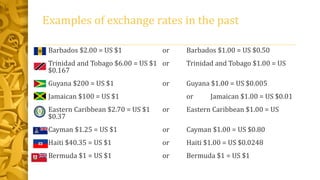
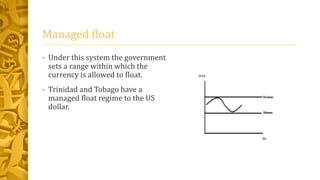
This document discusses different types of exchange rate regimes. It provides examples of historical exchange rates between Caribbean currencies and the US dollar. It then defines an exchange rate regime as the system that determines the value of a domestic currency in terms of foreign currencies. The three main types of regimes are floating, where supply and demand determine the rate; fixed or pegged, where a currency is tied to another; and managed float, where a currency floats within a predetermined range. It provides details on how each regime works.