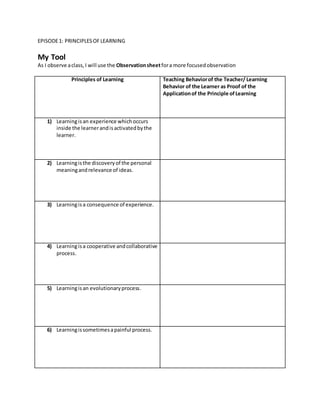
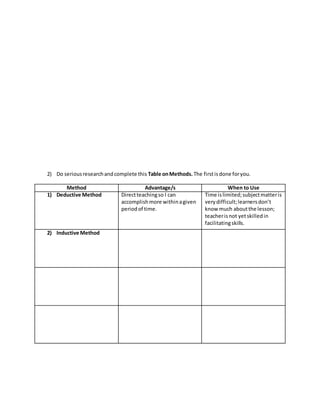
The document outlines principles of learning and teaching strategies. It discusses 7 principles of learning including learning as an active experience, discovery of personal meaning, and learning as an evolutionary process. It also covers lesson objectives, organizing content, selection of teaching methods, lesson development, and questioning techniques. The resource teacher's adherence to these concepts is observed and analyzed.