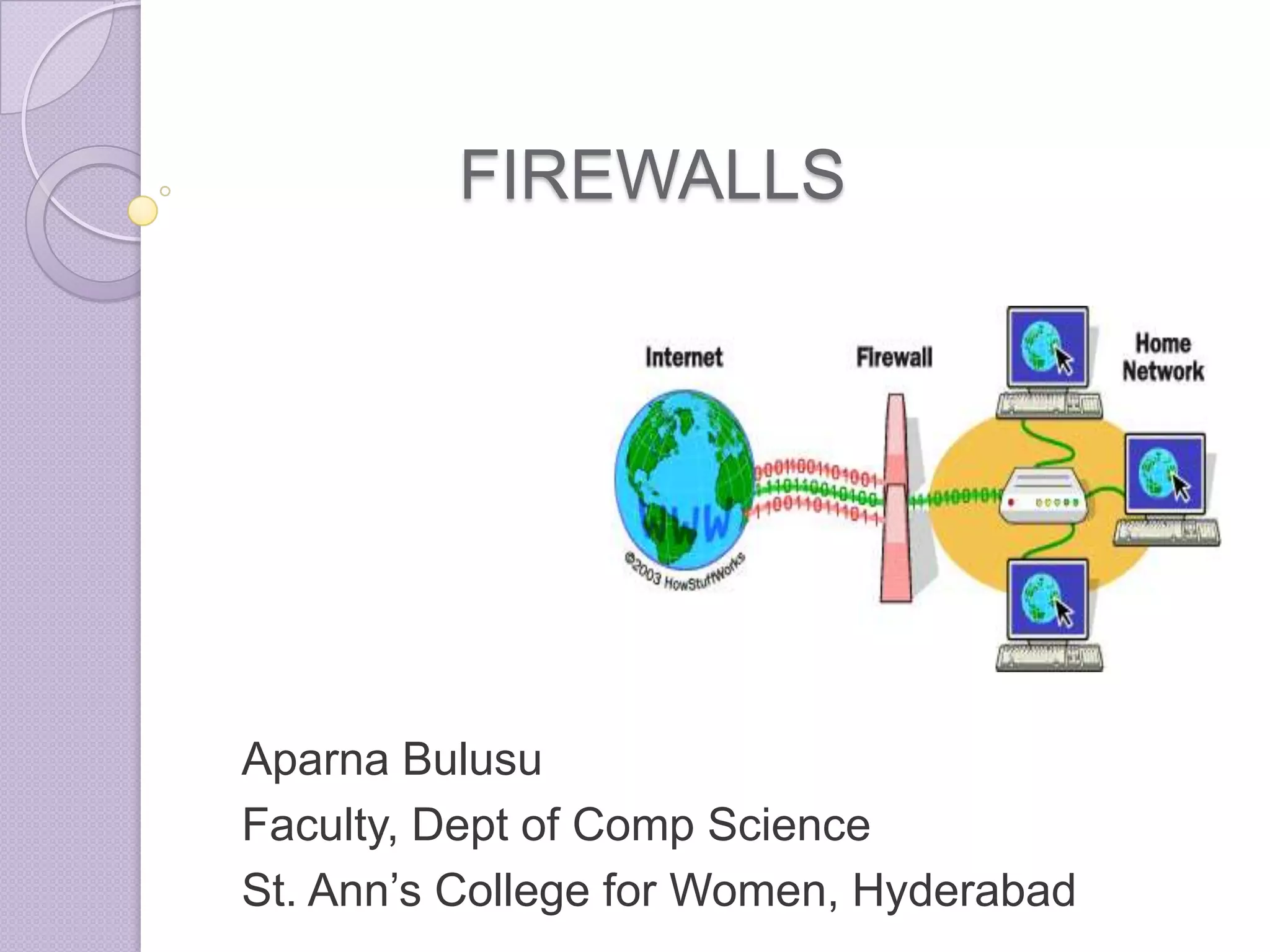
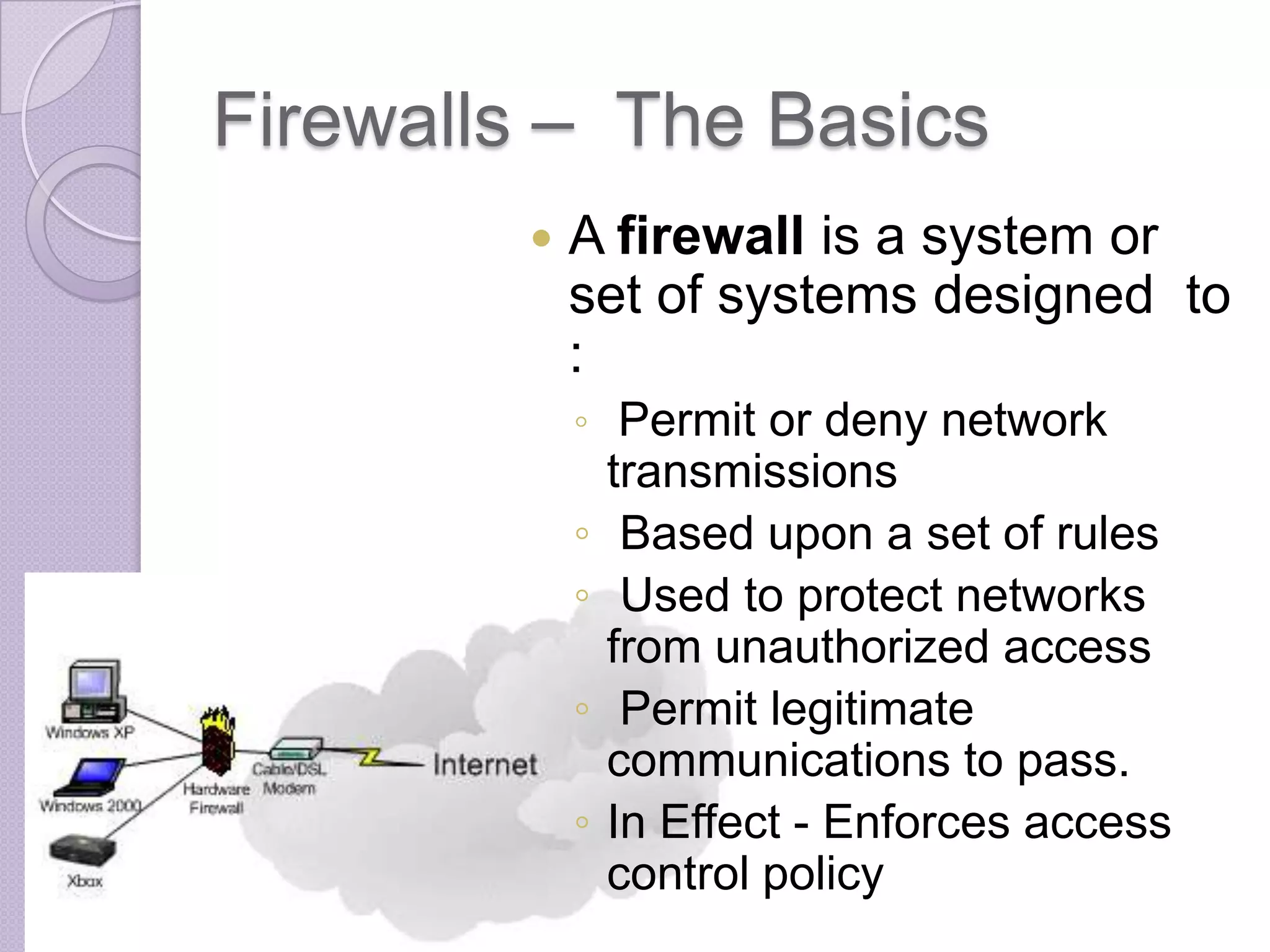
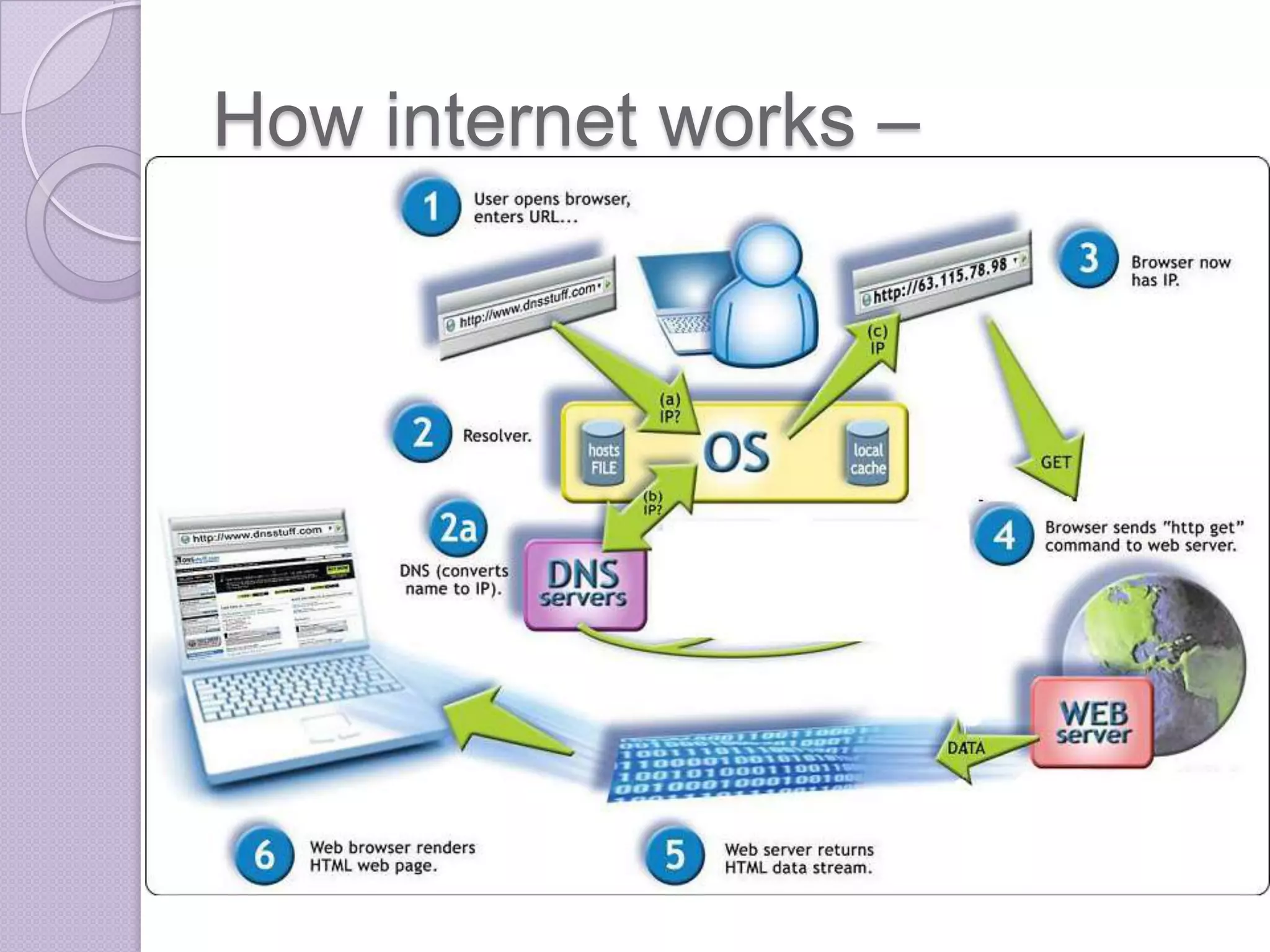
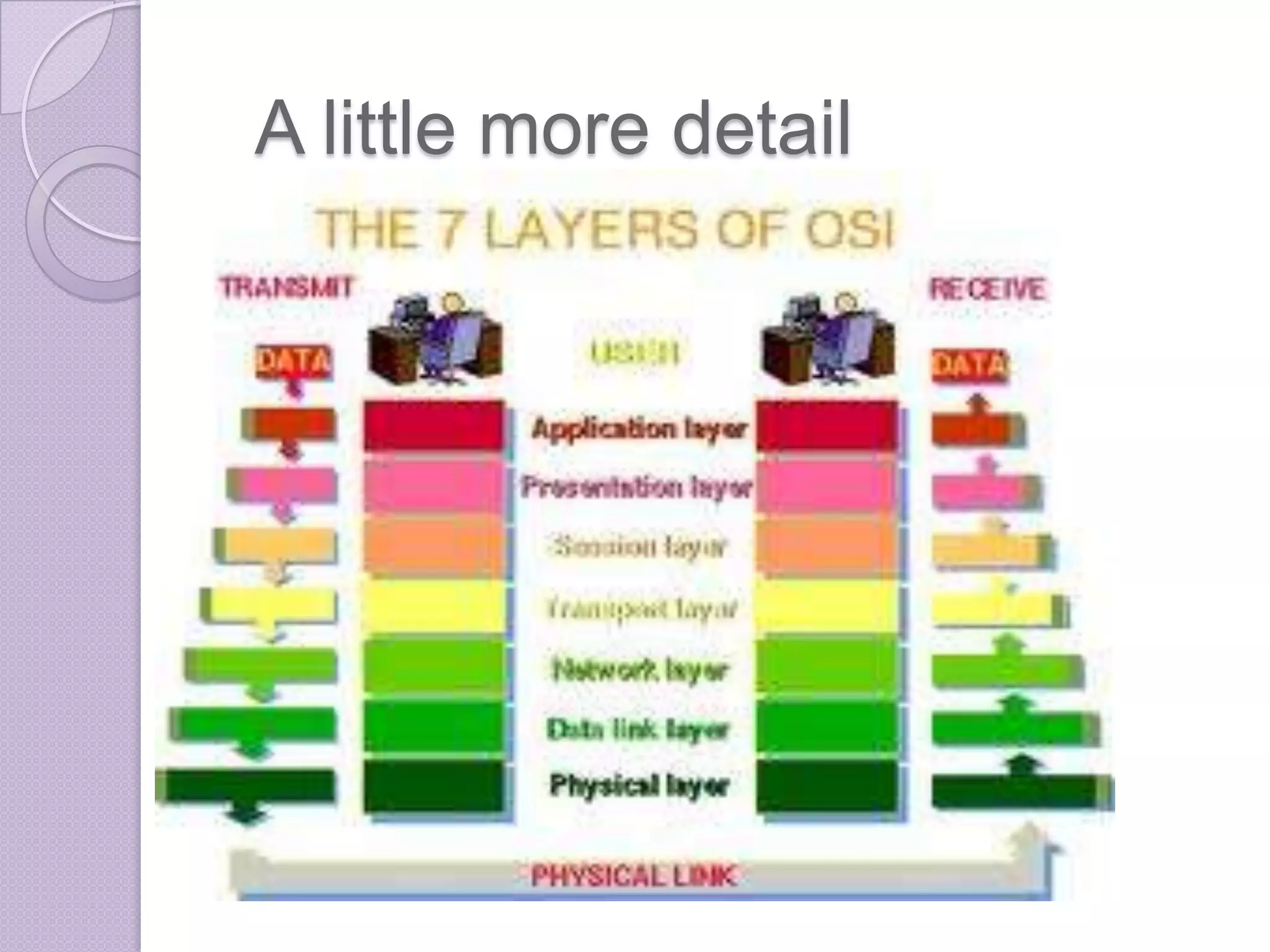
