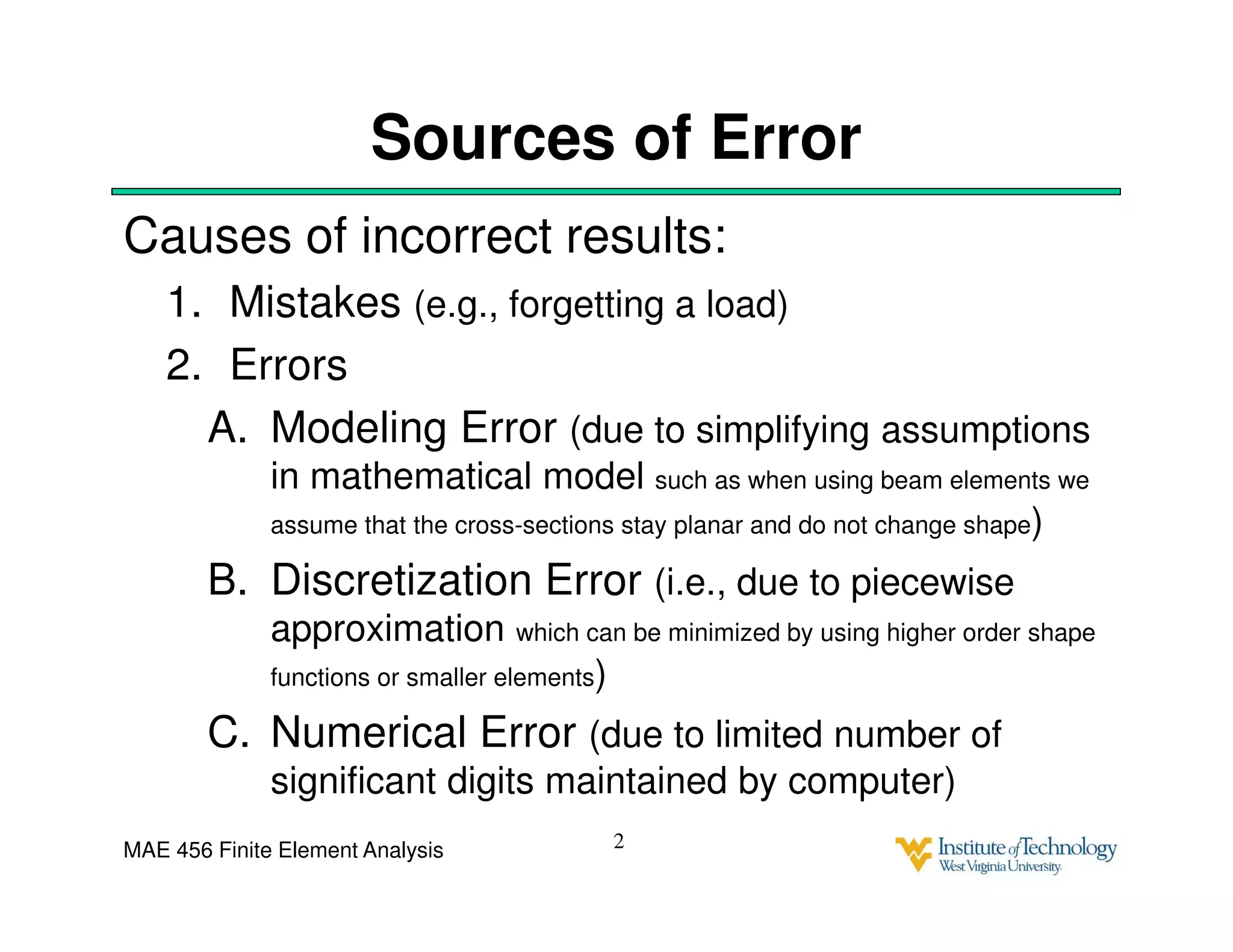
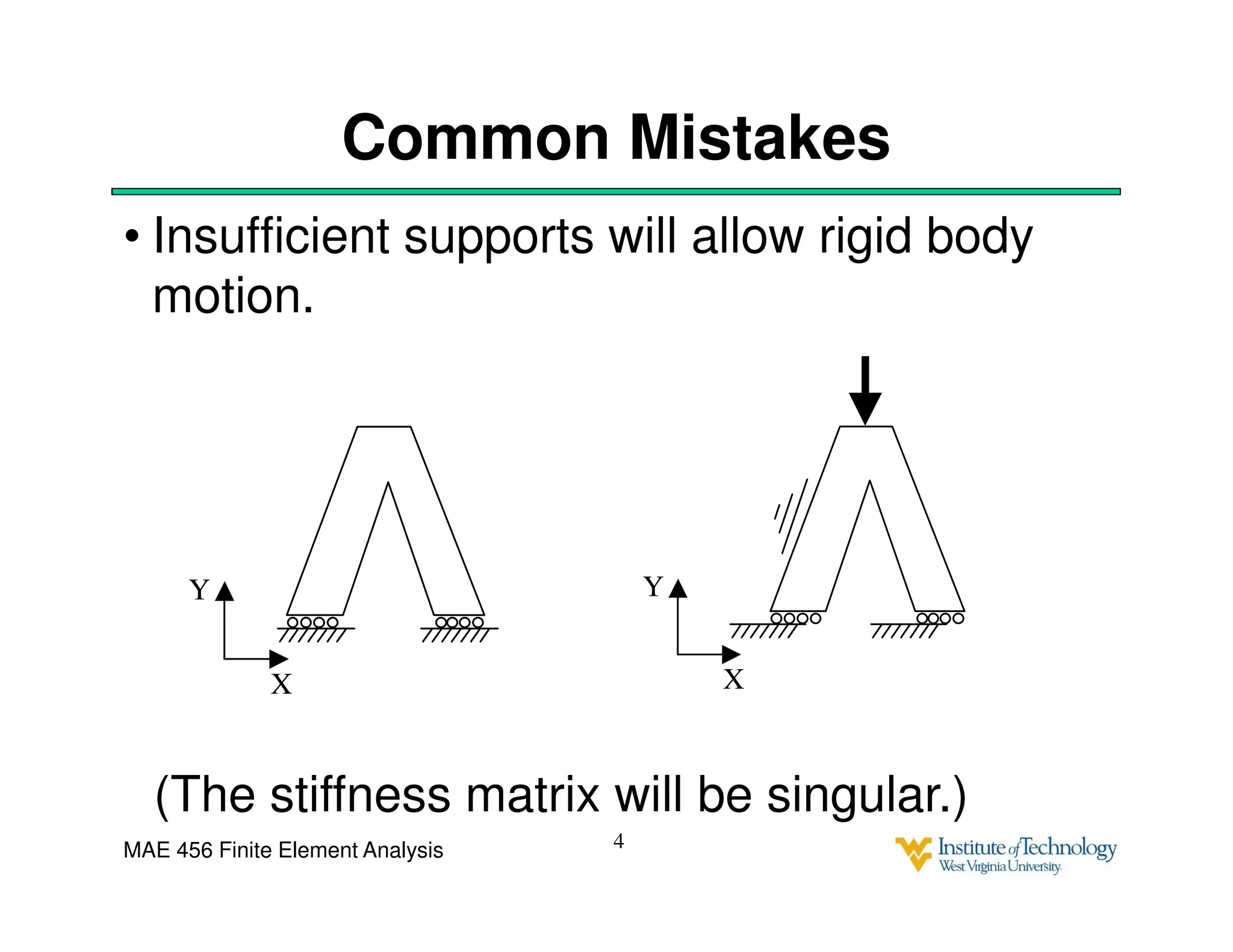
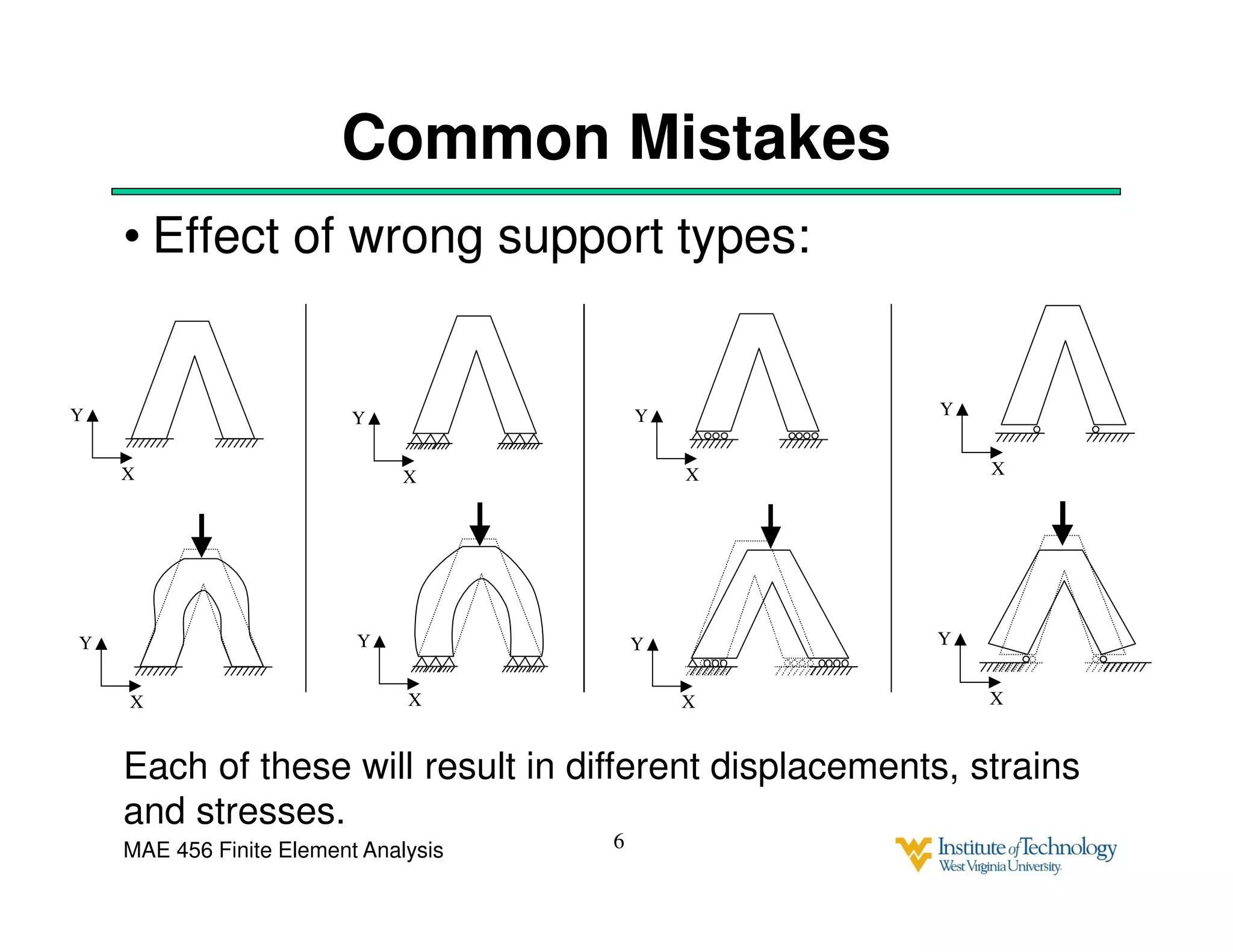
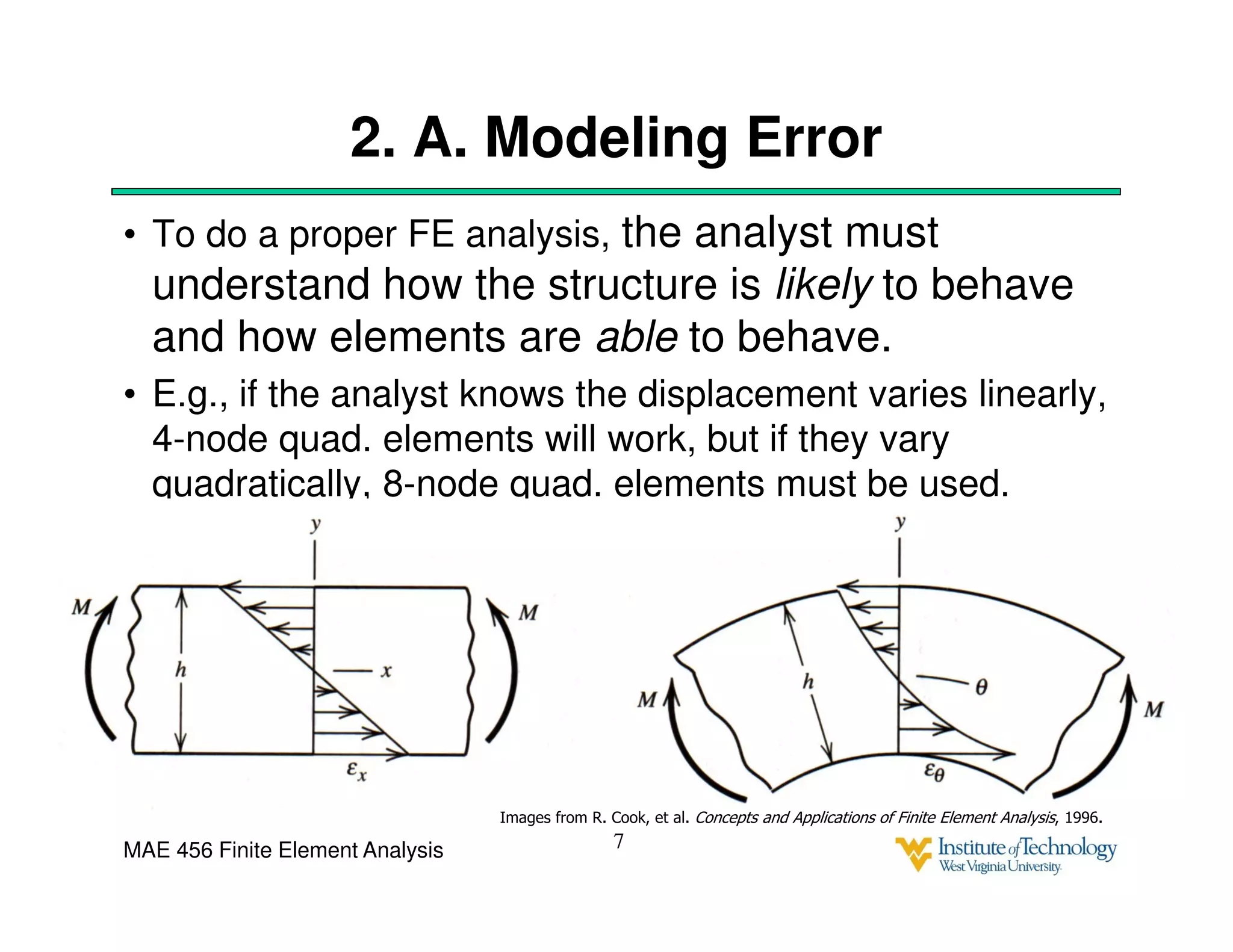
