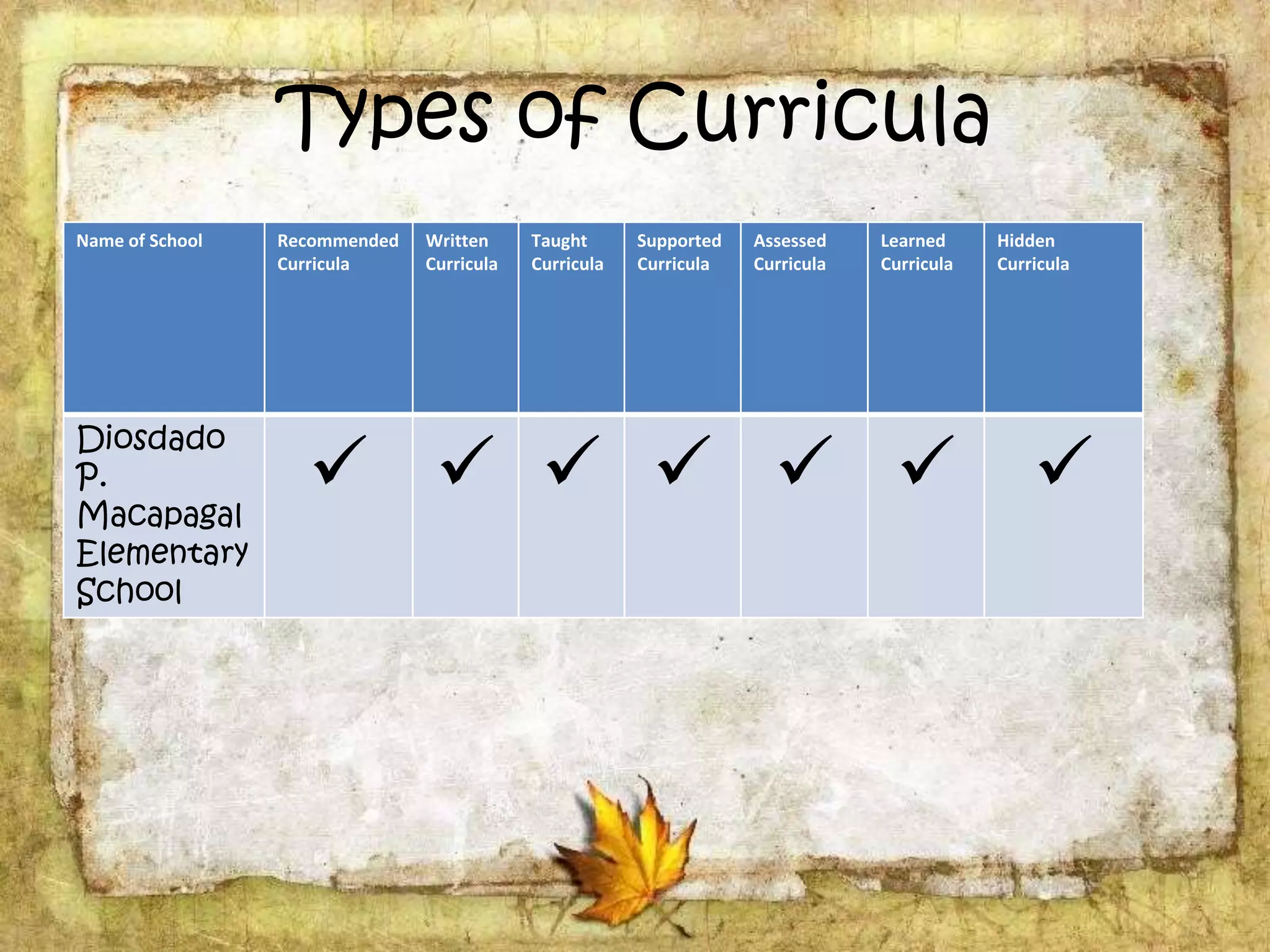
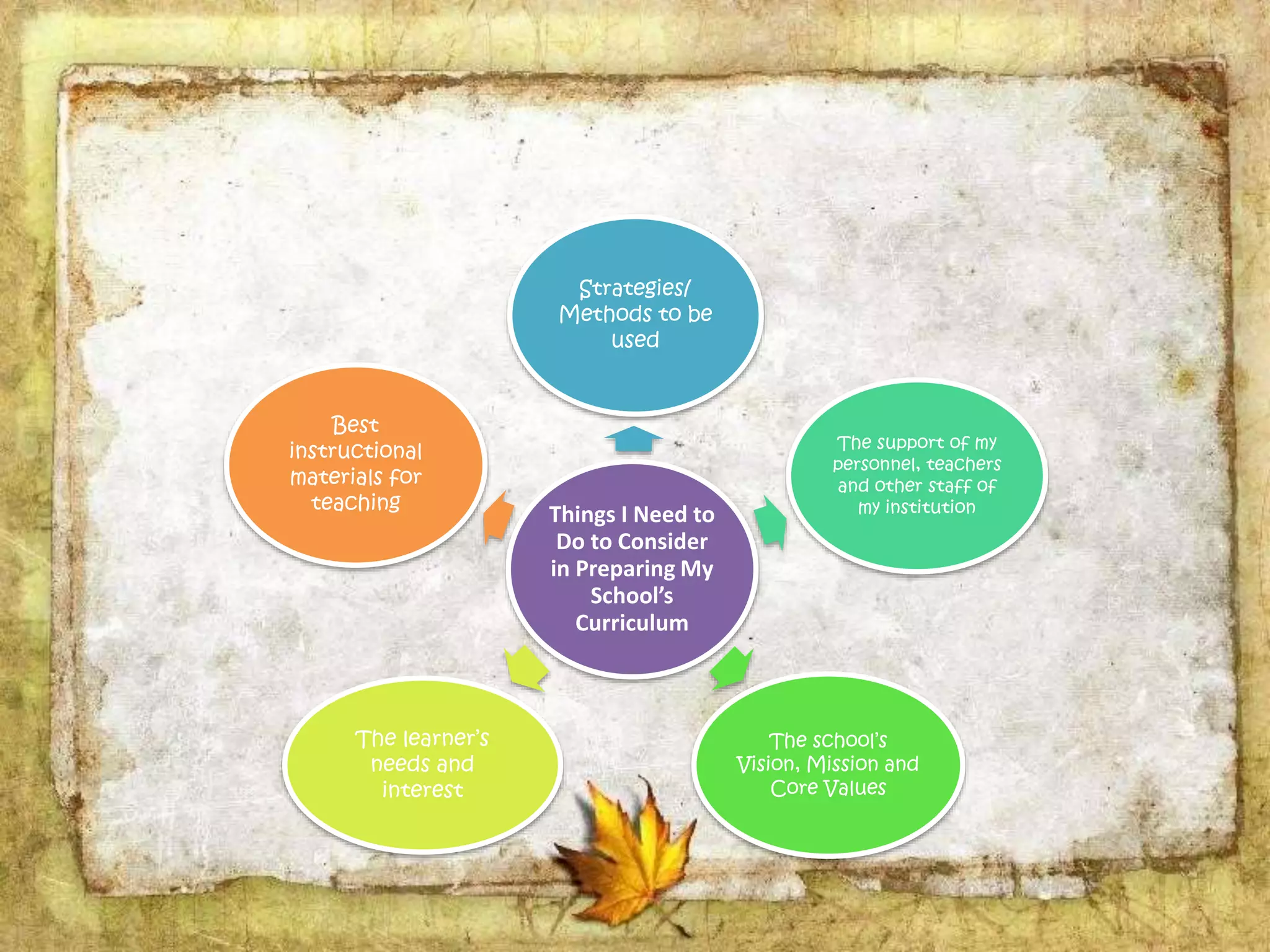
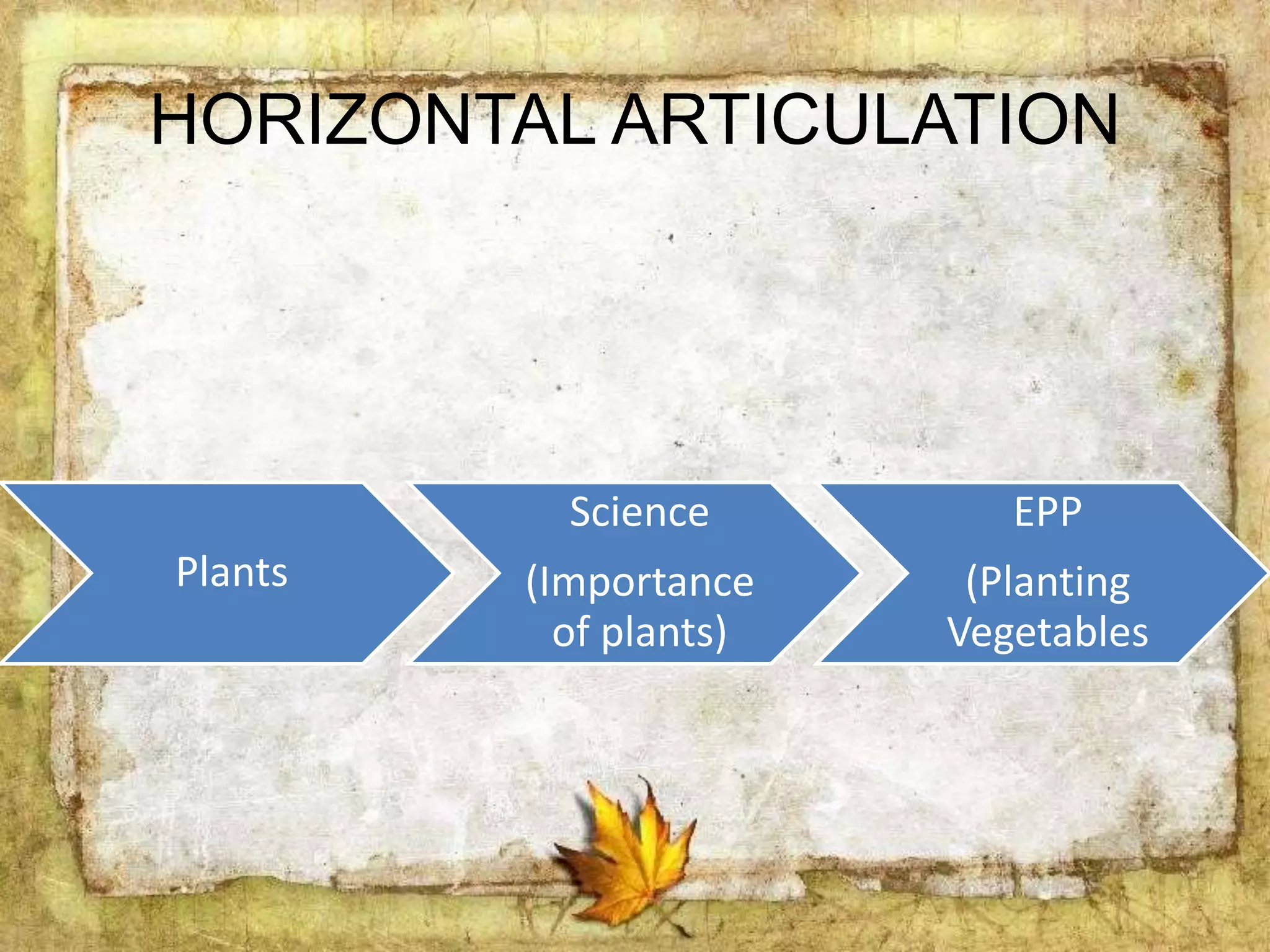
