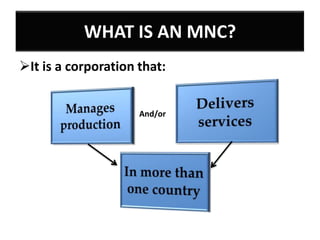
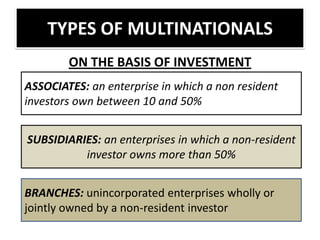
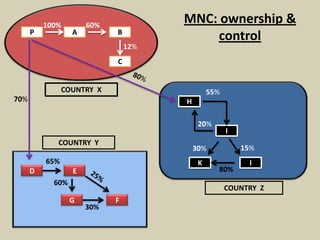
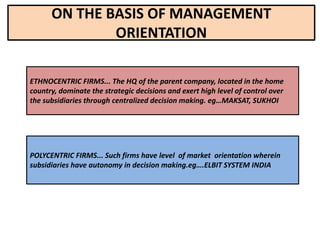
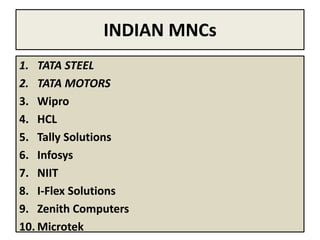
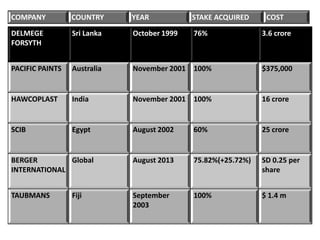
This document provides an overview of managing multinational corporations (MNCs). It defines MNCs and differentiates them from non-multinational firms. It outlines various types of MNCs based on investment, operations, and management orientation. The document discusses the impact of MNCs in India, including their positive and negative effects. It notes some of India's offerings to MNCs and provides examples of Indian companies in the Fortune 500 list. The document also examines trends of MNCs in India, their advantages, and key issues in the Indian context. It concludes with a case study of Asian Paints' growth into a global MNC.