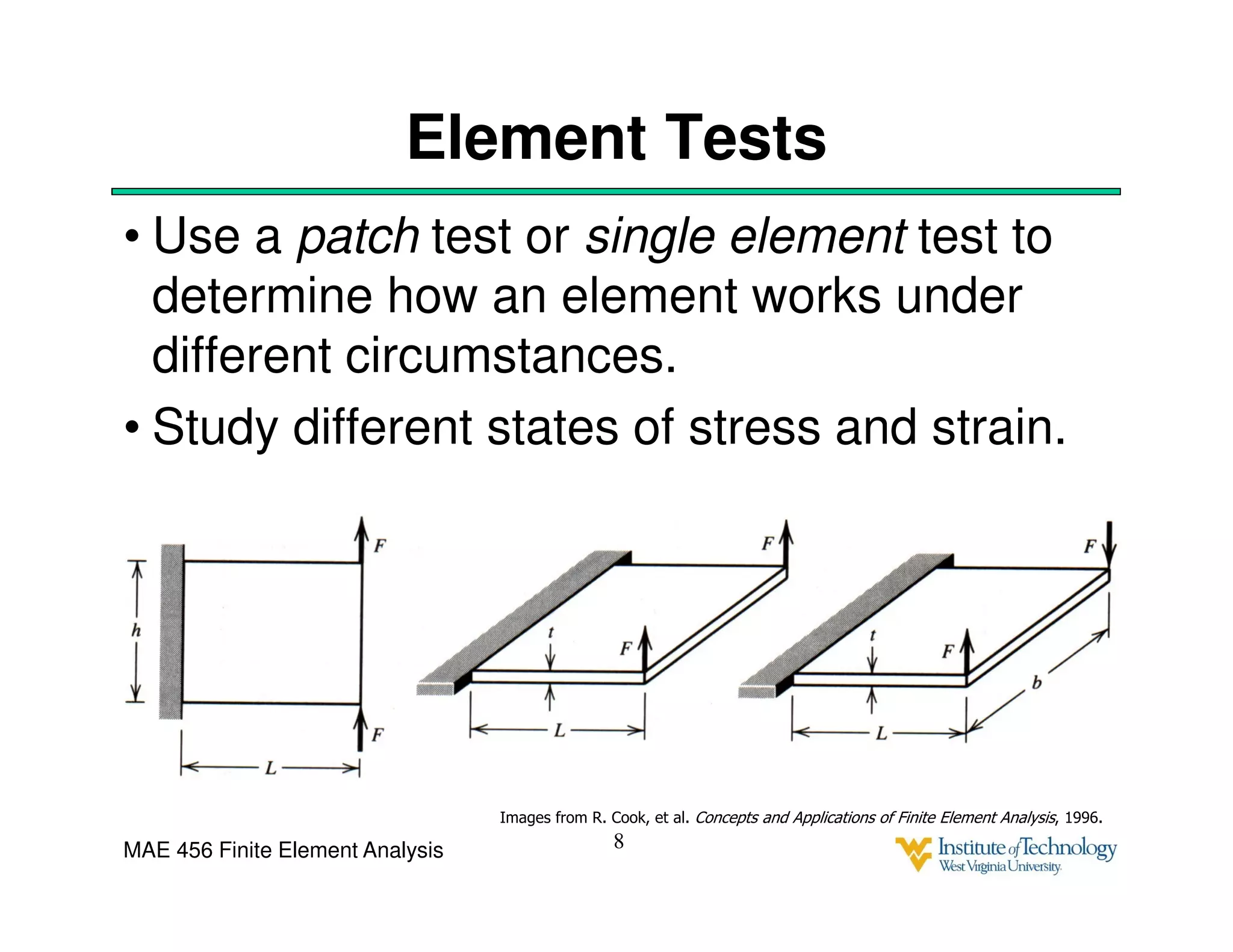
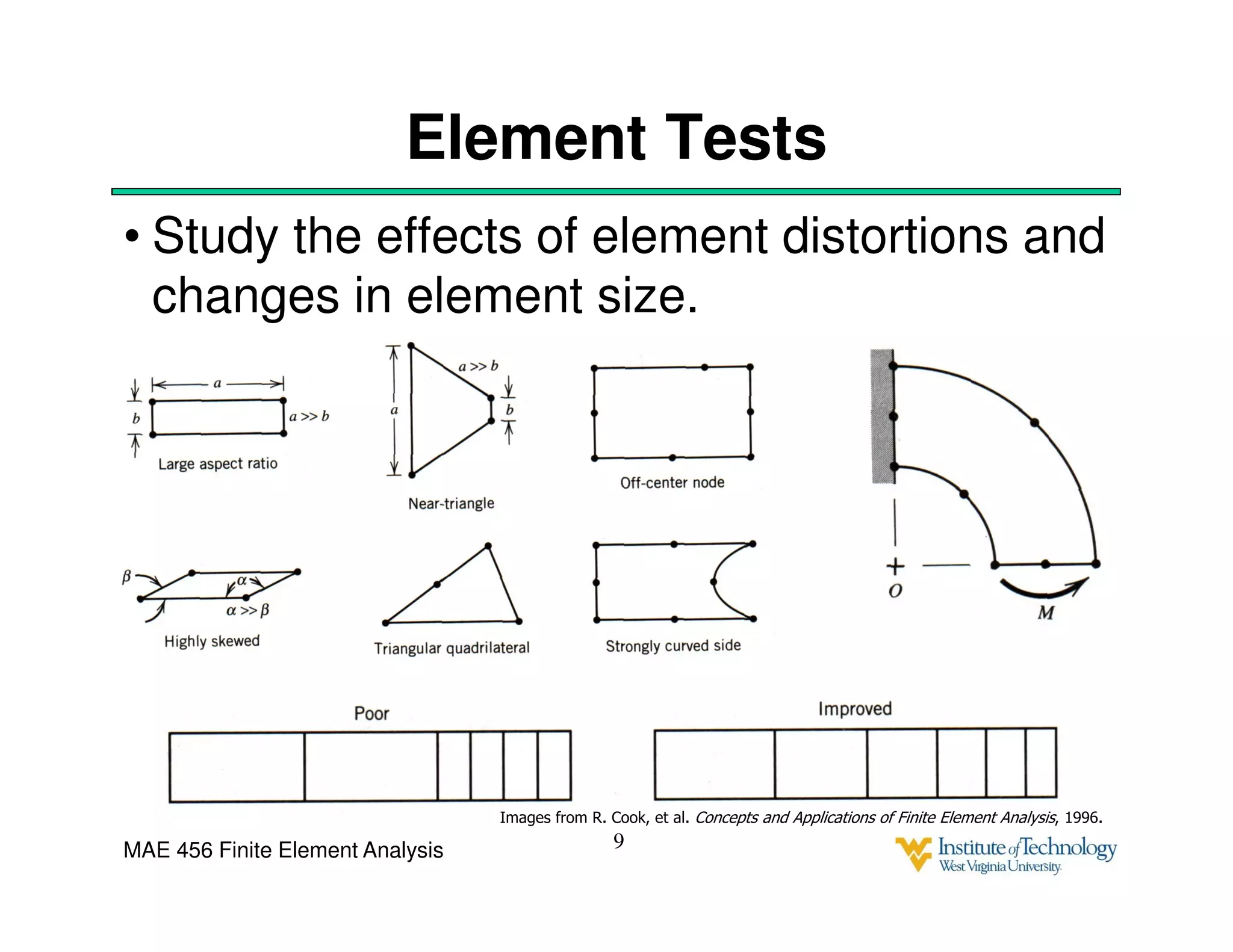
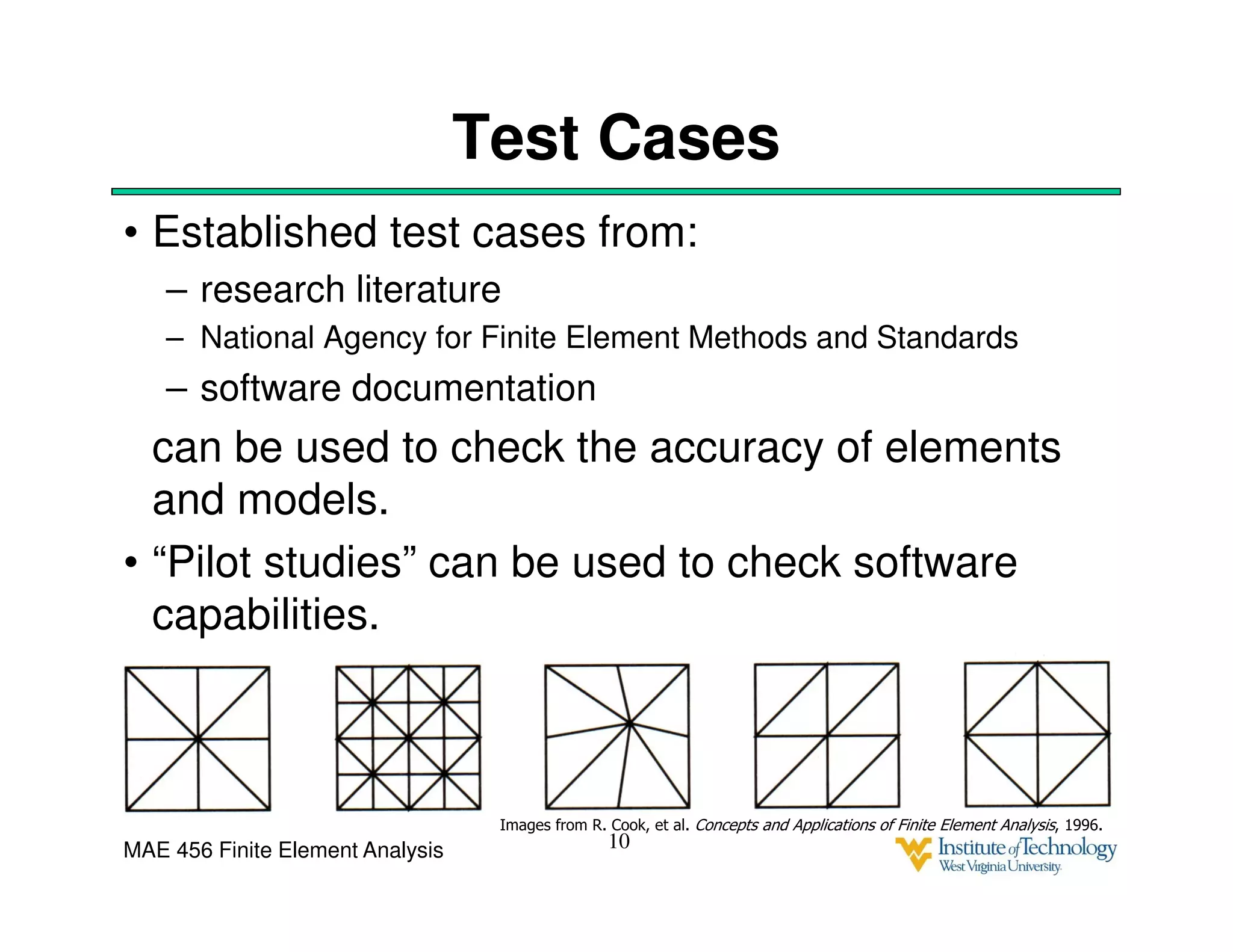
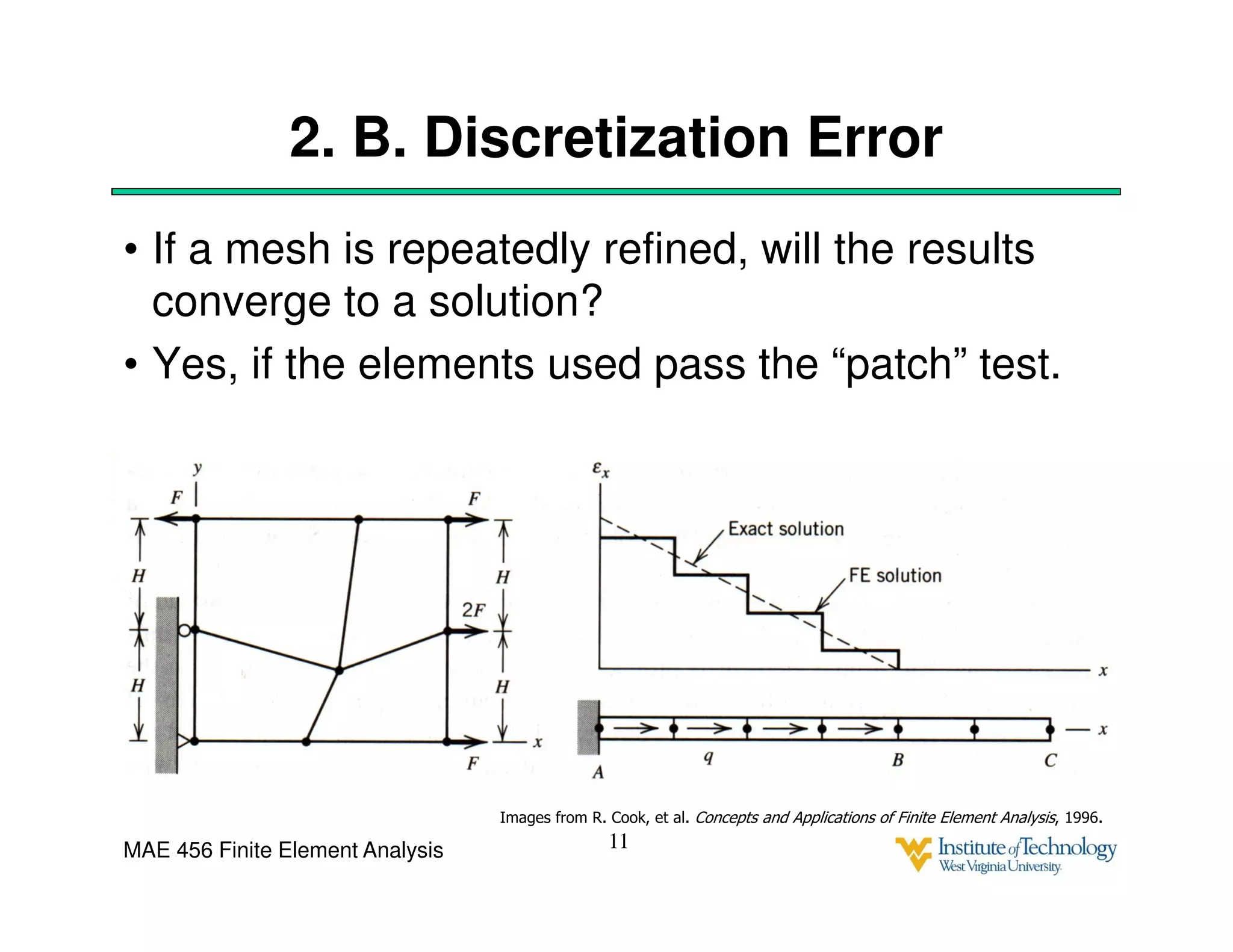