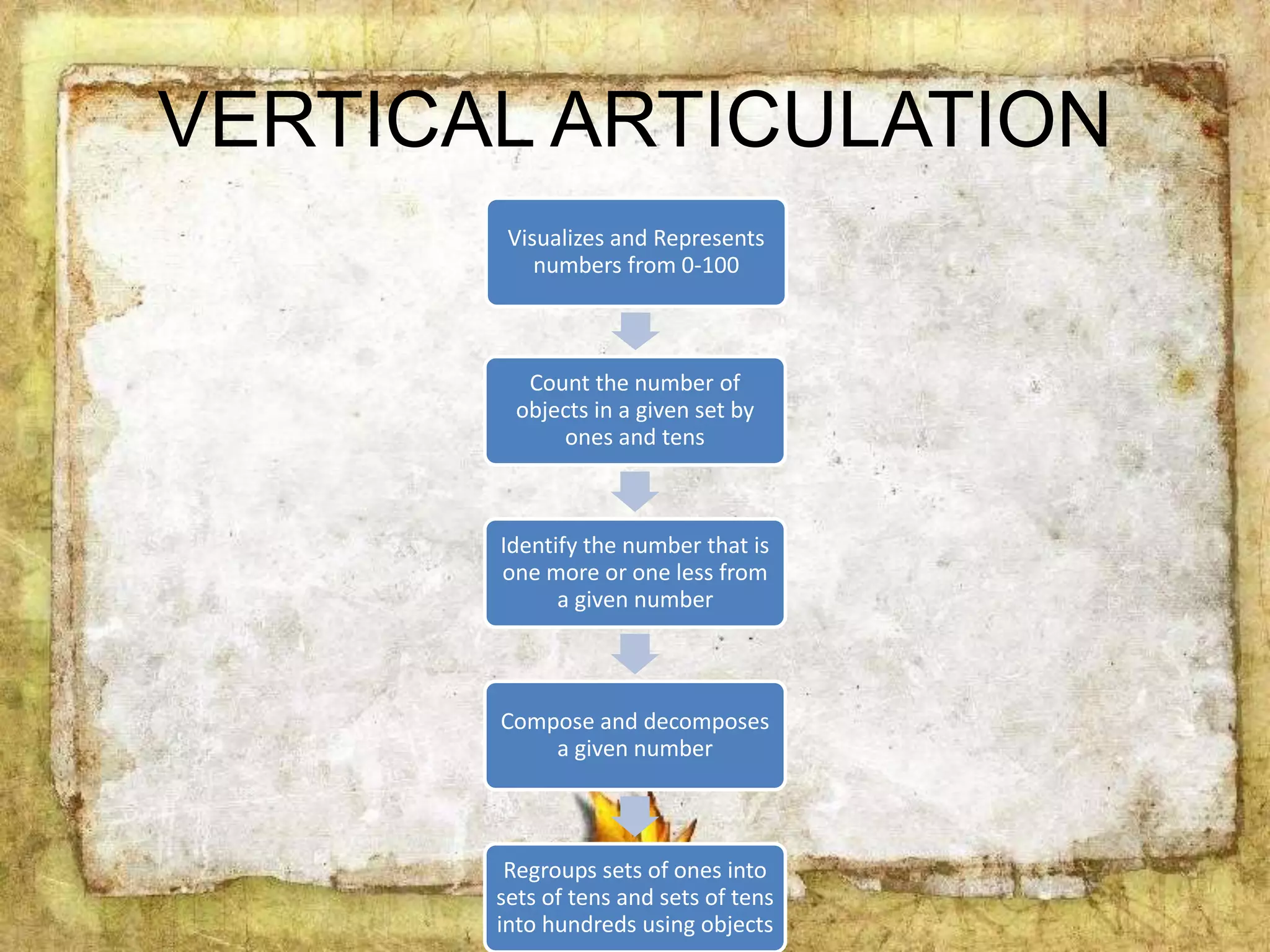
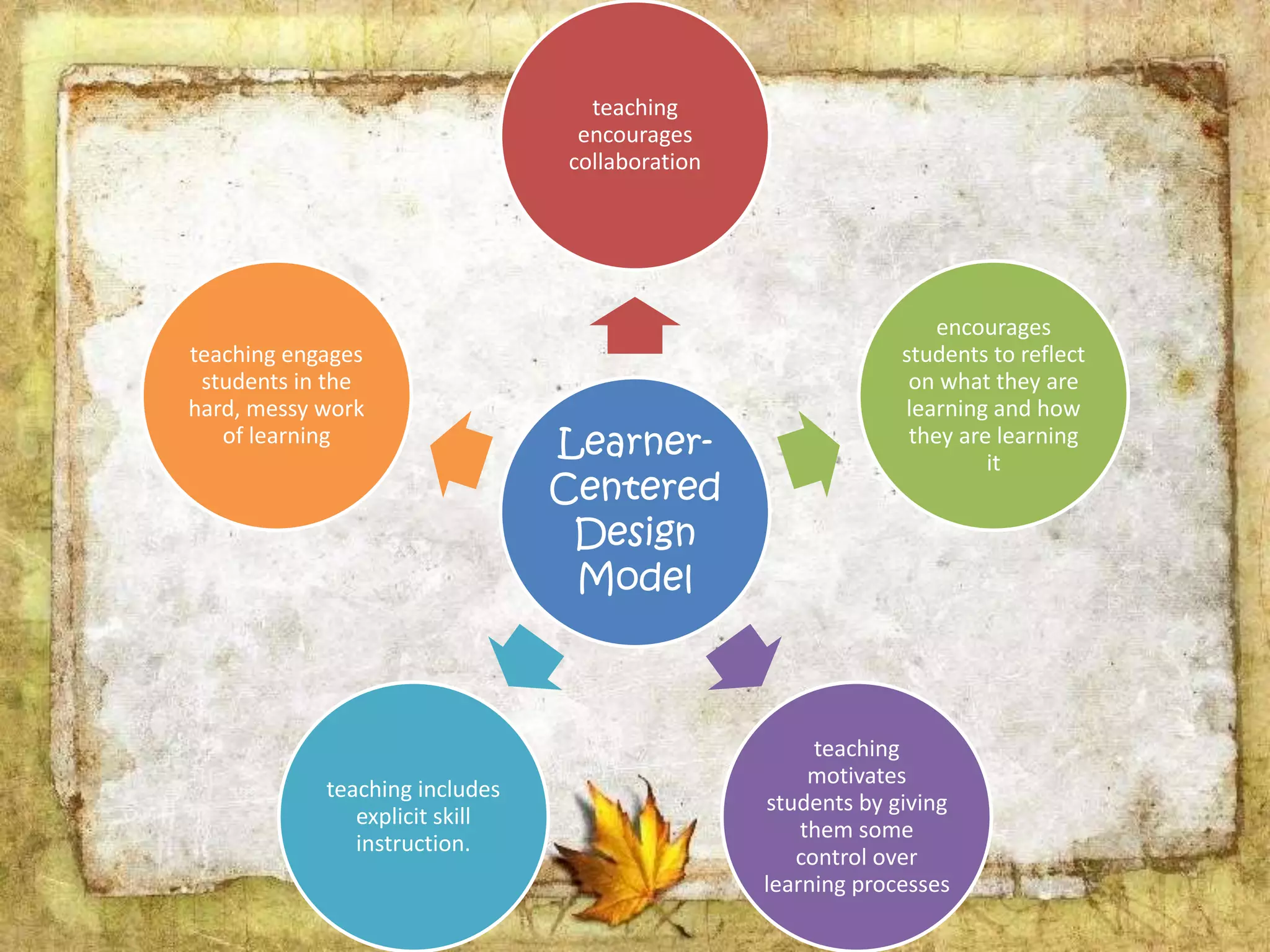
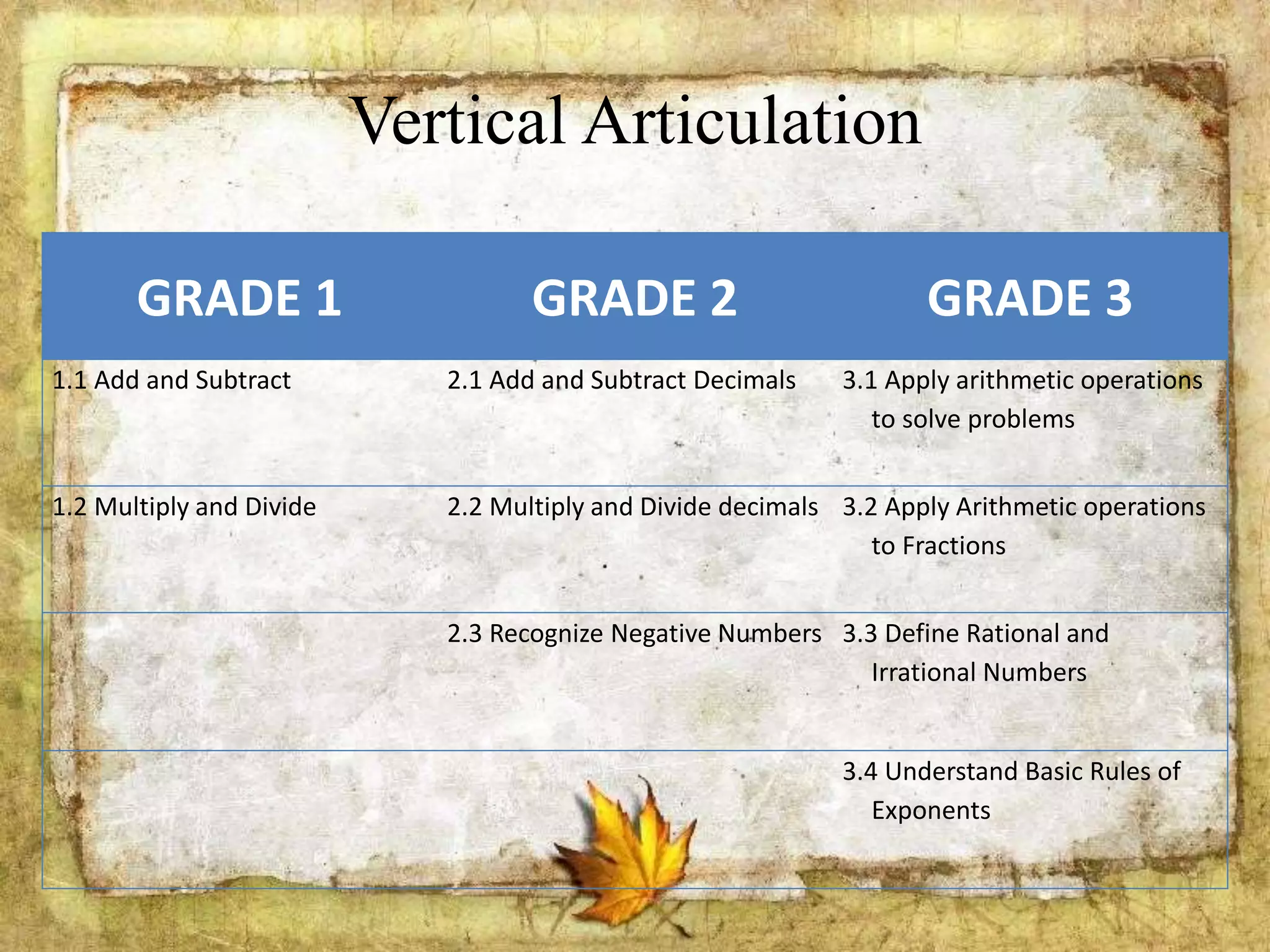
