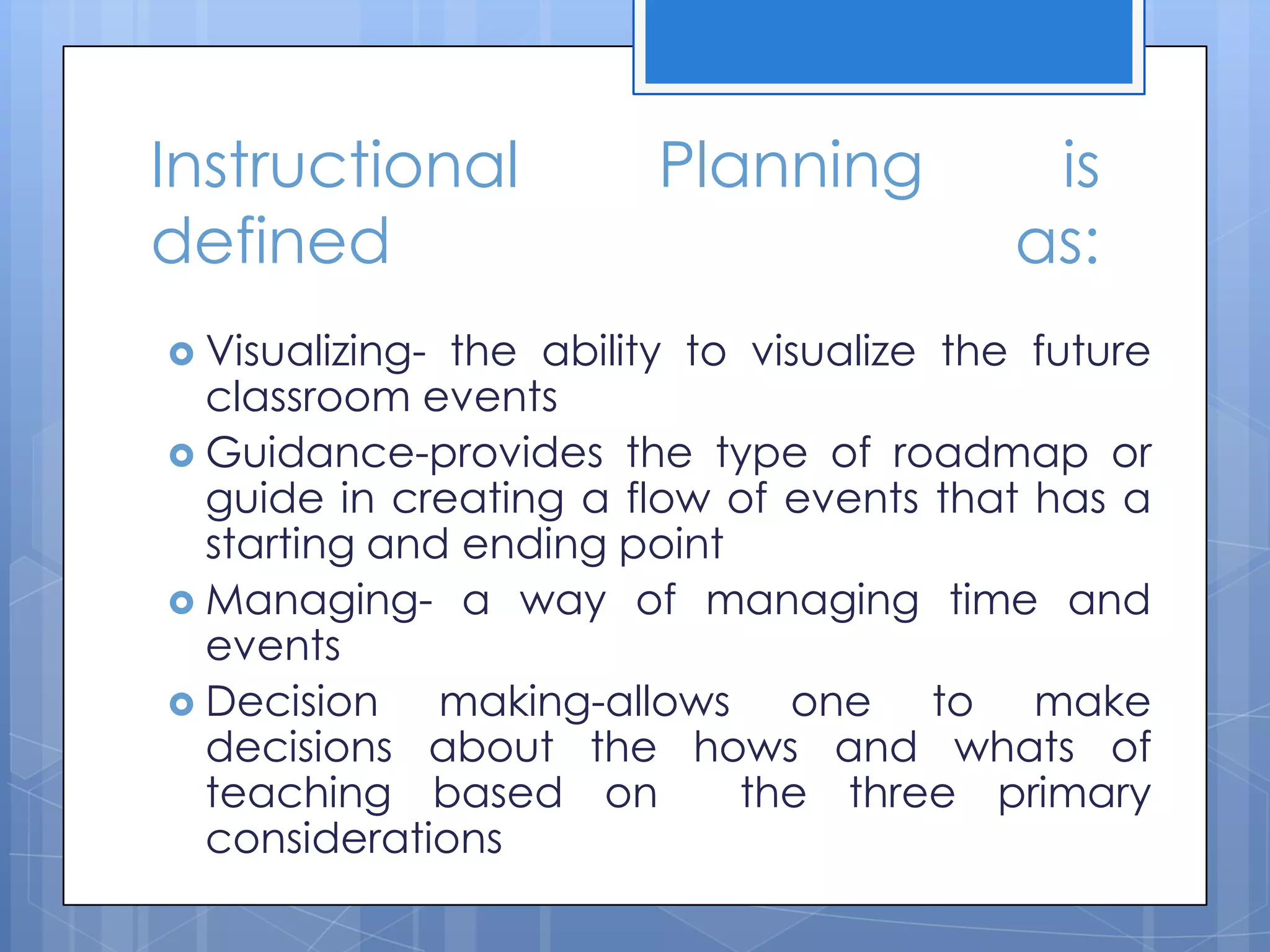
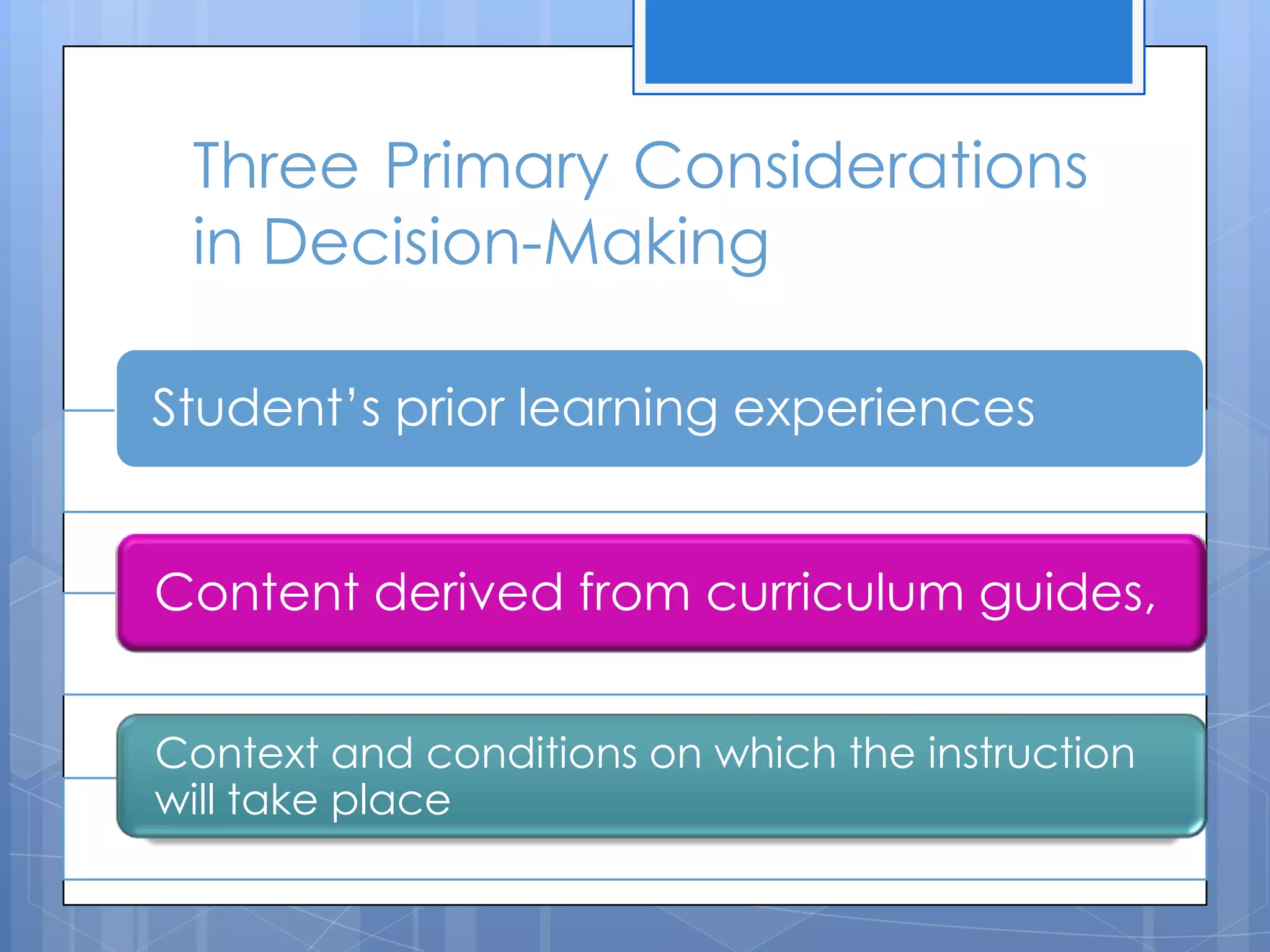
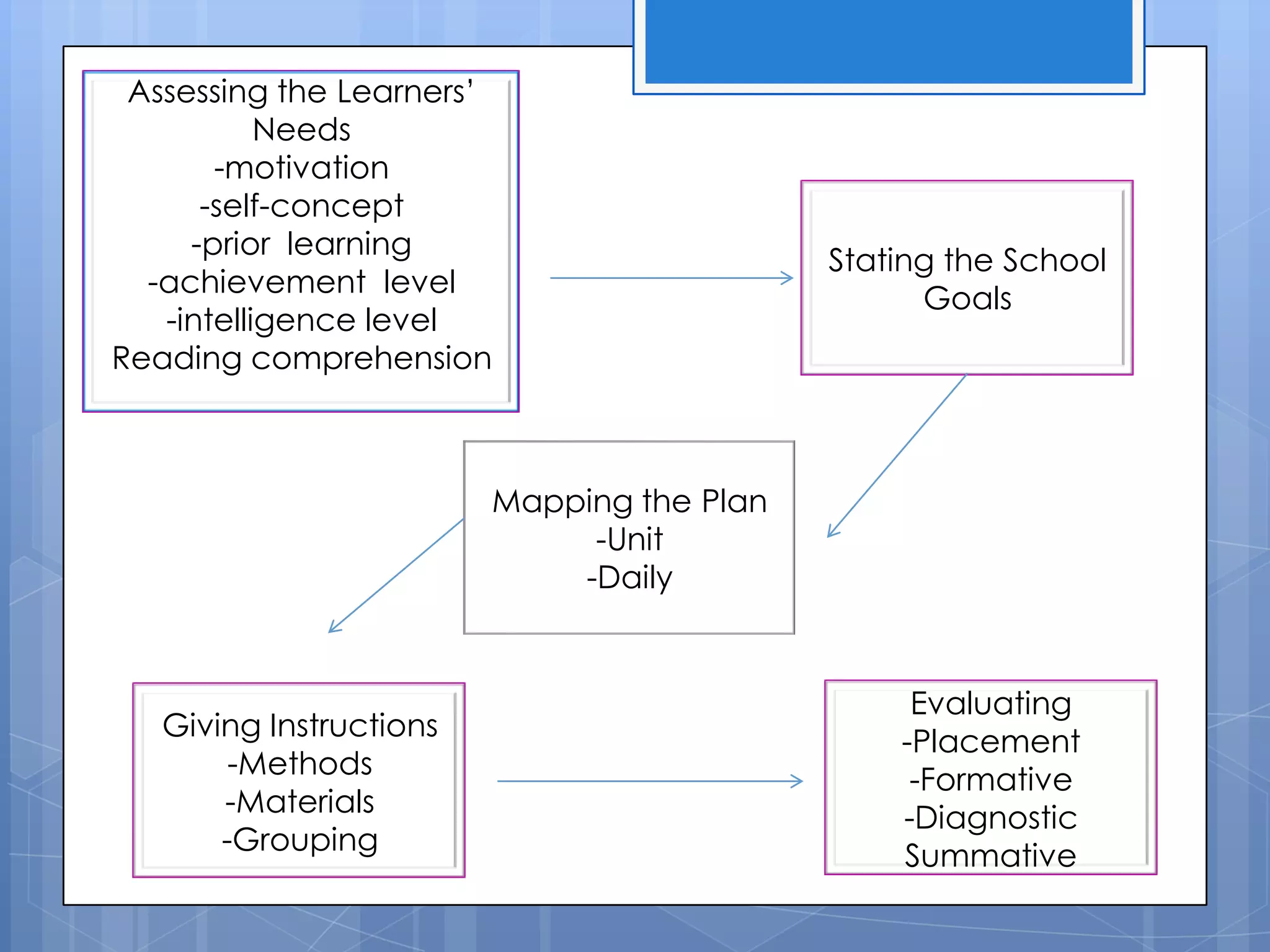