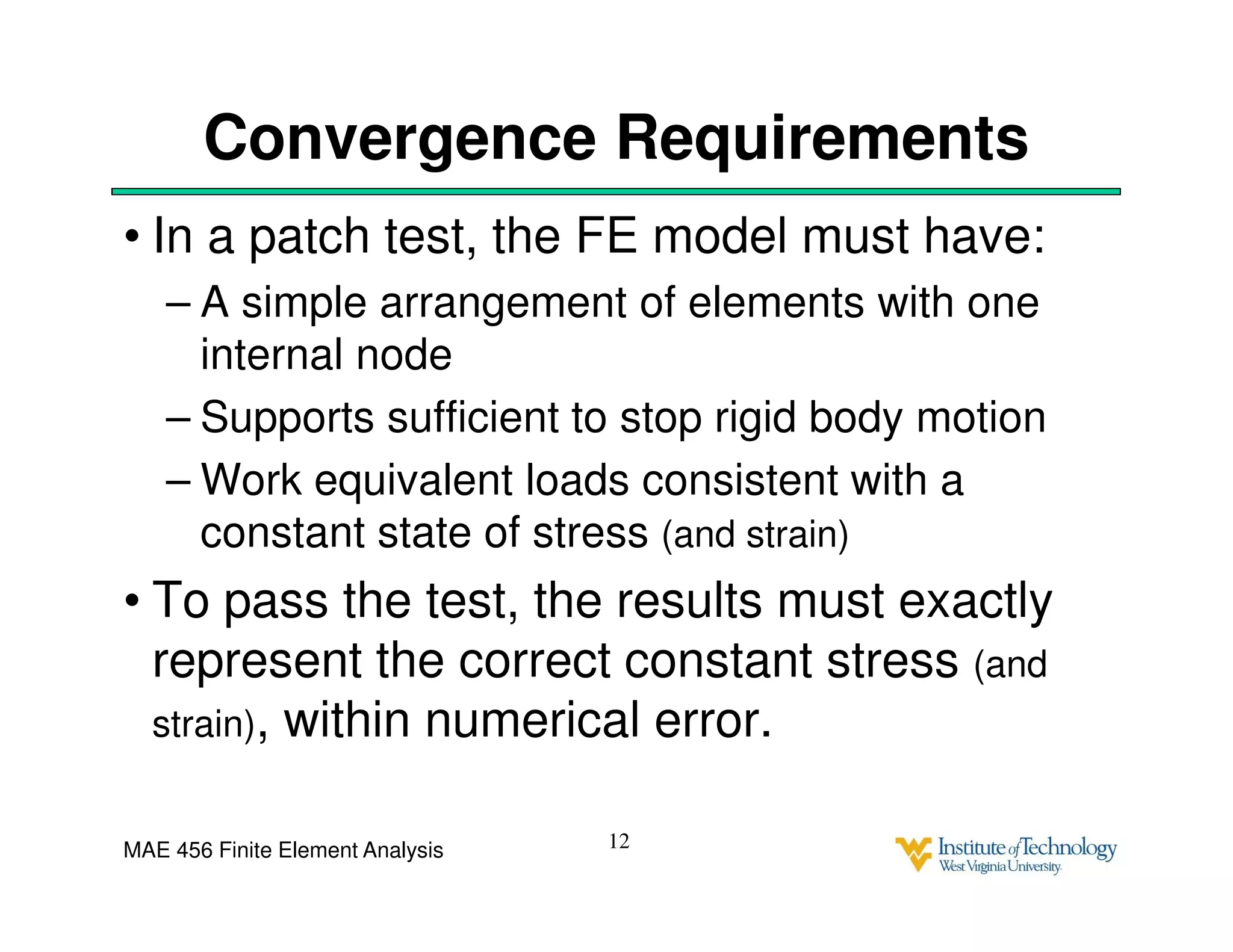
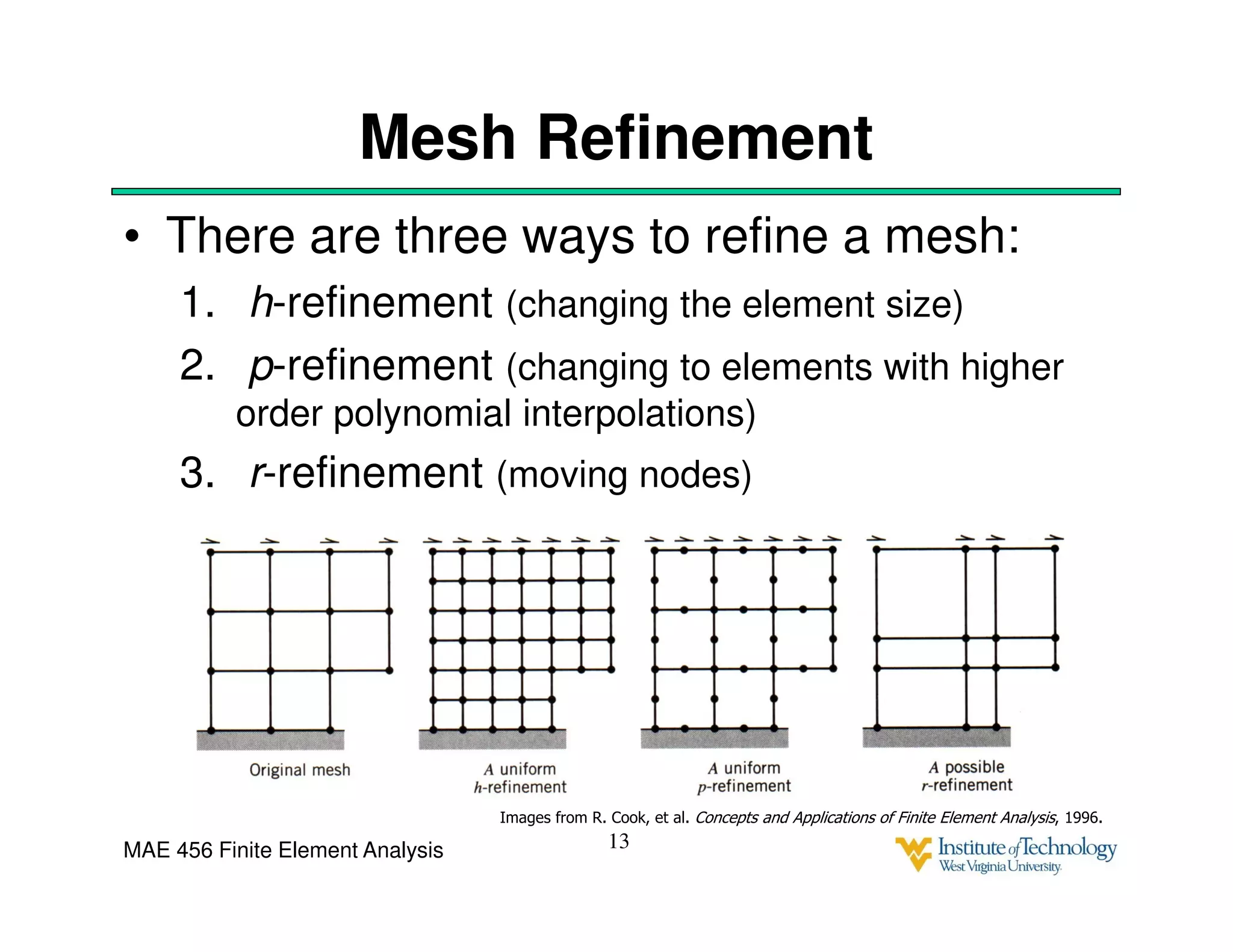
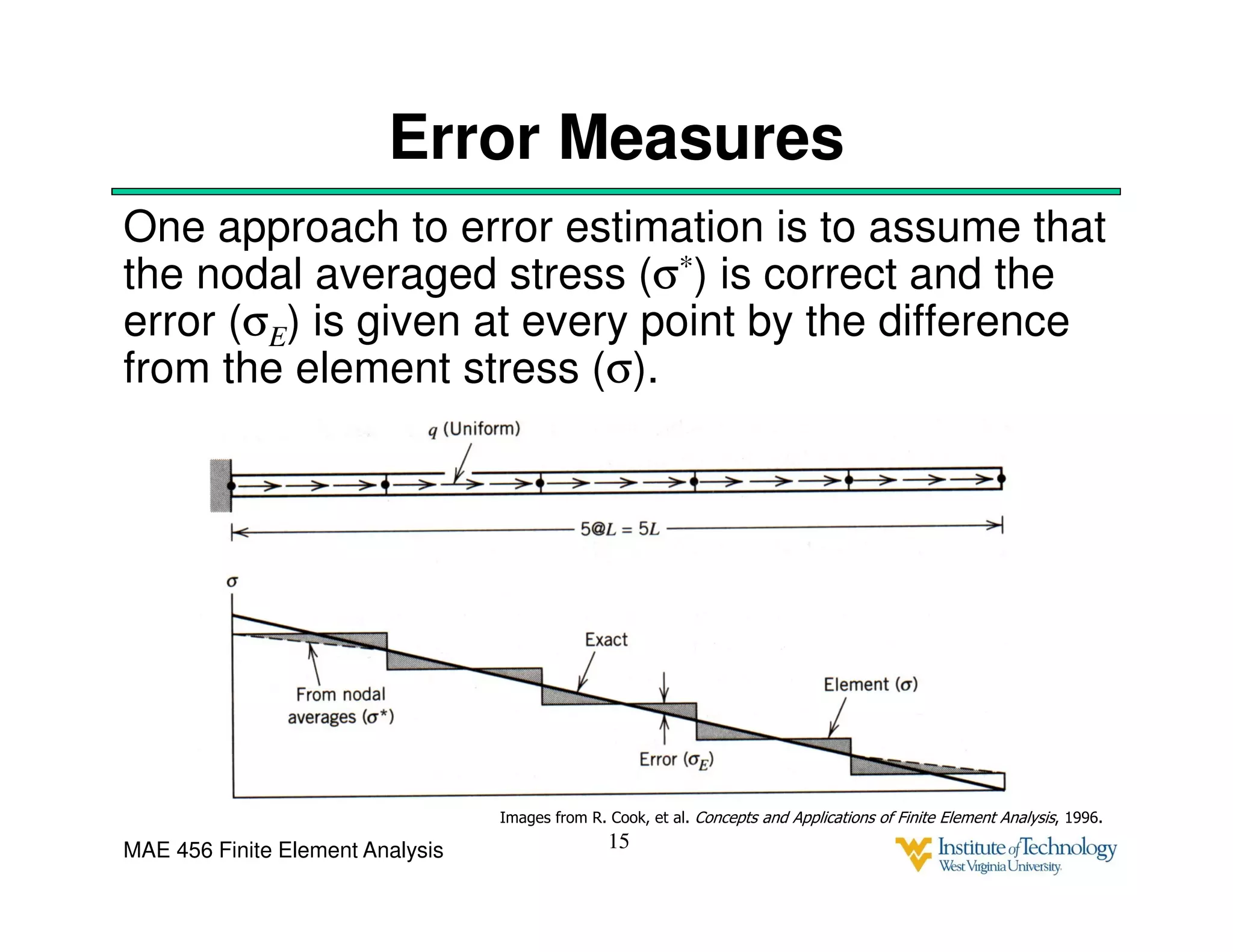
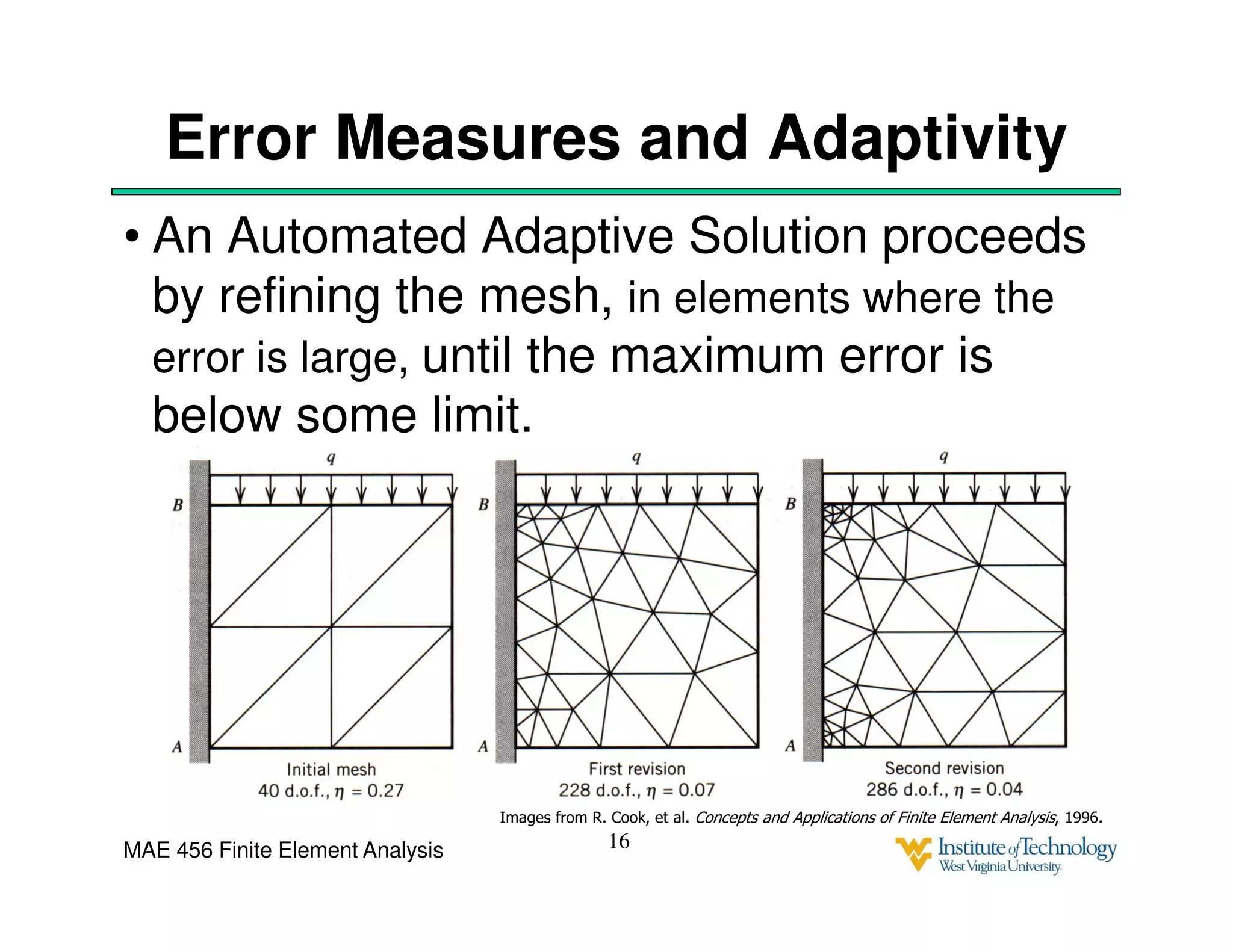