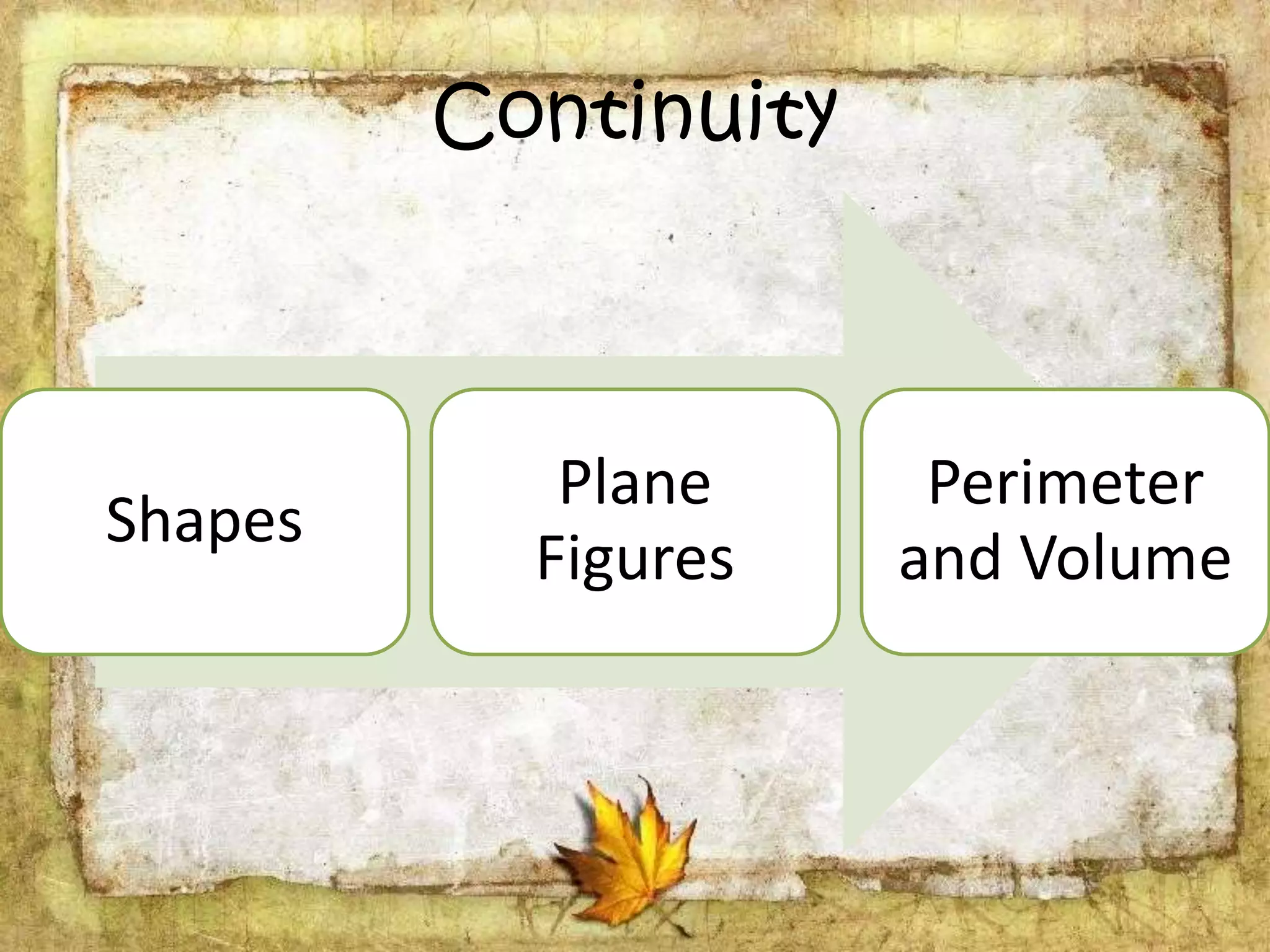
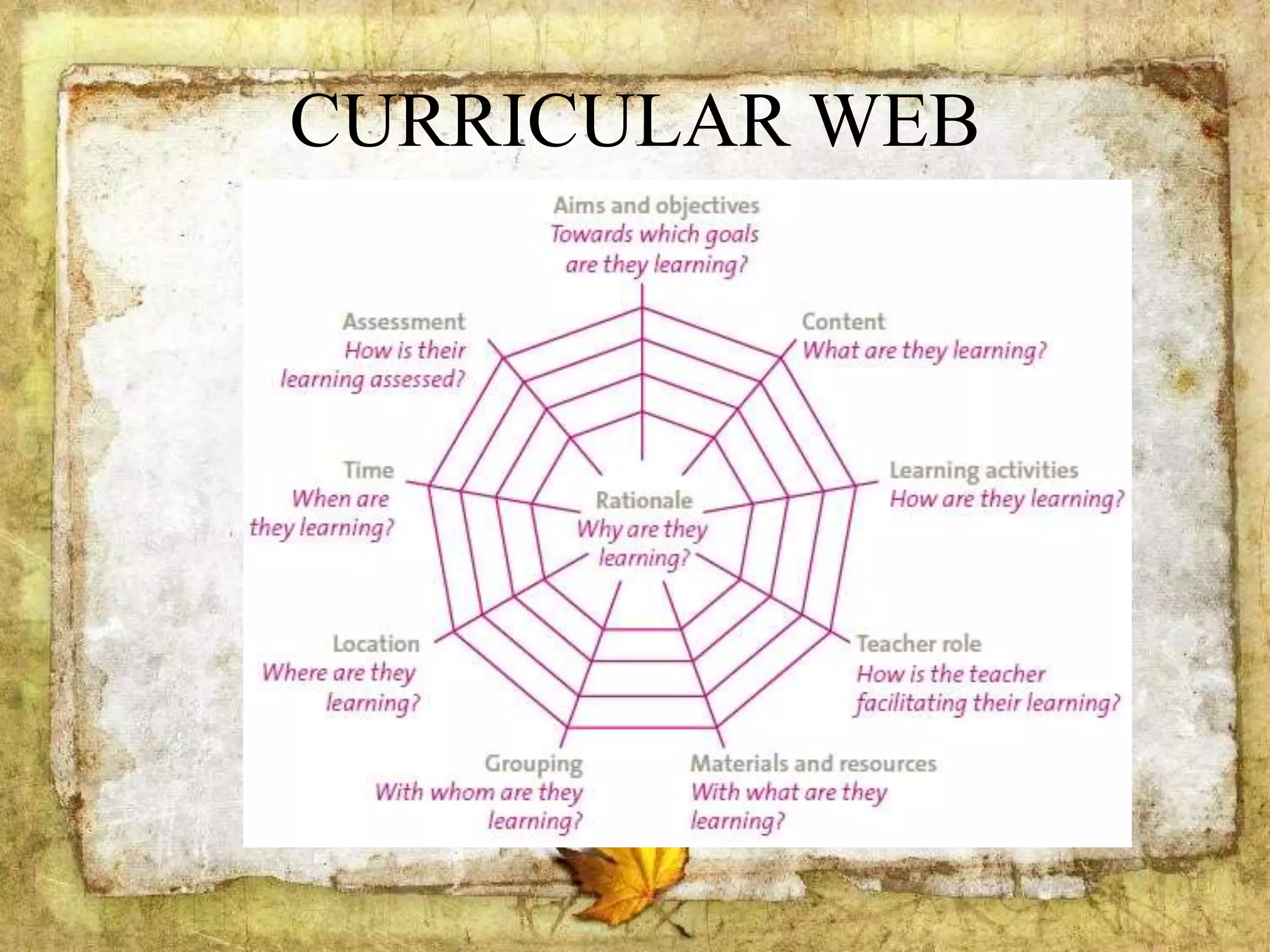
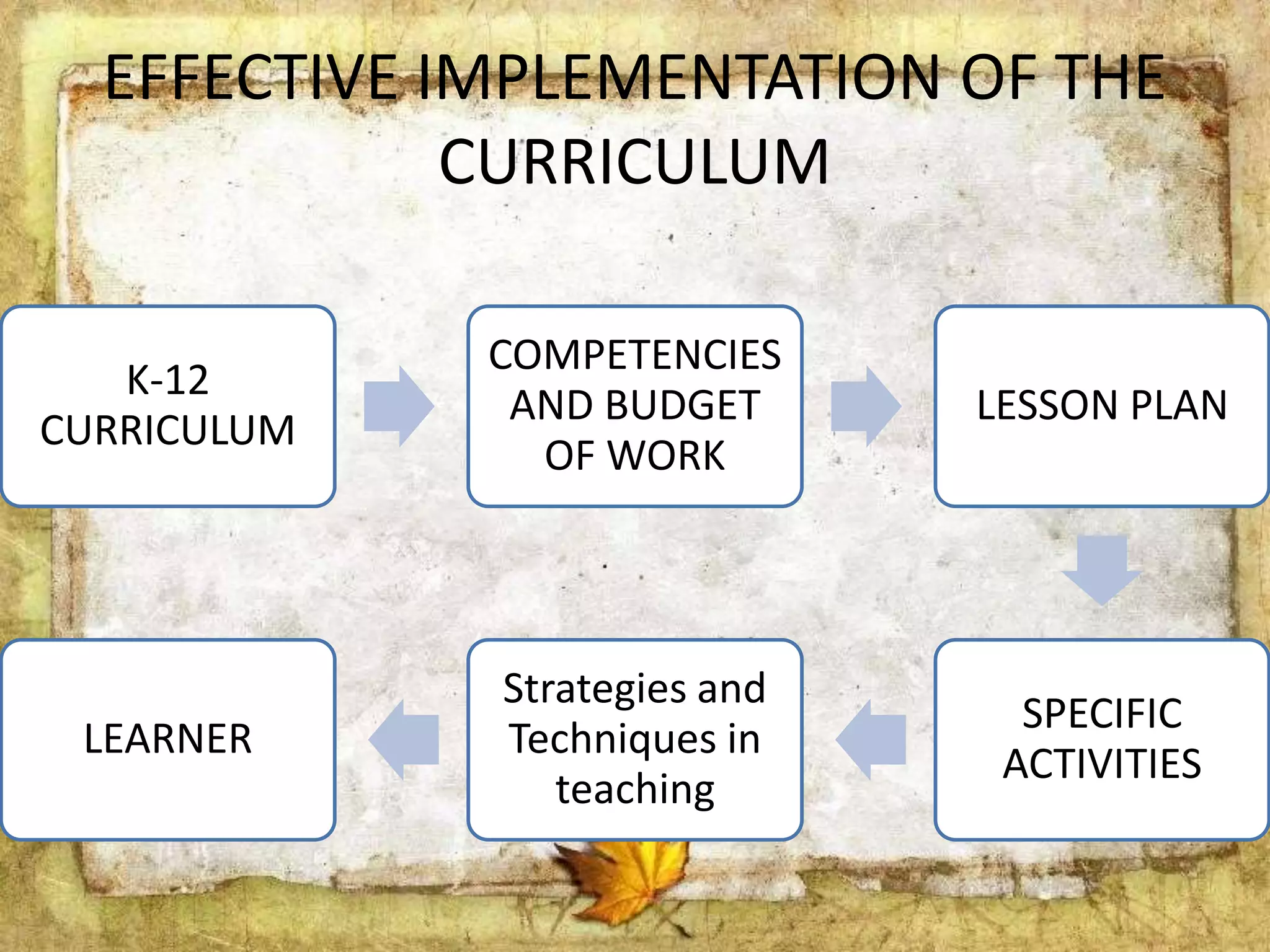