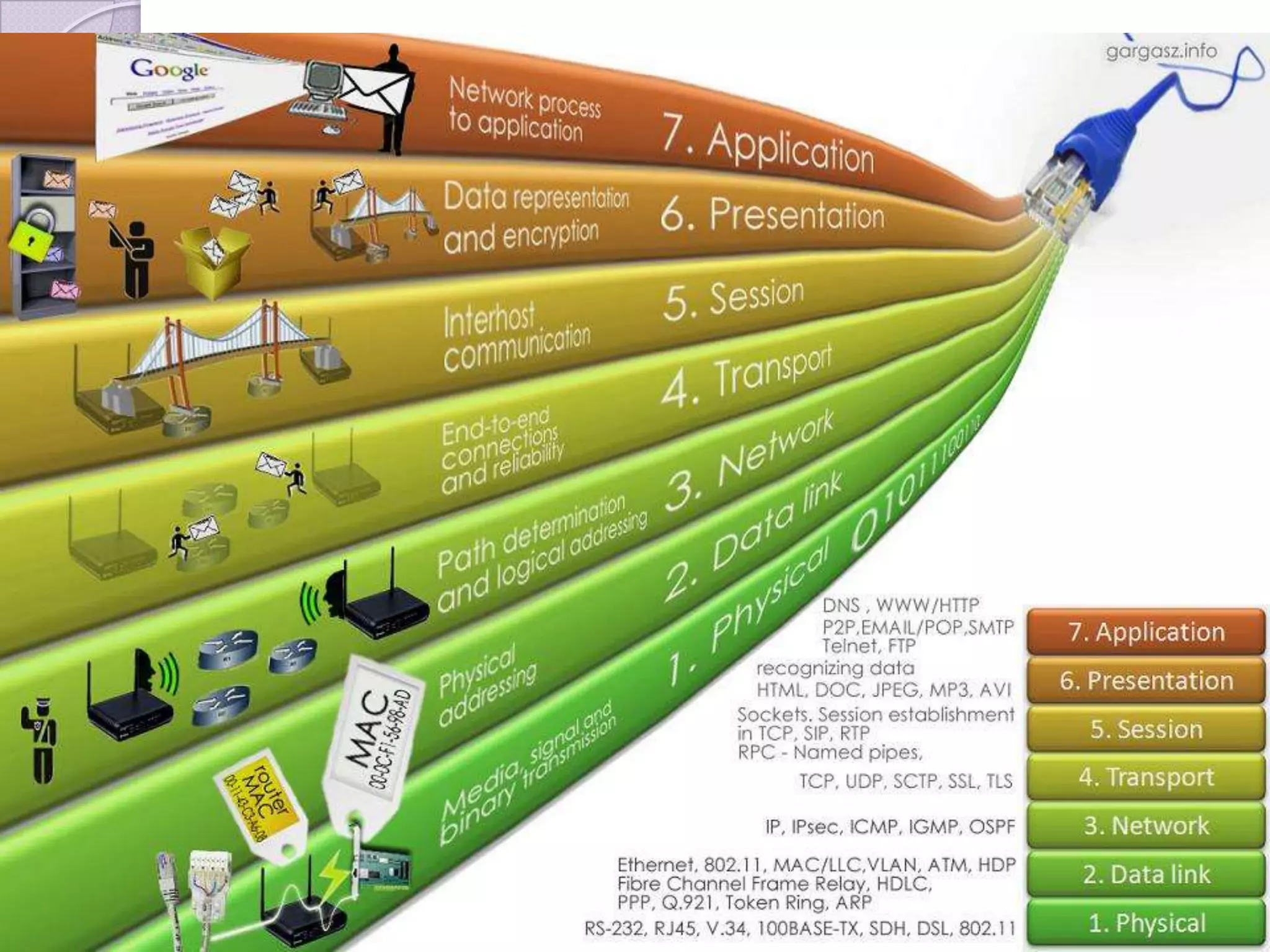
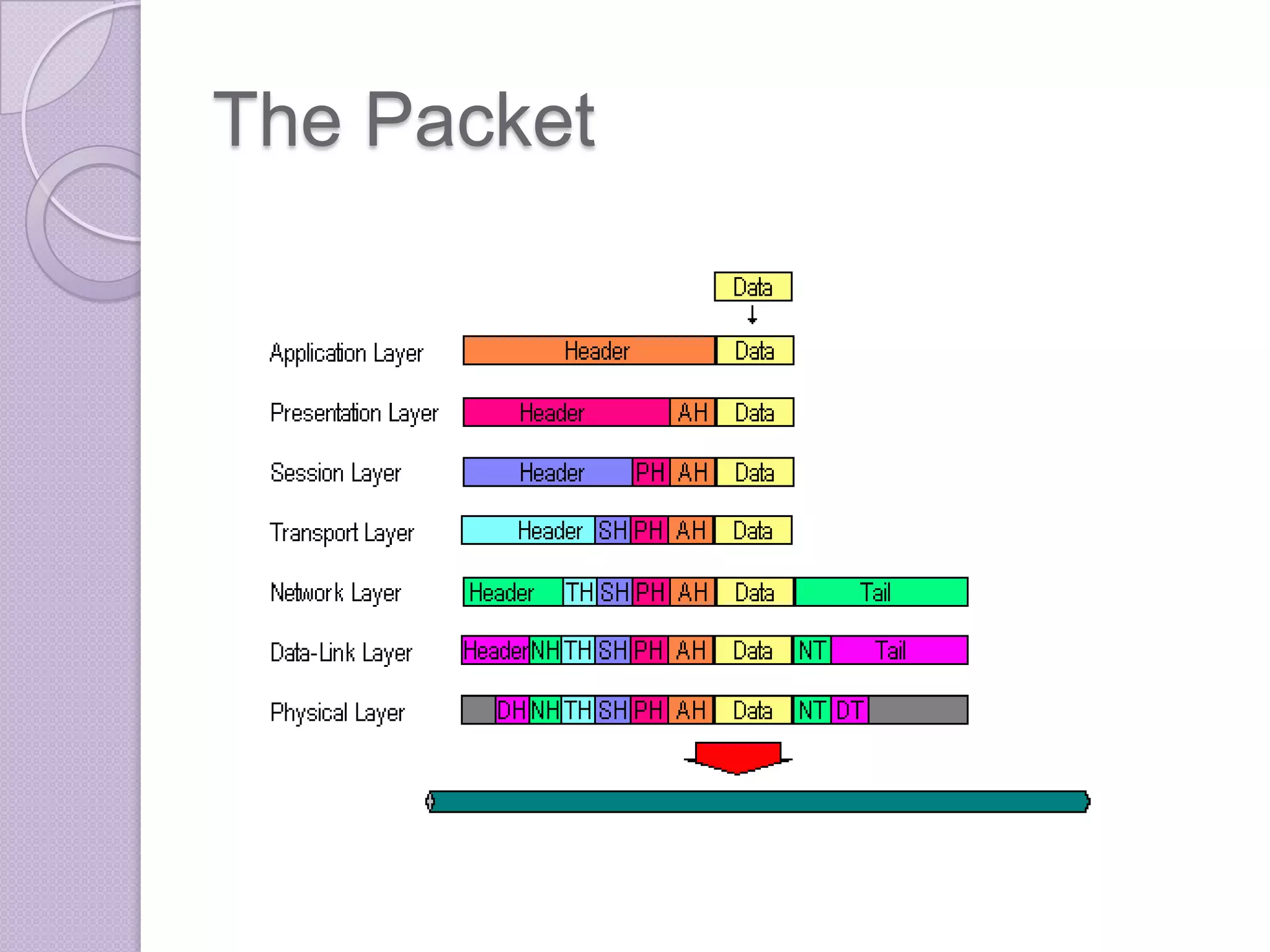
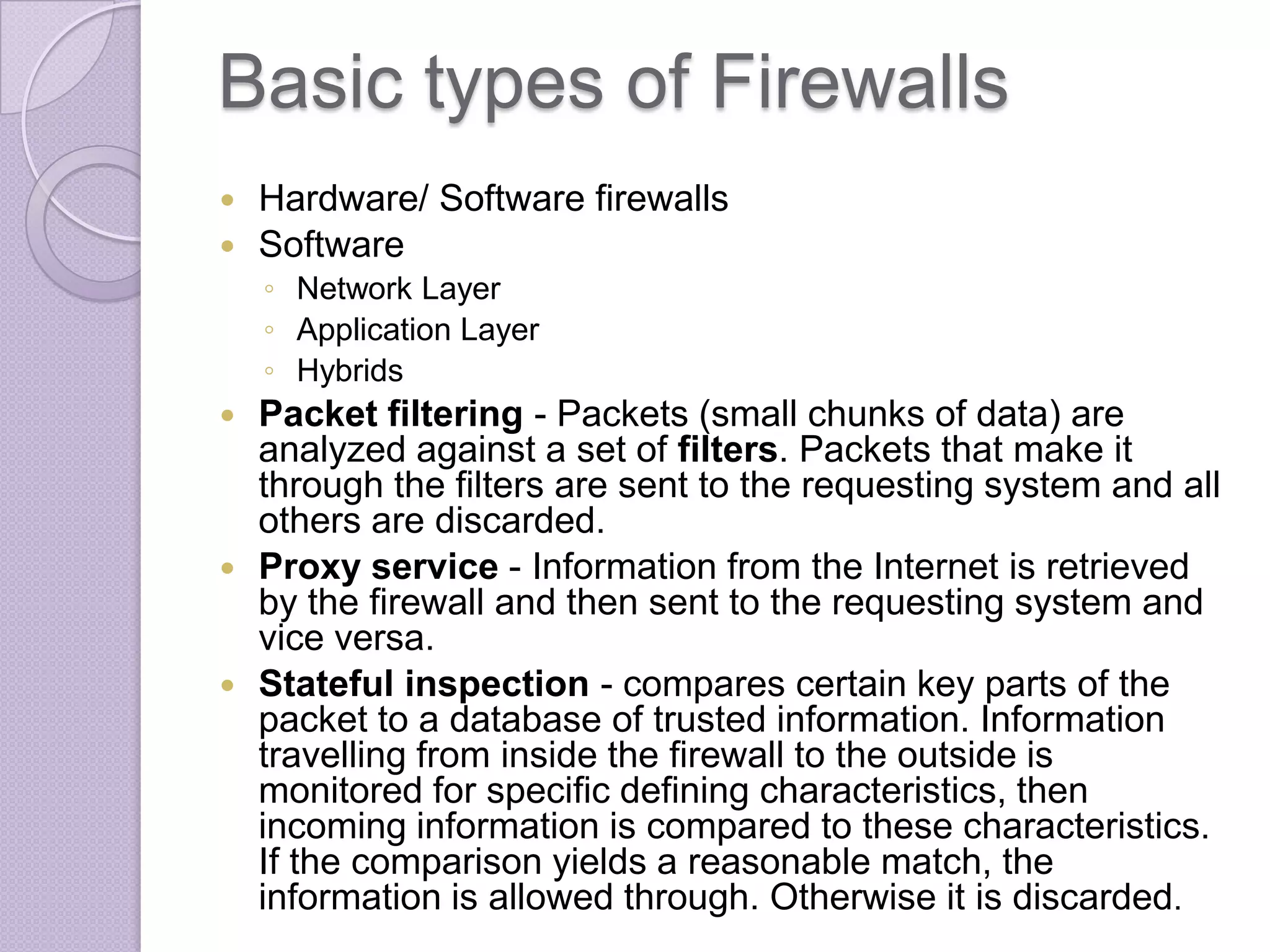