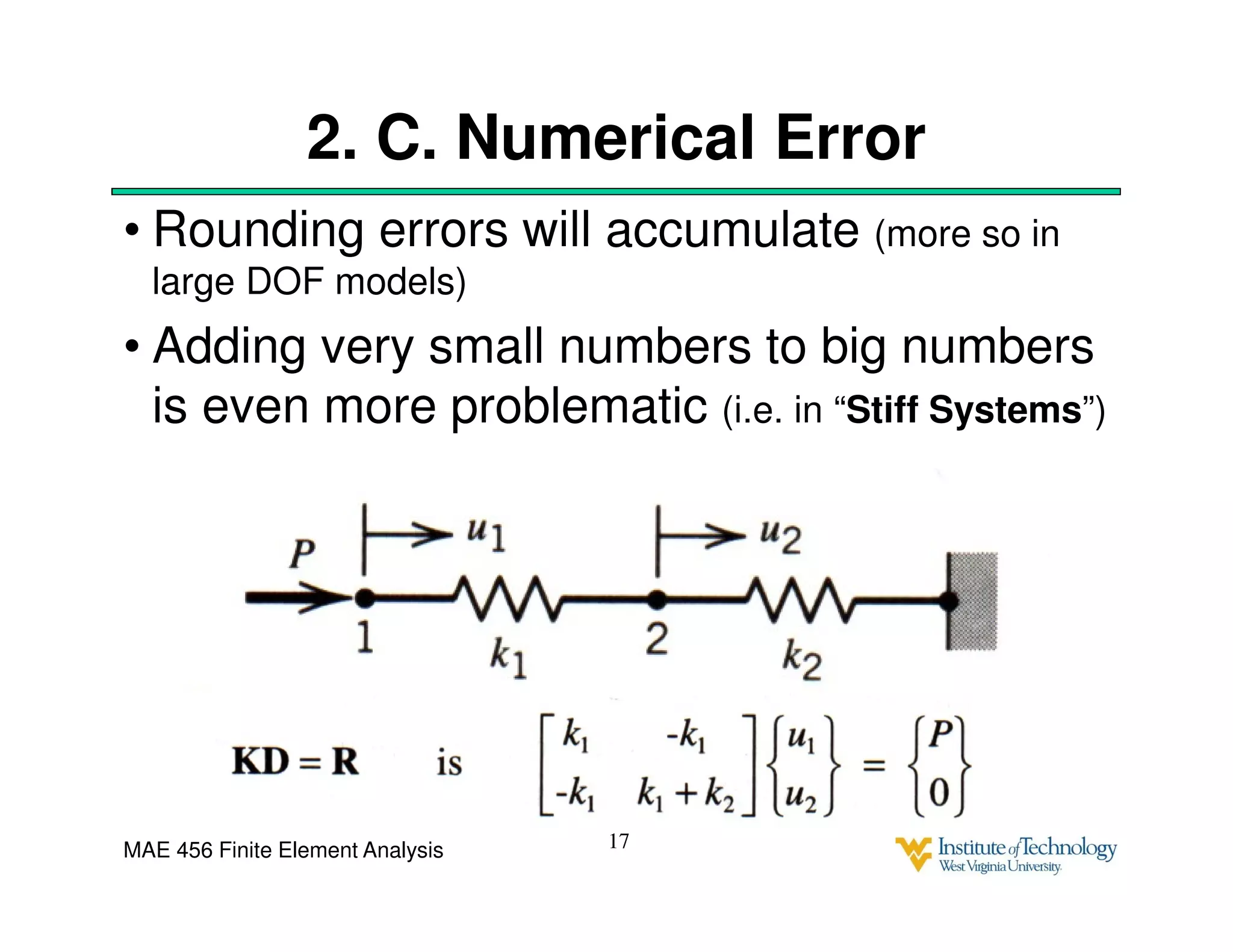
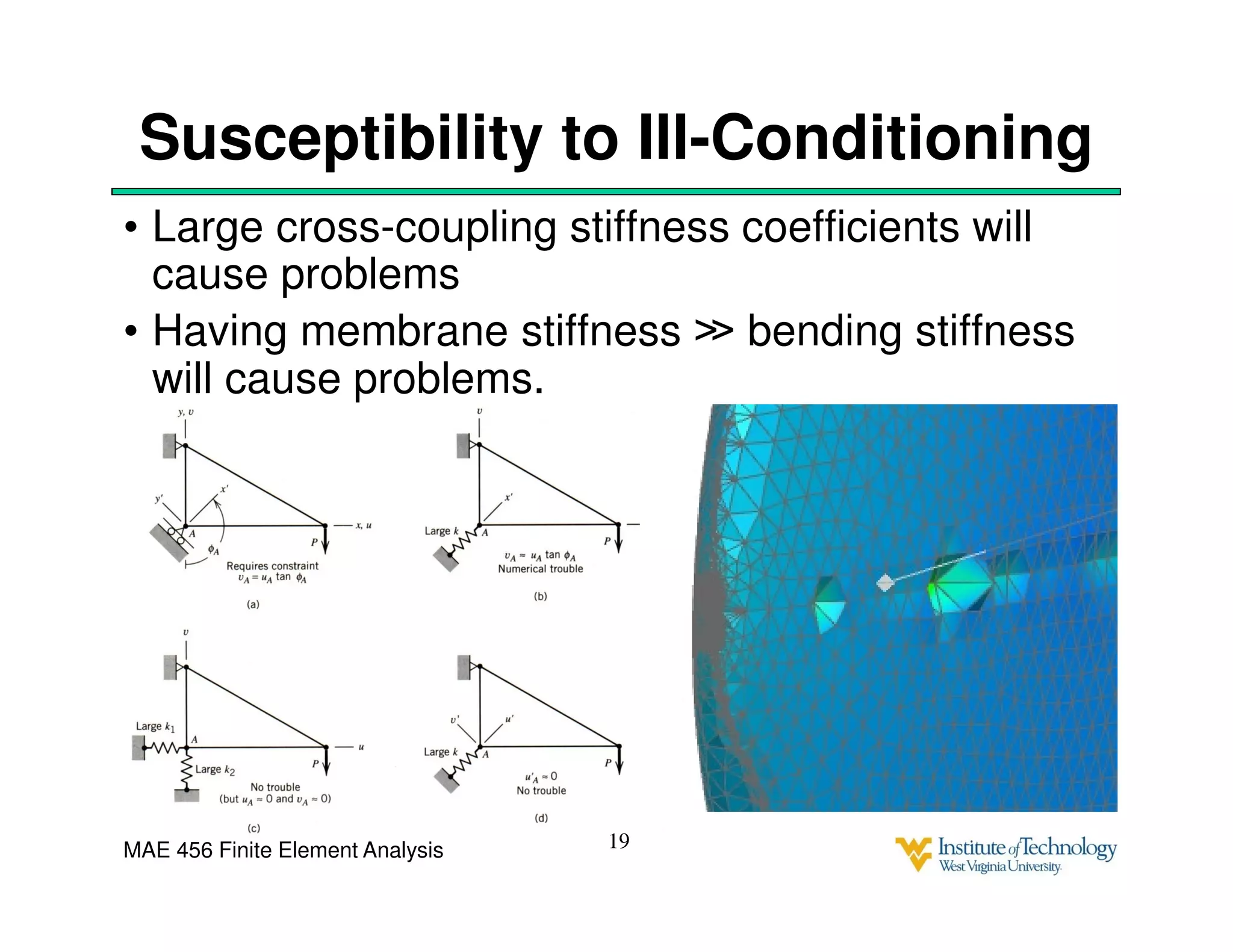
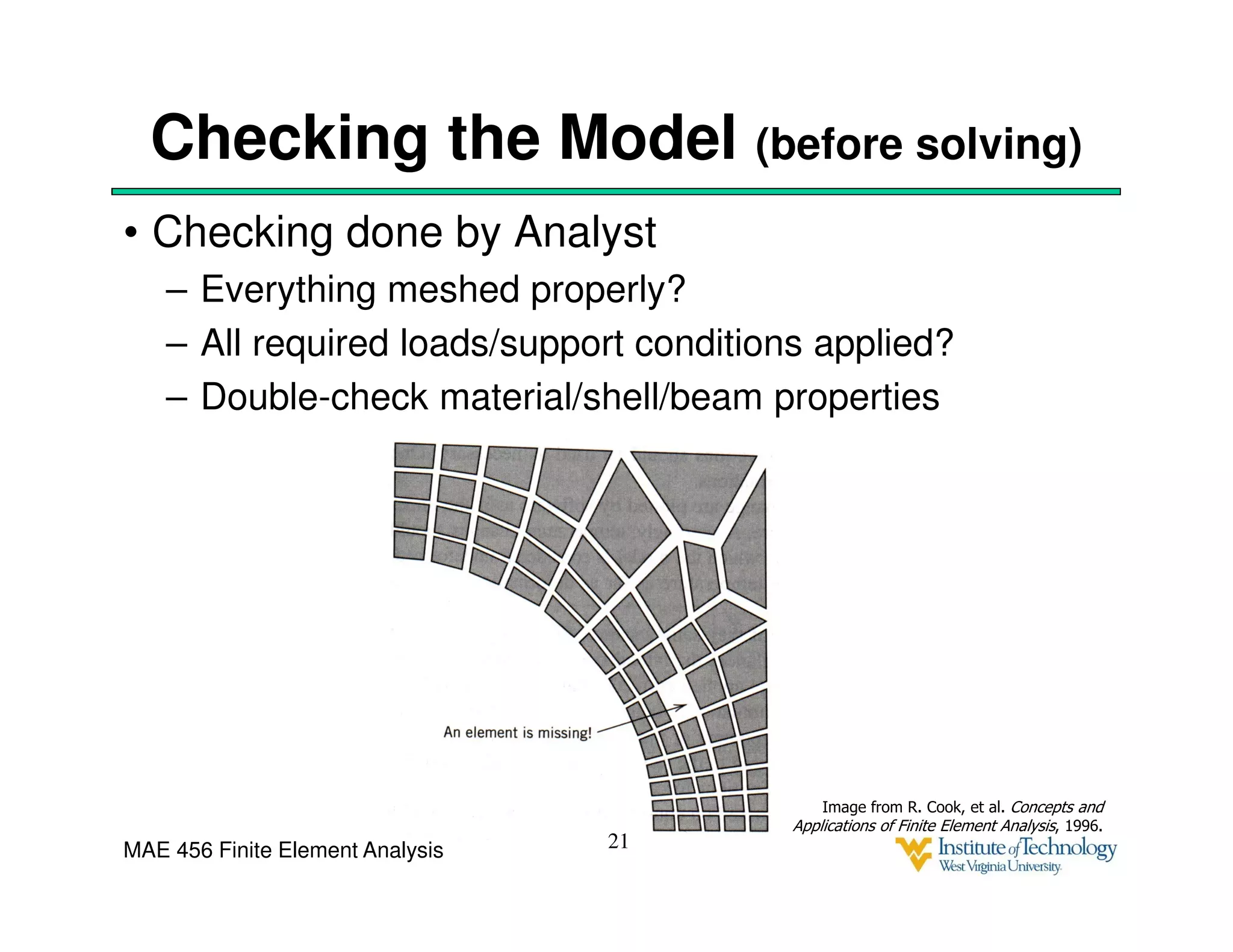
