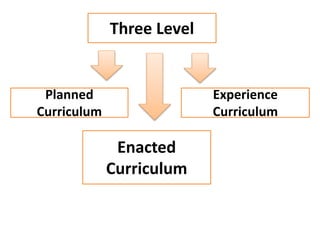
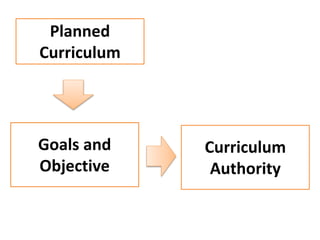
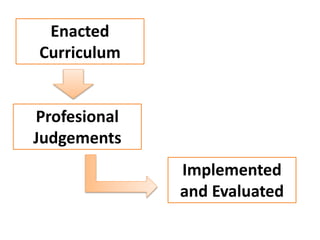
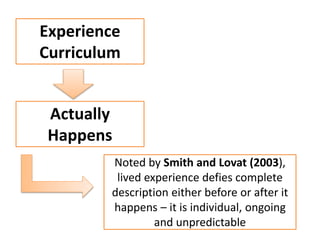
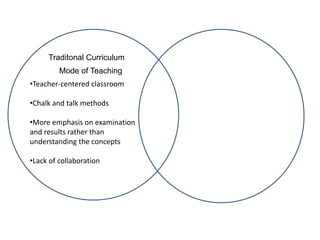
The document discusses various concepts of curriculum including traditional, emerging, and progressive perspectives. Under the traditional concept, curriculum is viewed as a program of subjects to be taught with the teacher at the center. An example is provided of the Philippines' Basic Education Curriculum from 2002 which follows this model. The emerging concept sees curriculum as evolving based on students' interests and needs, with more flexibility and collaboration. Key features include being non-linear, cyclical, and responsive. Progressive views define curriculum as the total experiences and learning of the individual, not just courses. Thinkers like Dewey, Caswell, and Tyler provided definitions and models that emphasized experience and reflective thinking over rigid subject listings.

























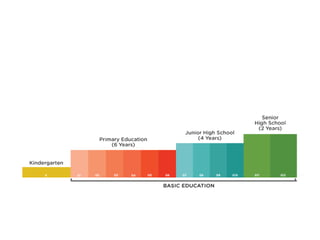
![WHAT IS K TO 12 PROGRAM?
• The K to 12 Program covers Kindergarten and
12 years of basic education (six years of
primary education, four years of Junior High
School, and two years of Senior High School
[SHS]) to provide sufficient time for mastery
of concepts and skills, develop lifelong
learners, and prepare graduates for tertiary
education, middle-level skills development,
employment, and entrepreneurship.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group1natureandpurposeofcurriculum-160908154245/85/Group-1-nature_and_purpose_of_curriculum-38-320.jpg)