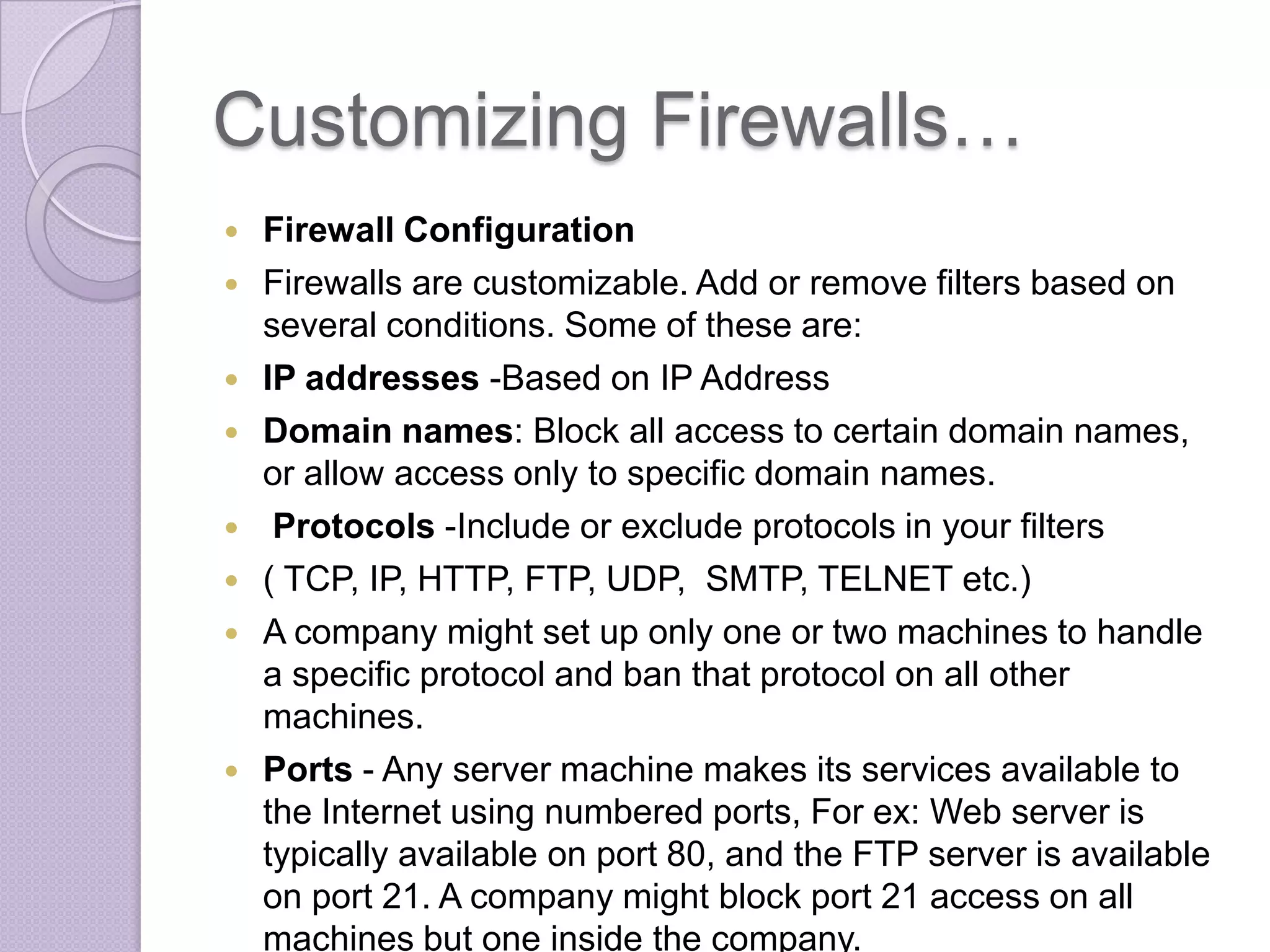
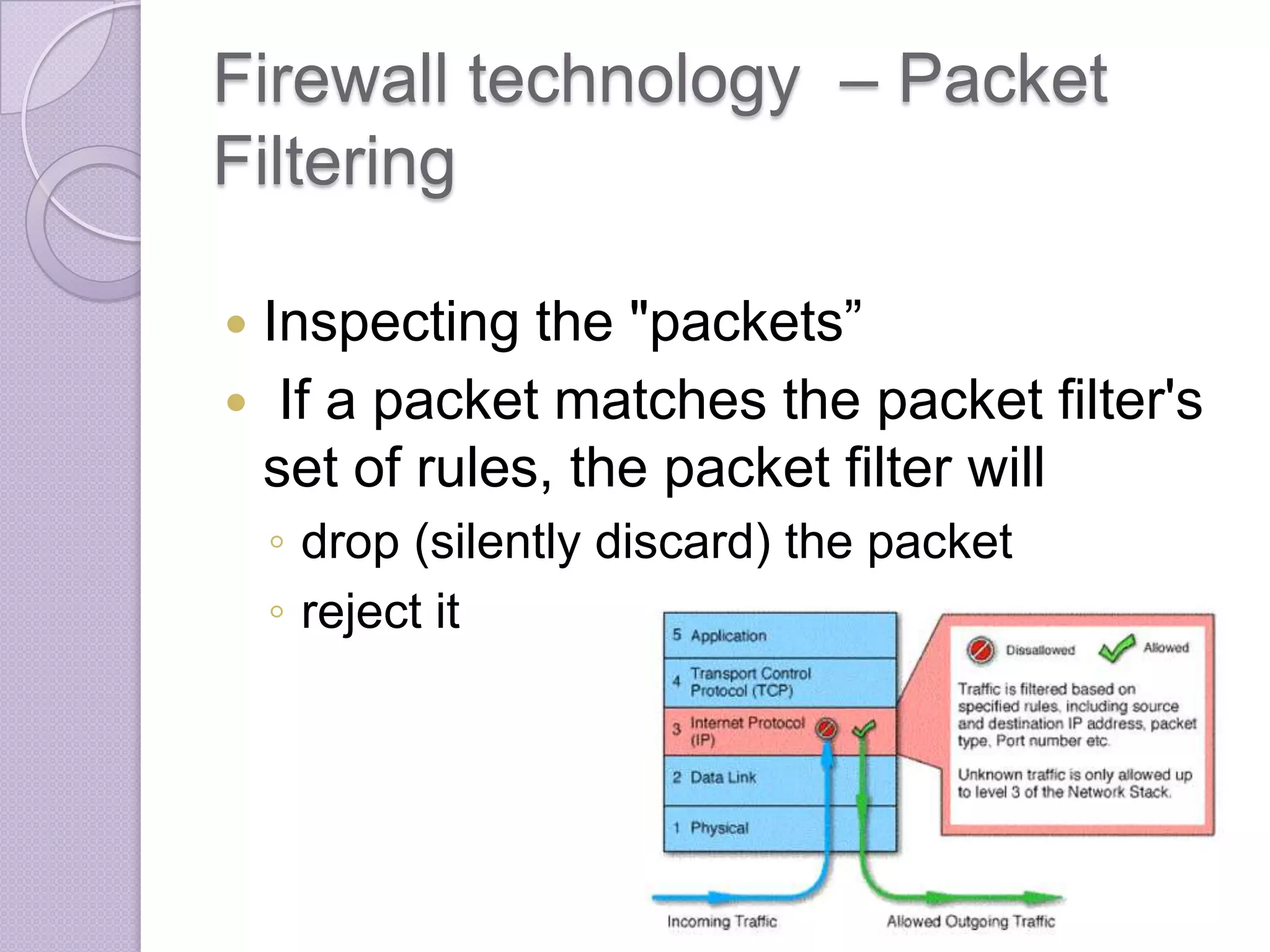
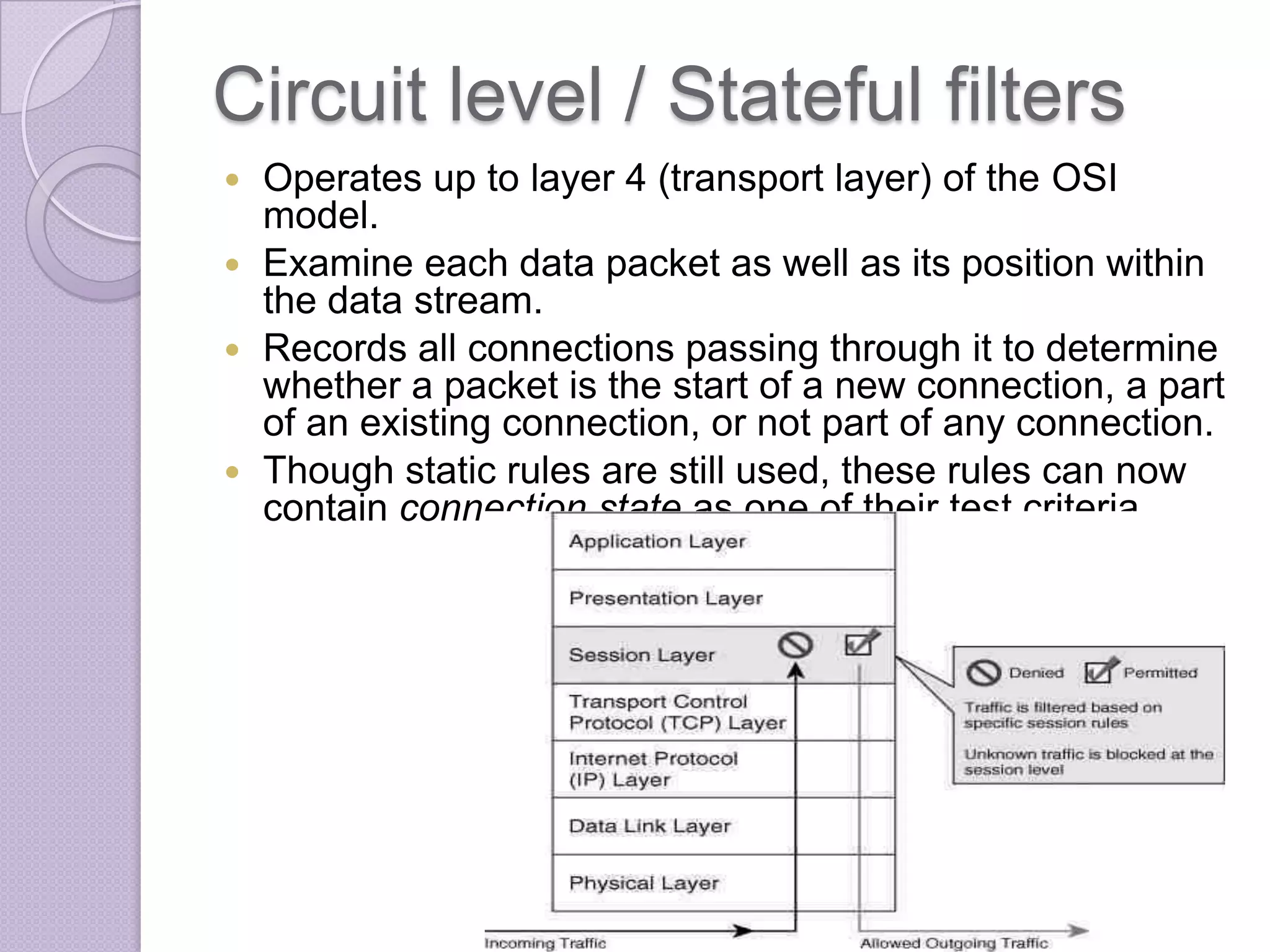
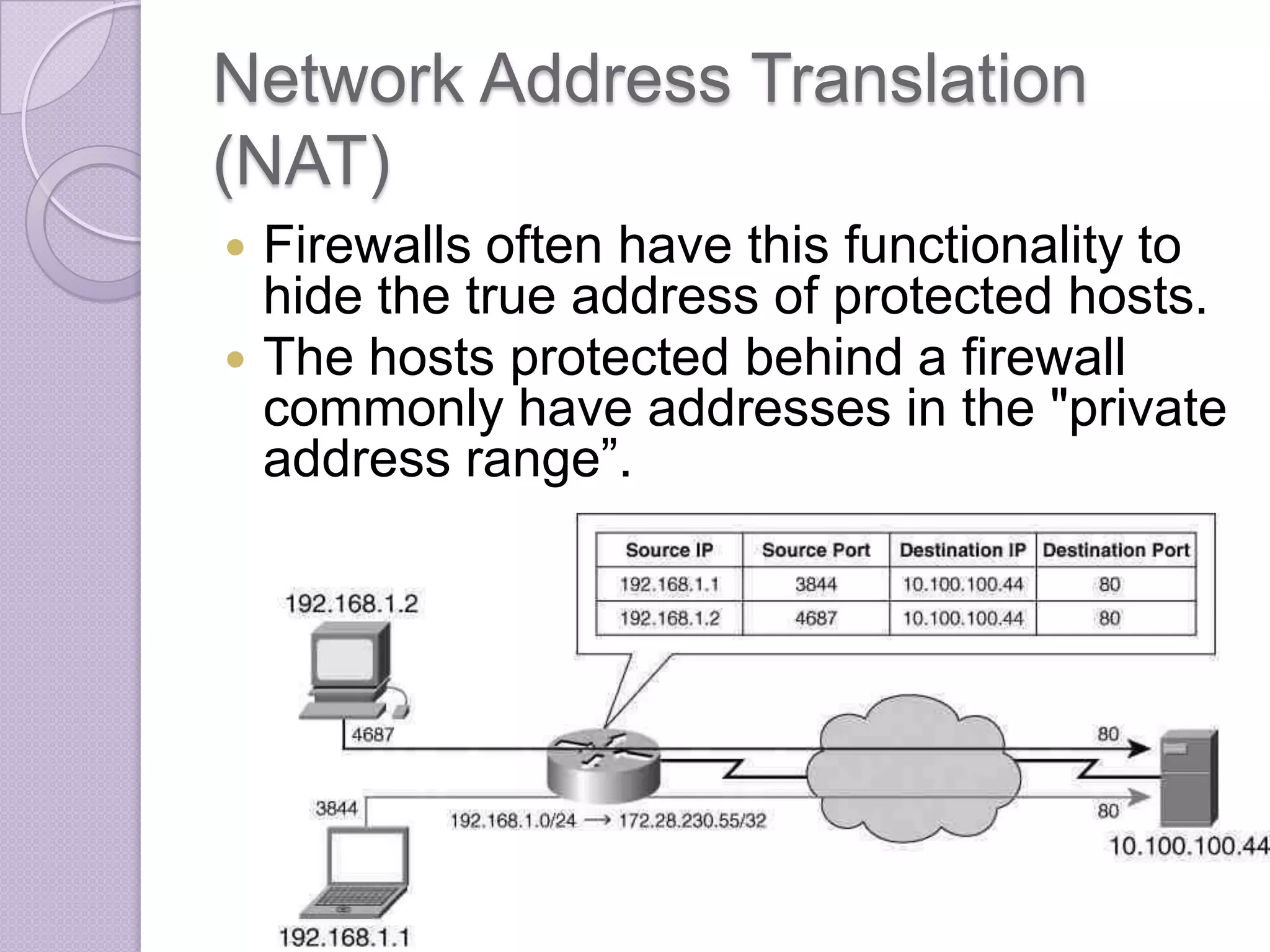