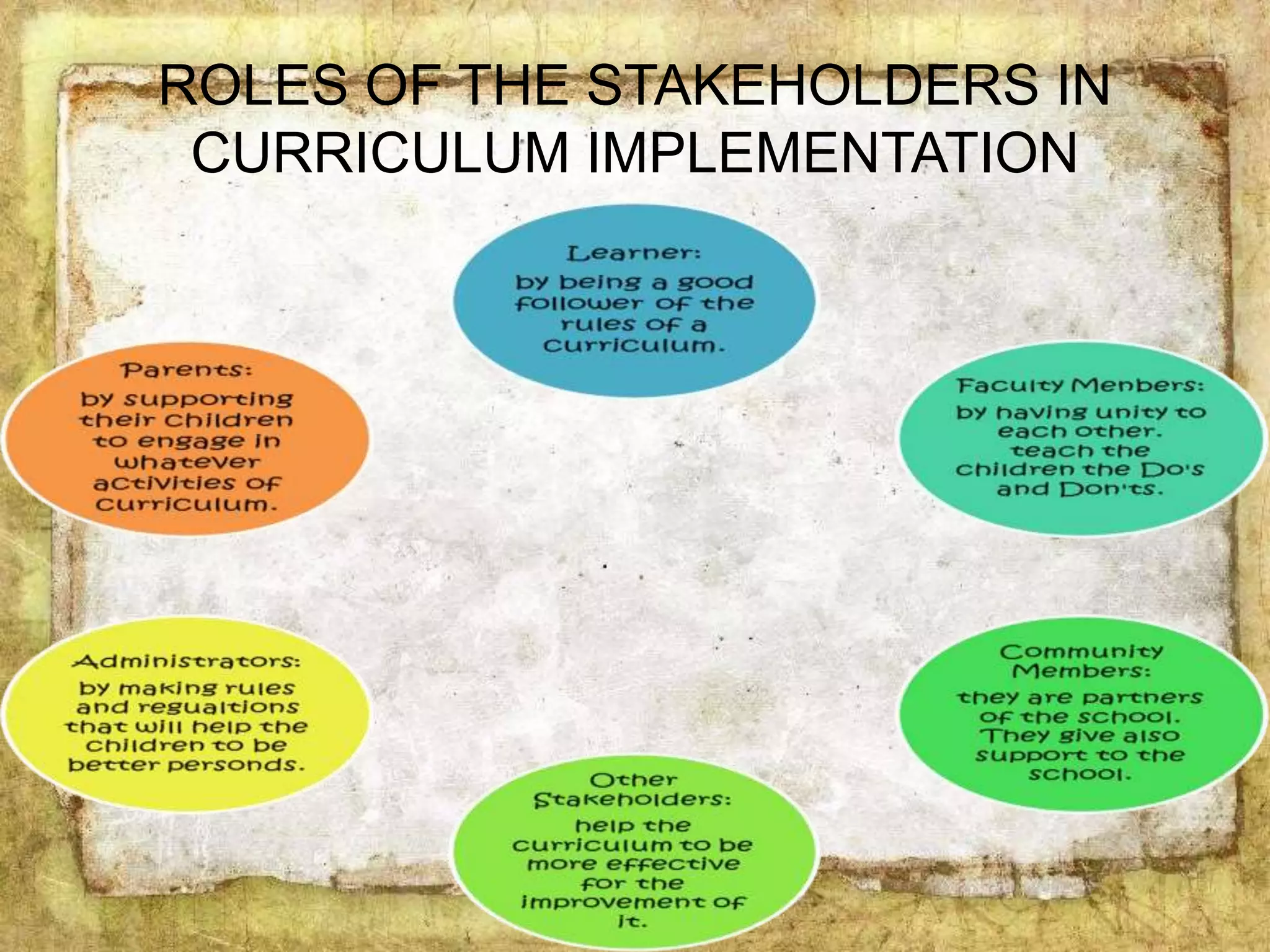
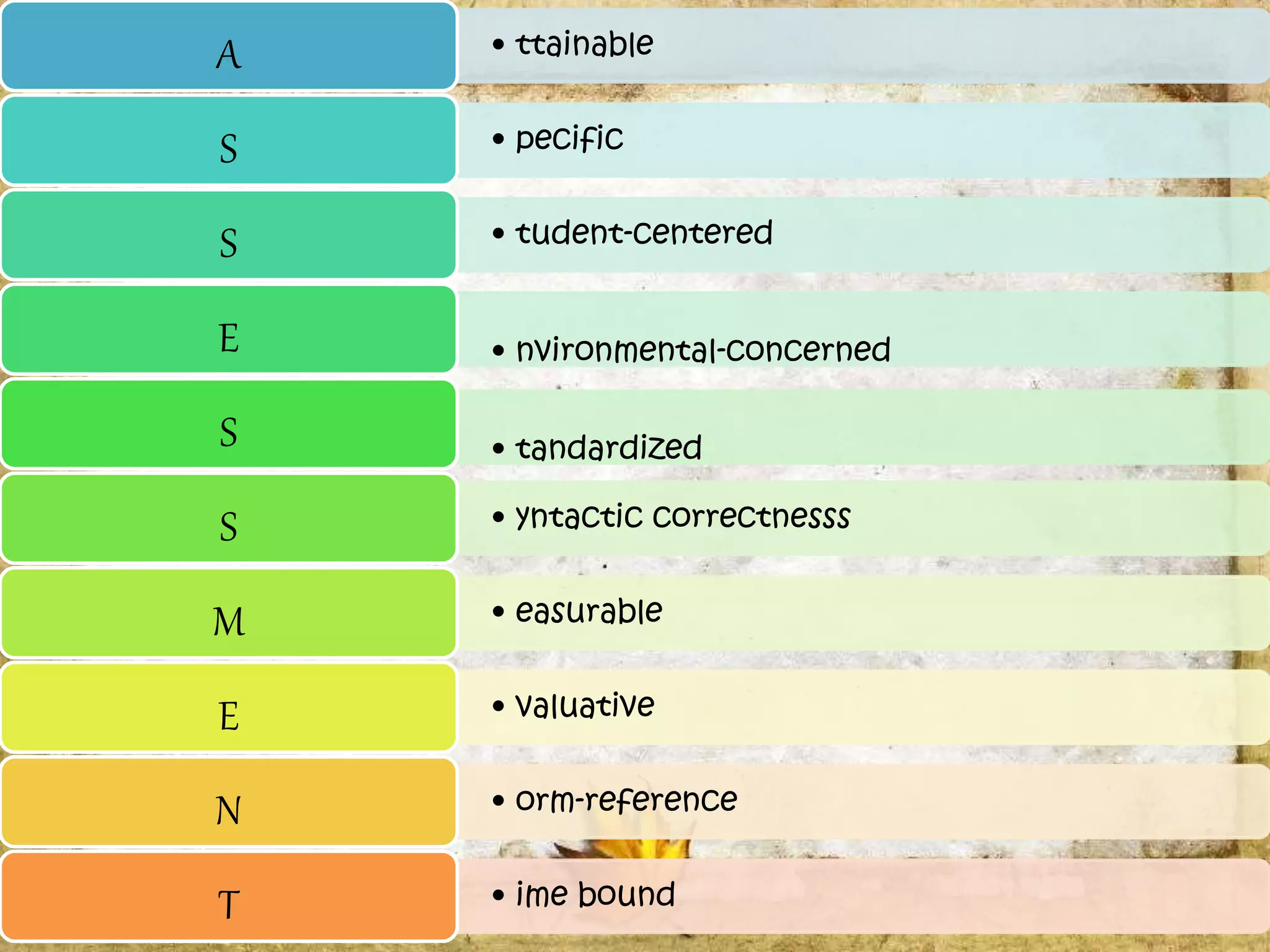
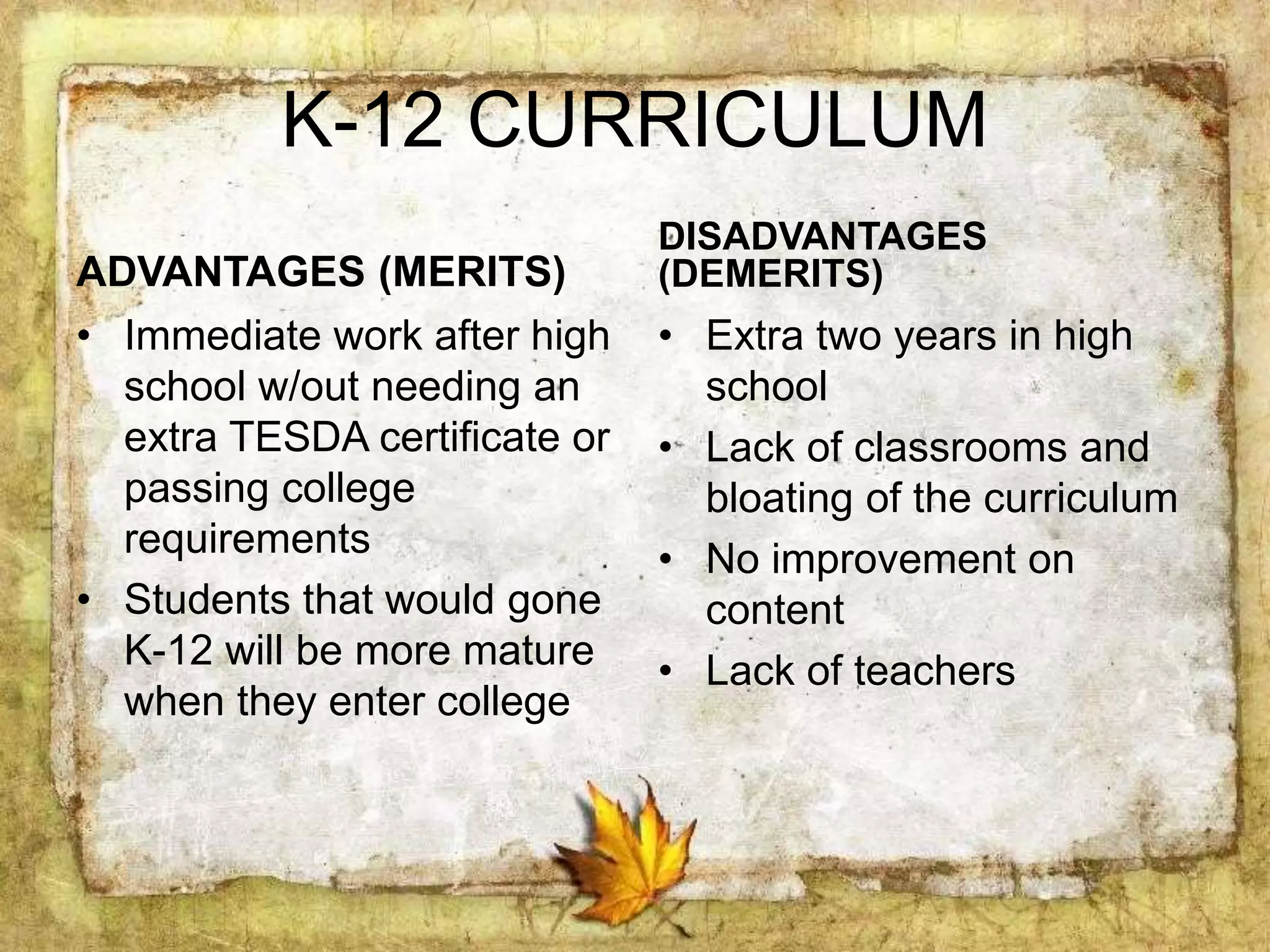
The document describes the organization and curriculum of the Diosdado P. Macapagal Elementary School. It outlines the school's administration structure, including the principal, teachers for different subjects, and other staff. It also discusses the school's curriculum approach, including the written, taught, supported, assessed, and learned curricula. Finally, it examines dimensions of curriculum design like basic concepts, articulation between grades, scope, sequence, integration and continuity.