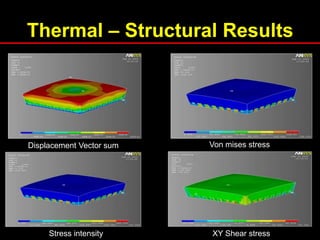
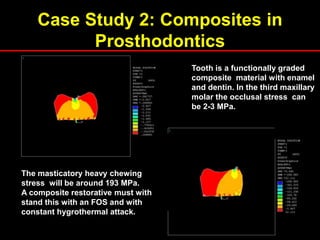
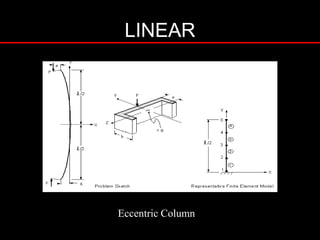
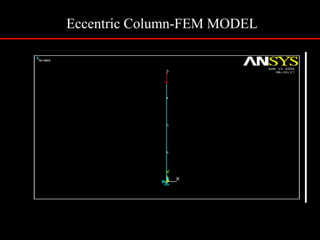
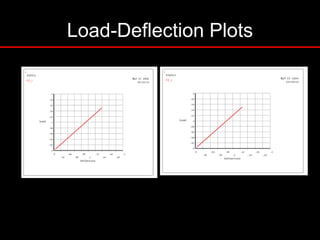
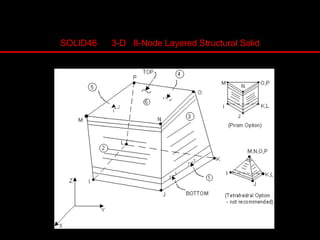
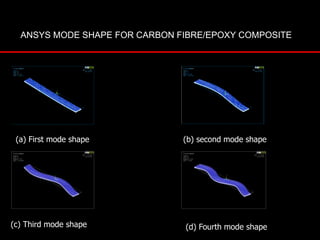
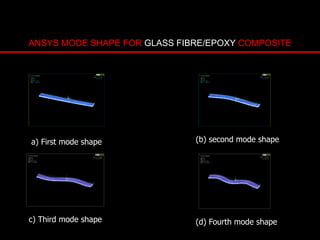
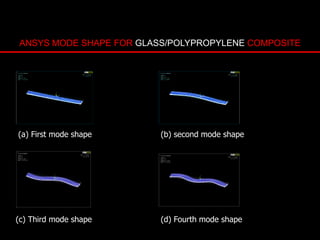
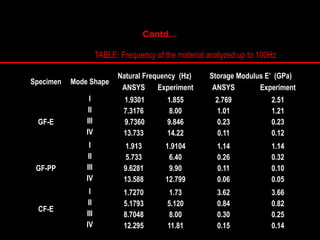
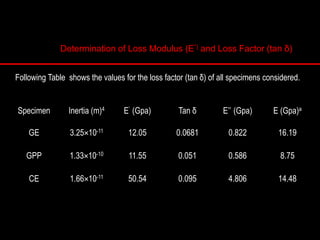
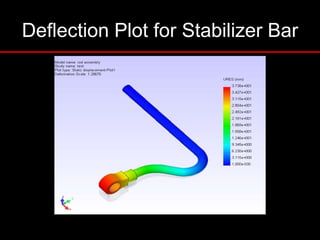
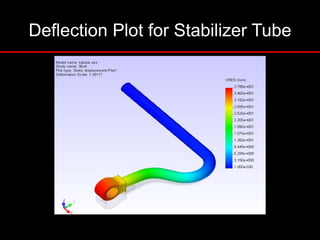
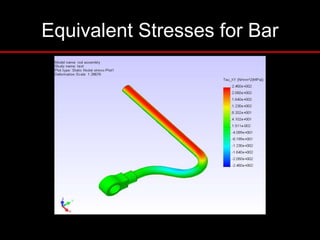
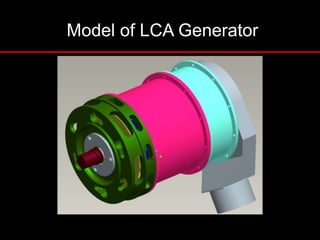
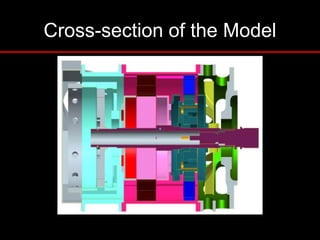
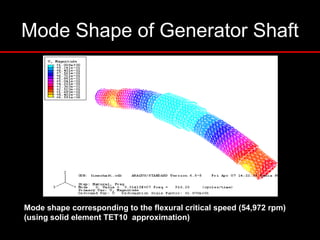
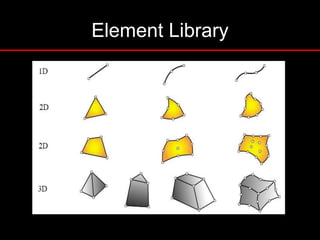
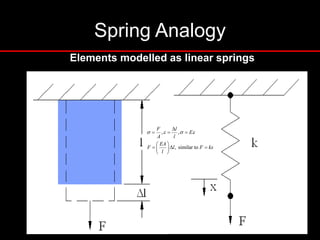
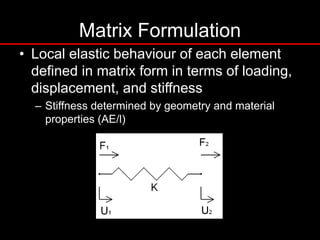
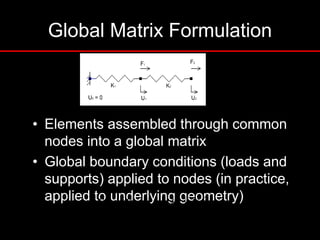
The document provides an introduction to finite element analysis (FEA) and its applications to engineering problems. It discusses that FEA is a numerical method used to solve problems that cannot be solved analytically due to complex geometry or materials. It involves discretizing a continuous structure into small, well-defined substructures called finite elements. The key steps in FEA include preprocessing such as defining geometry, meshing and material properties, solving the problem, and postprocessing results such as stresses and strains. The document also discusses various element types, assembly of elements, sources of error in FEA, and its advantages such as handling complex geometry, loading and materials.








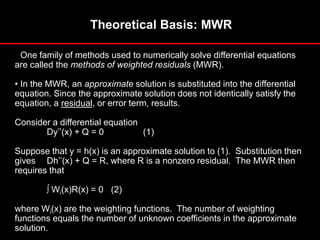

![Theoretical Basis: Variational Method
• The variational method involves the integral of a function that
produces a number. Each new function produces a new
number.
• The function that produces the lowest number has the
additional property of satisfying a specific differential equation.
• Consider the integral
p D/2 * y’’(x) - Qy]dx = 0. (1)
The numerical value of pcan be calculated given a specific
equation y = f(x). Variational calculus shows that the
particular equation y = g(x) which yields the lowest numerical
value for pis the solution to the differential equation
Dy’’(x) + Q = 0. (2)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitifdocuments-230505084245-d5bbe0c7/85/Unit-I-fdocuments-in_introduction-to-fea-and-applications-ppt-15-320.jpg)