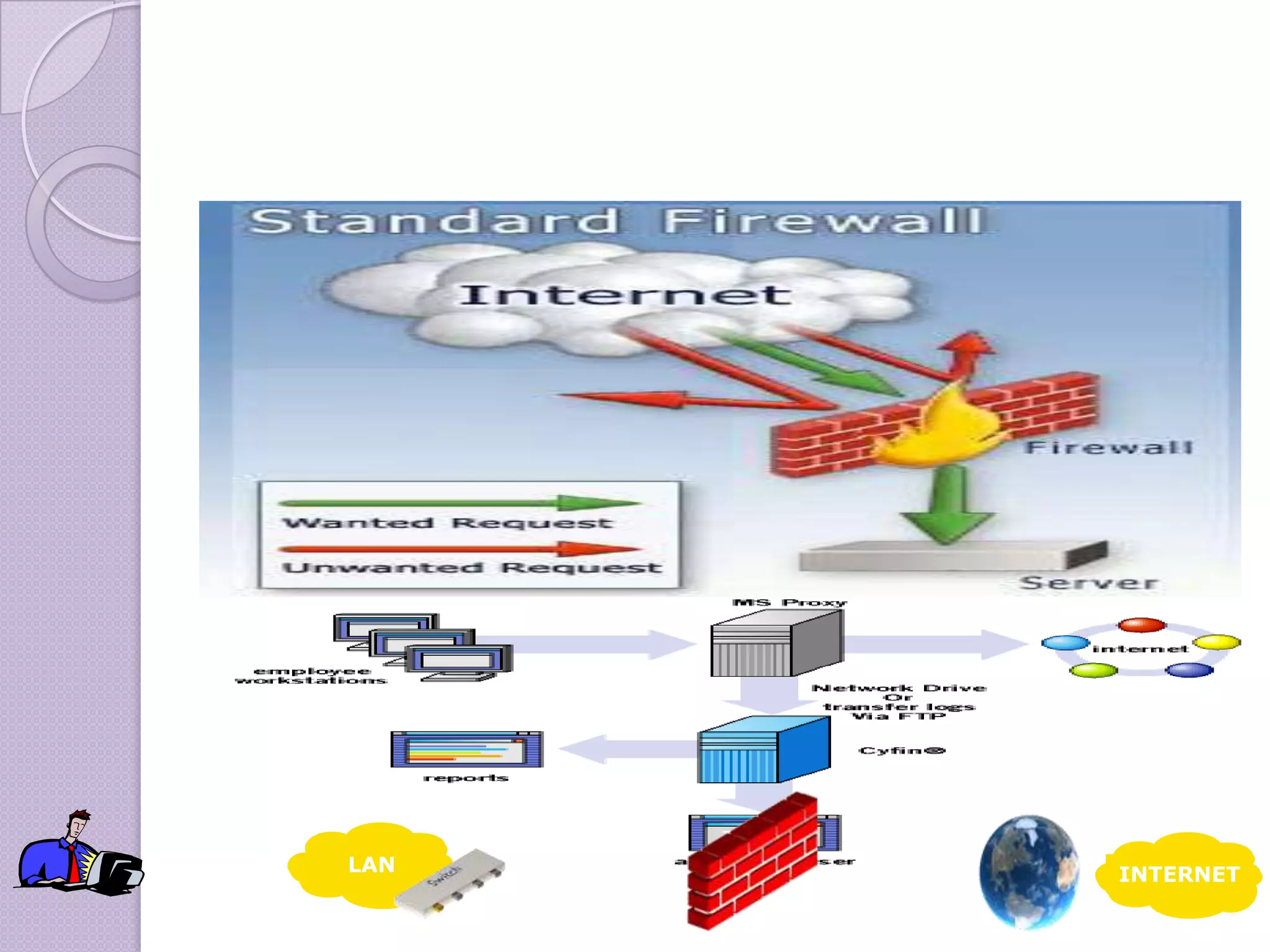
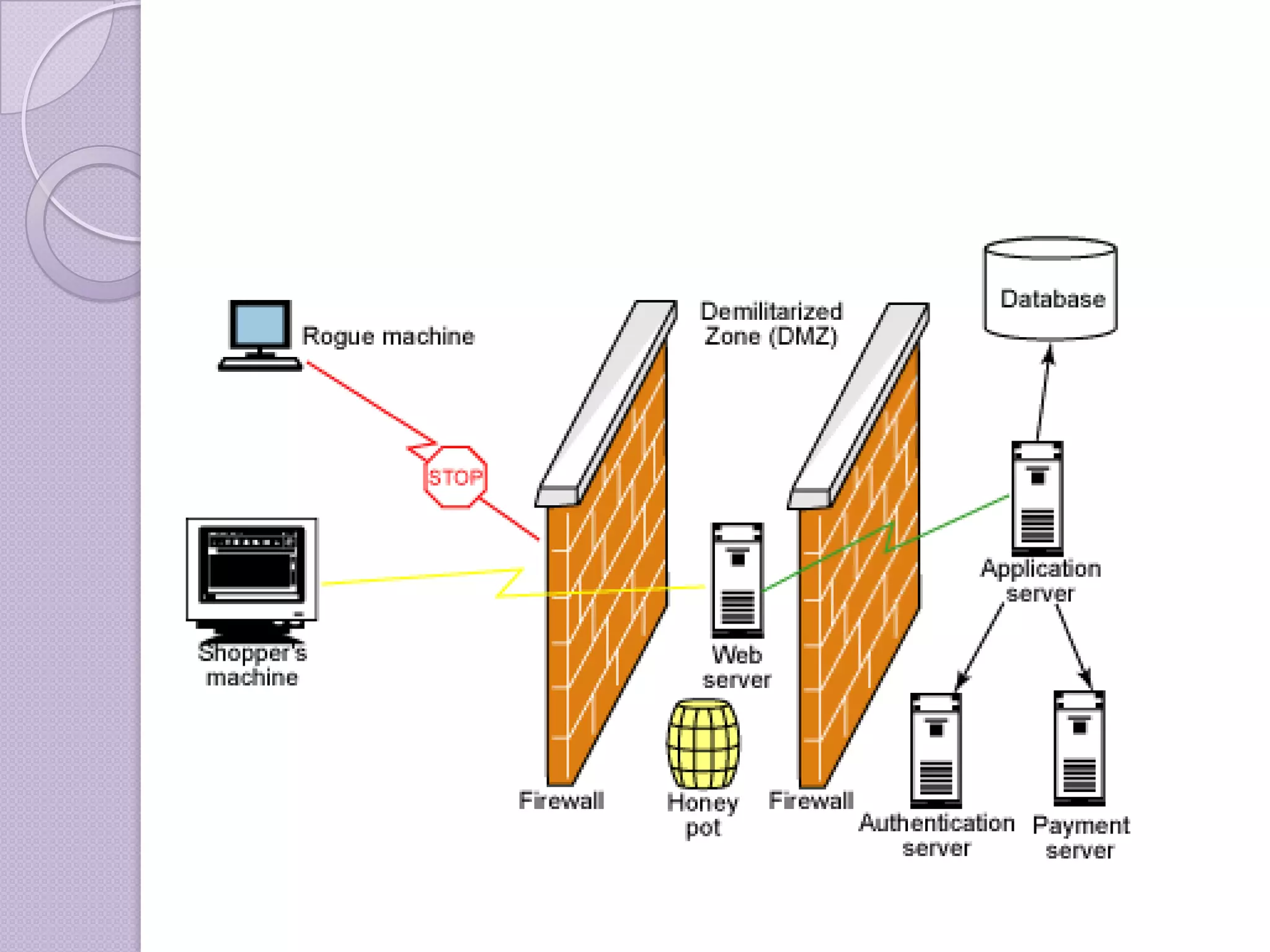
Firewalls are systems designed to control network access by enforcing an access control policy. They work by examining packets and filtering them based on rules like IP addresses, protocols, and ports. There are different types of firewalls including packet filtering, proxy, and application layer firewalls. While firewalls help protect networks from unauthorized access and provide logging, they have limitations as they only control connectivity and not other aspects of security like encryption. It is important to take additional precautions like using strong passwords, keeping software updated, and practicing safe online habits.