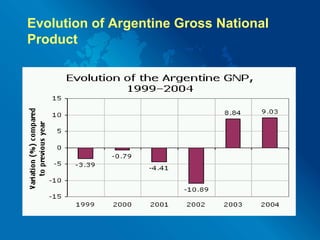
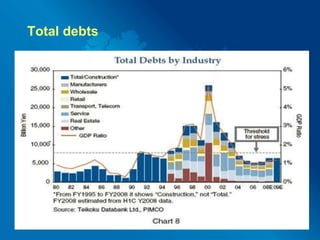
Financial globalization has led to speculation and ruin in many parts of the globe. It occurs in a series of steps: first, multinational companies exploit customers and domestic competitors; second, they exert political influence and set unfair prices; third, they destabilize local economies and corrupt political systems. A fourth problem is that foreign investment can undervalue the currencies of poorer countries, slowing their development and potentially causing banking crises or recessions. Several contemporary examples illustrate these issues, such as the financial crises that struck Mexico, Indonesia, Argentina, Thailand, Japan, and Malaysia in the late 20th century. Recommendations include developing strong domestic policies, capping financial globalization, not giving all power to foreign investors,