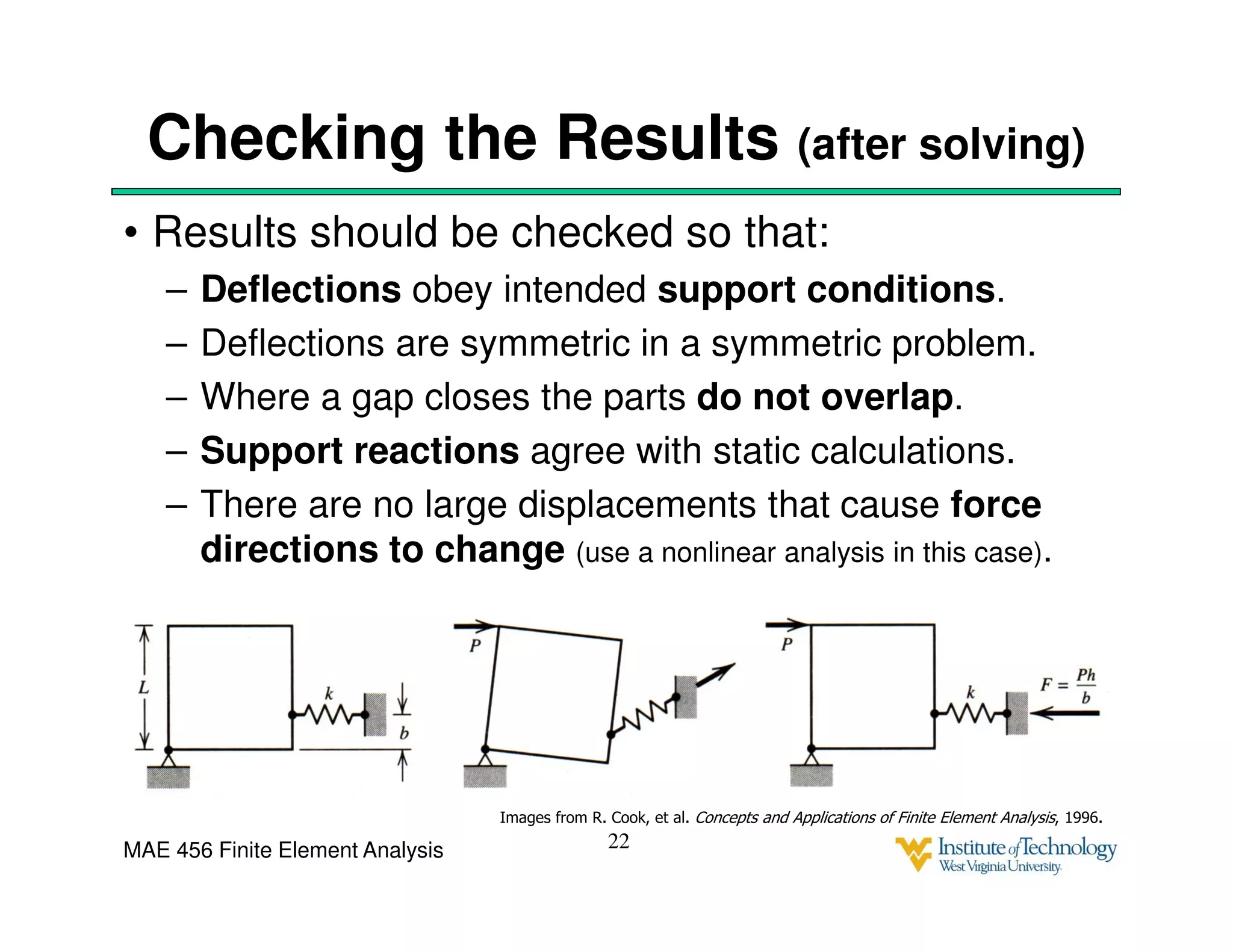
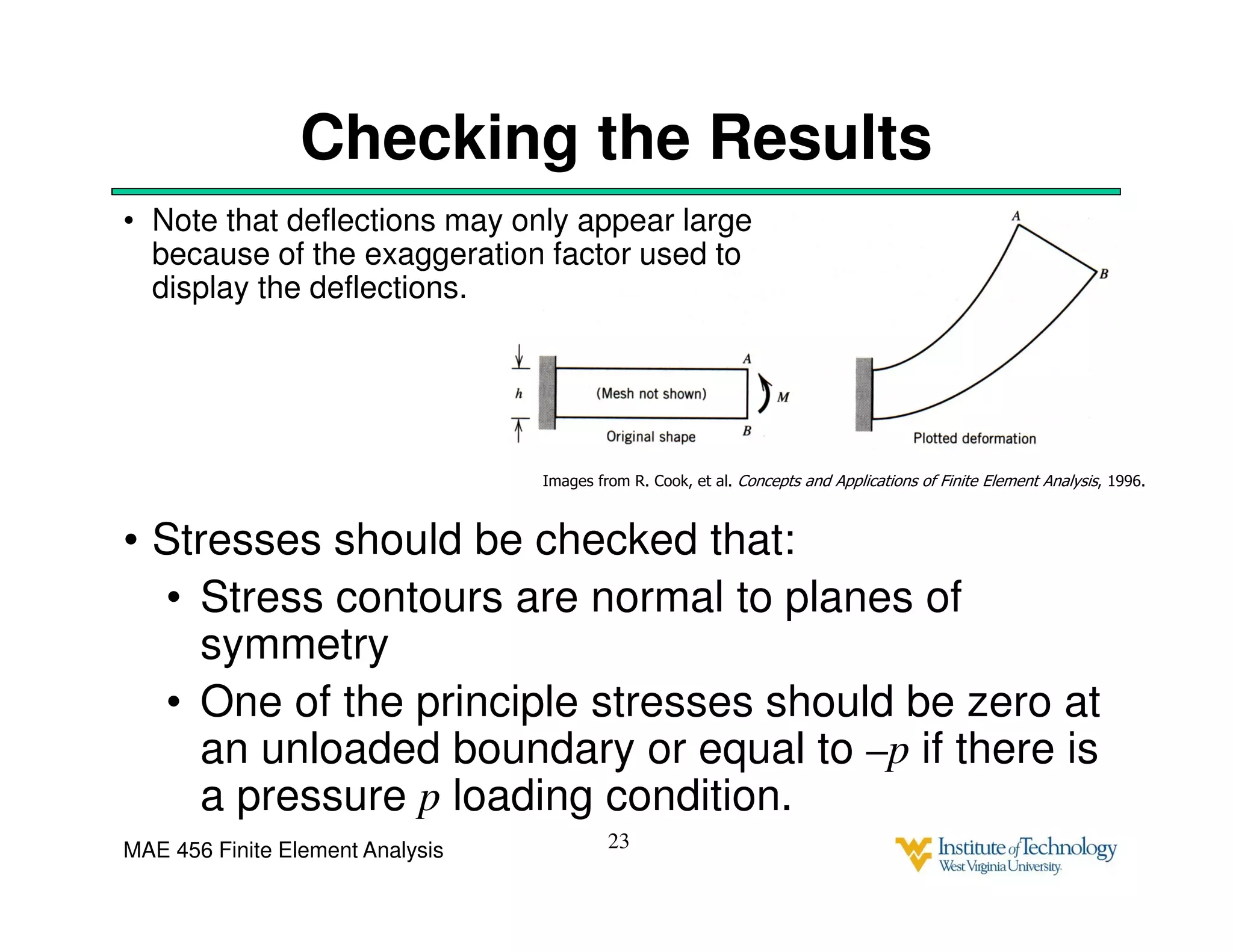
This document discusses sources of error in finite element analysis, including modeling errors due to simplifying assumptions, discretization errors from approximating solutions, and numerical errors from limited computer precision. It provides examples of common mistakes that can cause incorrect results, such as incorrect material properties or insufficient boundary constraints. It also discusses best practices for verifying models, such as element testing, mesh refinement studies, and checking results against analytical solutions or boundary conditions.