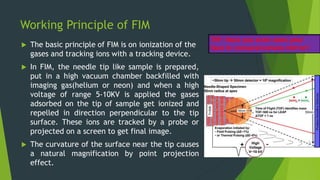
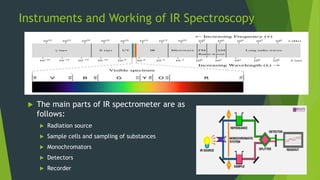
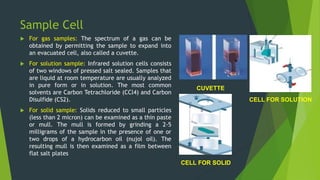
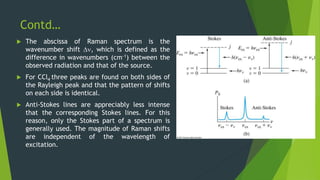
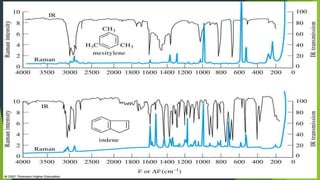
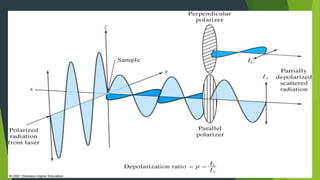
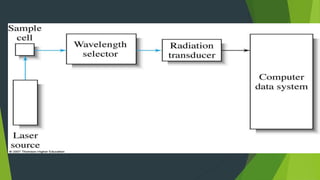
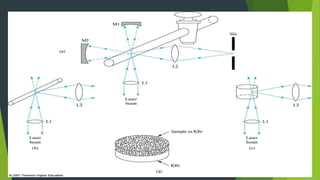
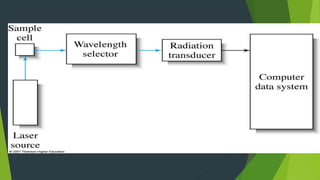
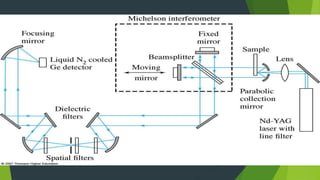
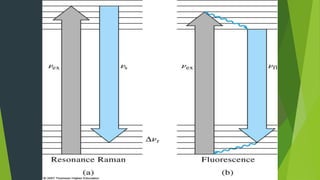
Field ion microscopy uses a high electric field to ionize gas atoms on the tip of a sample, which are then detected to create an atomic-scale image of the sample surface. Infrared spectroscopy analyzes the absorption of infrared light by molecules to determine their structure. Raman spectroscopy analyzes the inelastic scattering of monochromatic light when it interacts with molecular vibrations, rotations, and other low frequency modes to provide molecular fingerprint information. Both techniques produce spectra that can be used to identify chemicals based on the frequencies of molecular vibrations they produce.