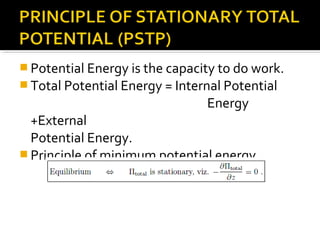
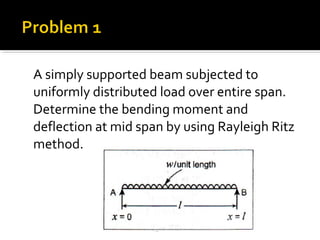
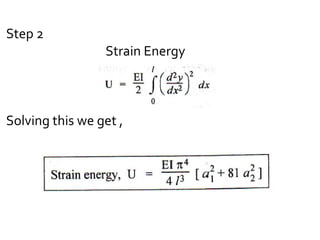
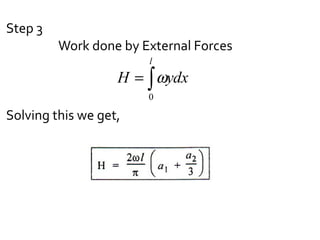
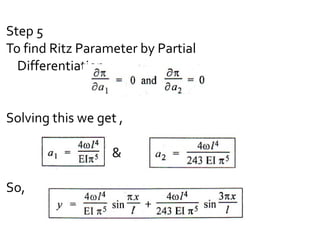
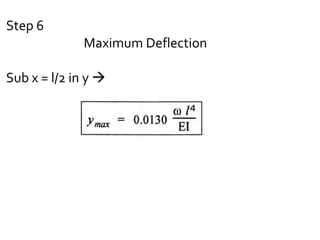
The document discusses numerical methods for solving structural mechanics problems, specifically the Rayleigh Ritz method. It provides an overview of the Rayleigh Ritz method, indicating that it is an integral approach that is useful for solving structural mechanics problems. The document then provides a step-by-step example of using the Rayleigh Ritz method to determine the bending moment and deflection at the mid-span of a simply supported beam subjected to a uniformly distributed load over the entire span.