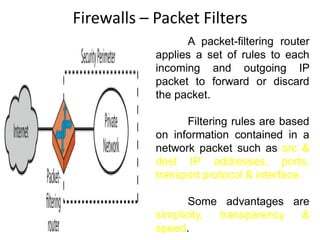
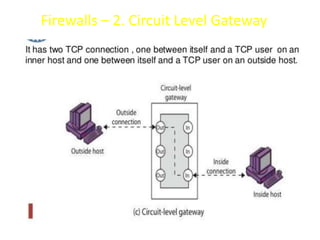
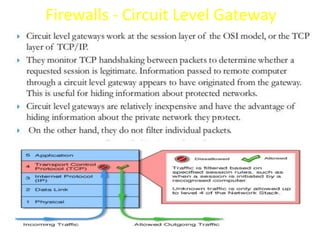
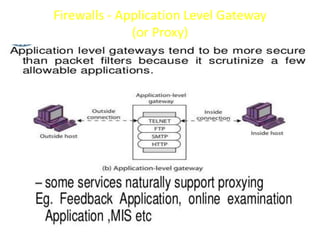
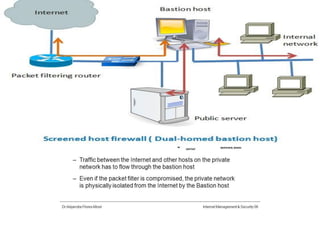
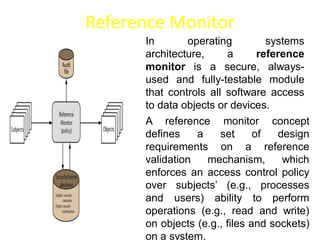
The document explains firewalls as crucial network security systems that regulate network traffic based on predetermined security rules to prevent unauthorized access. It covers various types of firewalls including packet filters, circuit-level gateways, and application-level gateways, along with their functions, advantages, and vulnerabilities. Additionally, the document discusses access control methodologies like the Bell–LaPadula model and the Common Criteria framework for evaluating security in computer systems.