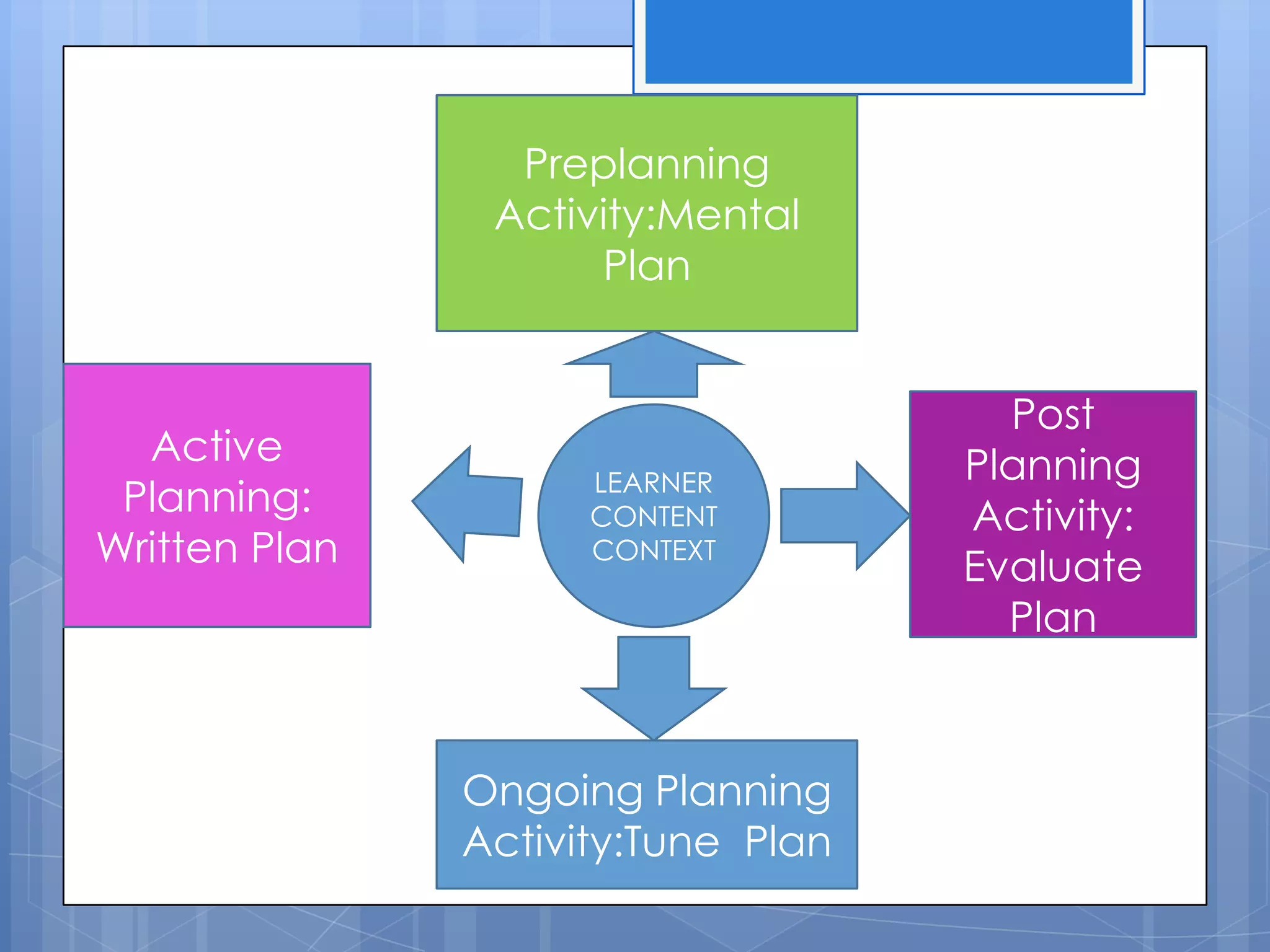
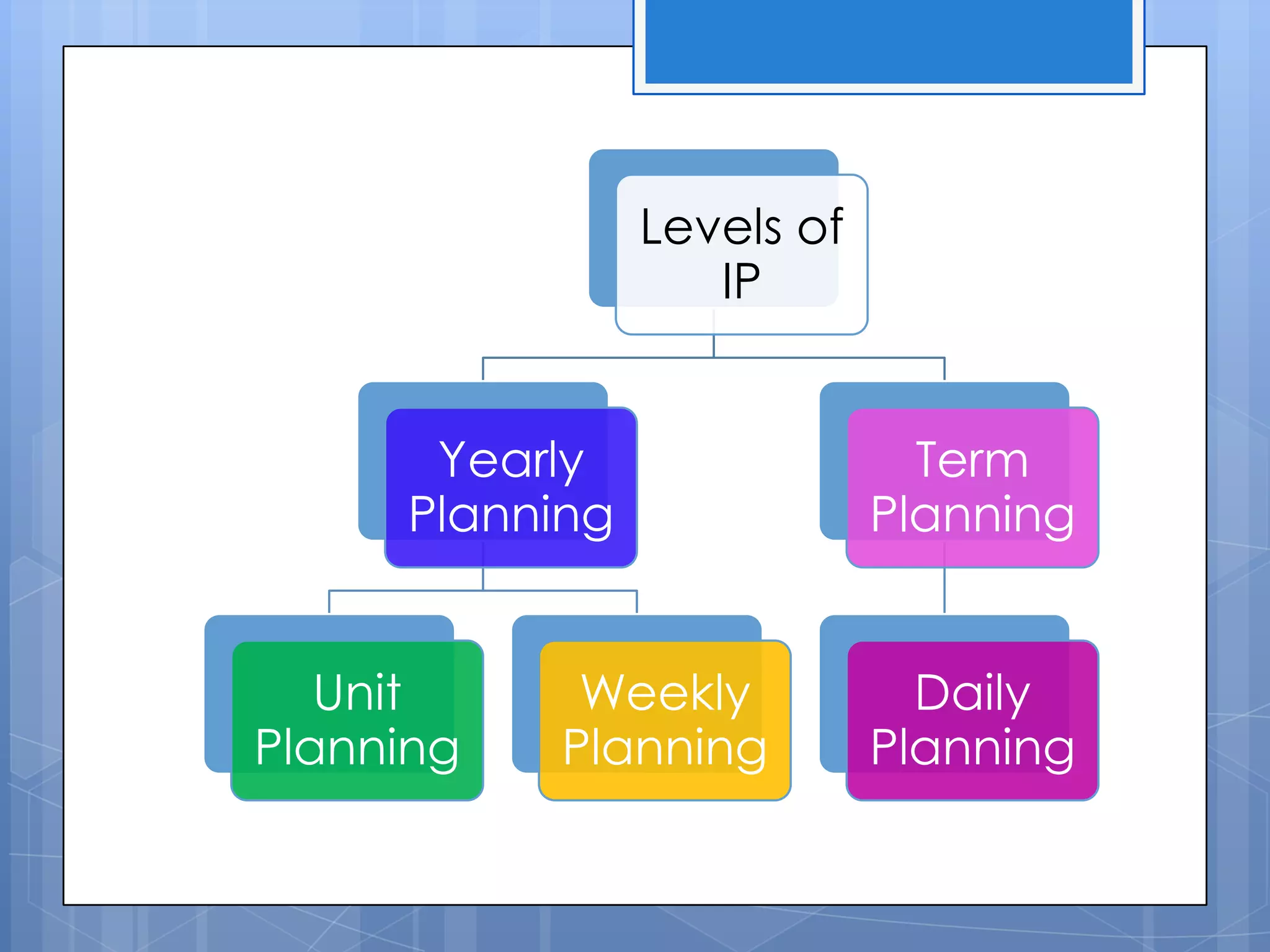
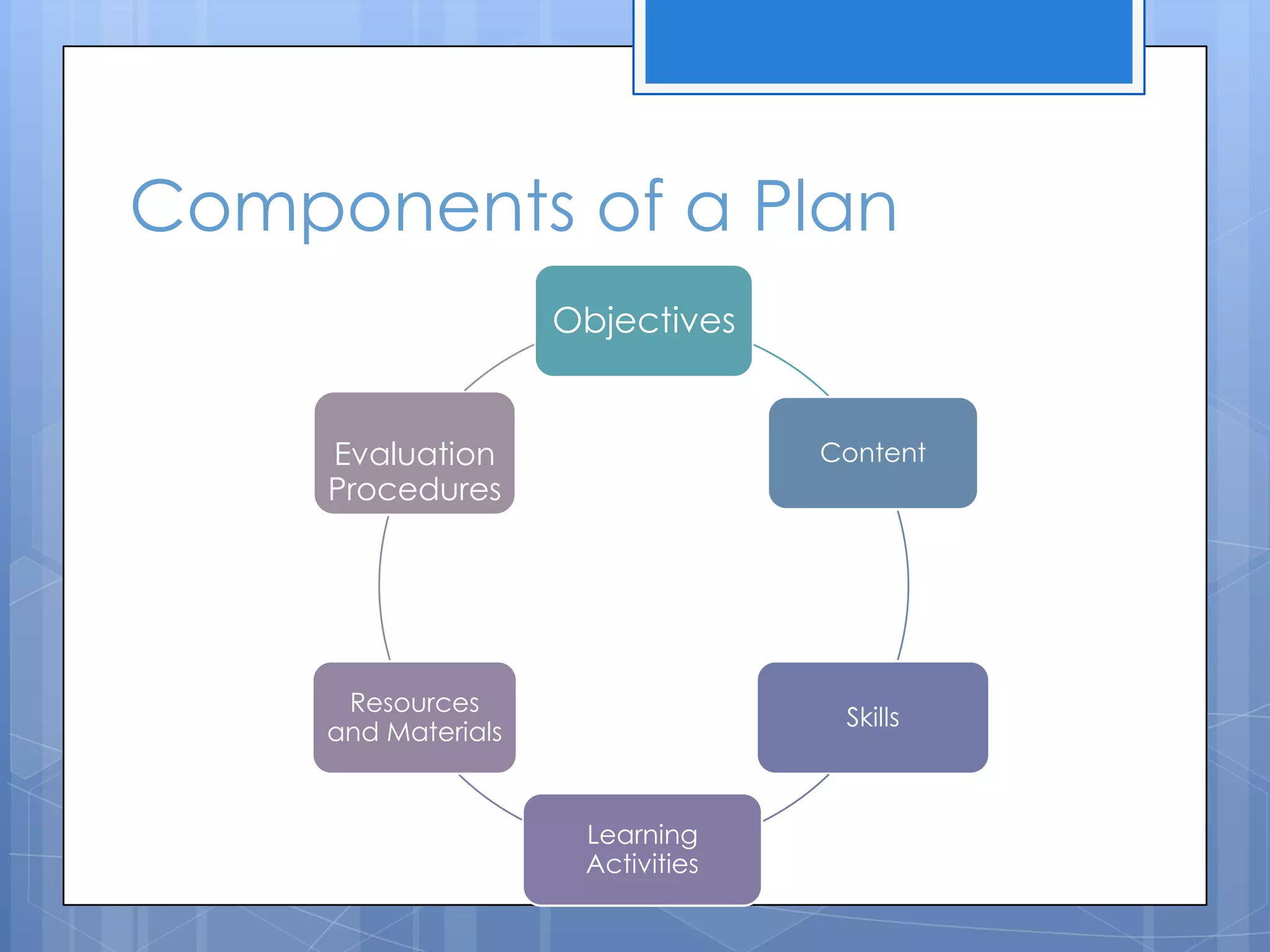
The document discusses instructional planning, defining it as visualizing classroom events, providing guidance through a roadmap, and managing time and events. It outlines the instructional planning sequence, which includes assessing learner needs, mapping the plan, giving instructions, and evaluating. Finally, it describes the different levels of instructional planning from yearly to daily and the components that make up an effective lesson plan.