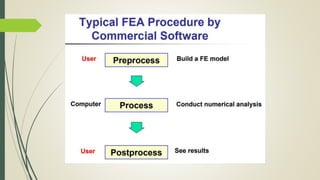
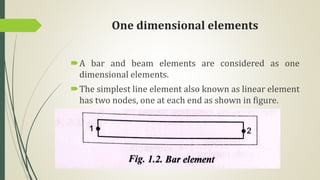
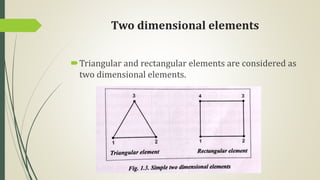
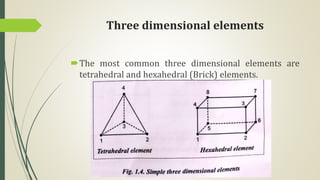
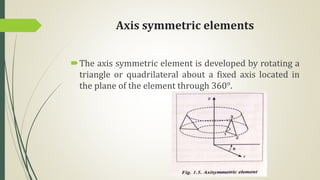
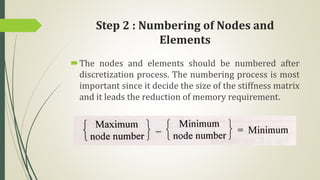
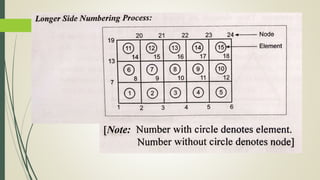
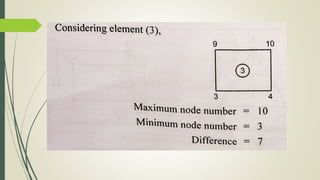
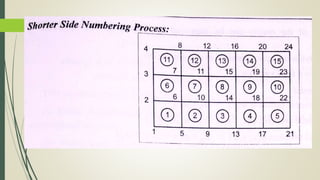
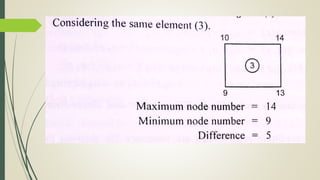
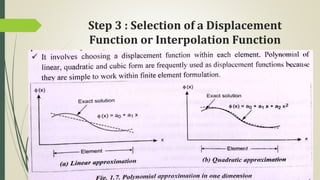
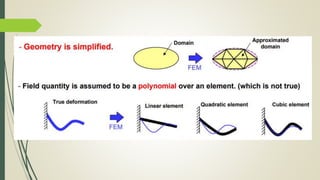
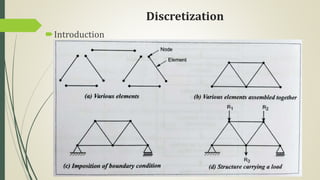
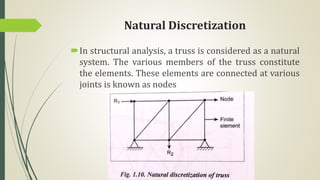
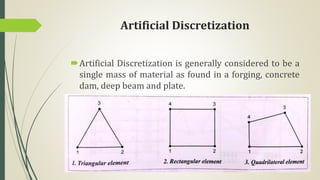
This document discusses the finite element method (FEM) for engineering analysis. It explains that FEM involves discretizing a continuous structure into smaller, finite elements and then solving the equations for each element. The general steps of FEM are: 1) discretizing the structure into elements connected at nodes, 2) numbering nodes and elements, 3) selecting displacement functions, 4) defining material behavior, 5) deriving element stiffness matrices, 6) assembling element equations, 7) applying boundary conditions, 8) solving for displacements, 9) computing element strains and stresses, and 10) interpreting results. One-, two-, and three-dimensional elements as well as axisymmetric elements are discussed.