Infrared spectroscopy measures the bond vibrations in molecules to determine their functional groups. There are two main types of instruments - dispersive and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Dispersive instruments use gratings to separate infrared frequencies, while FT-IR uses interferometers and Fourier transforms. Samples can be analyzed as solids, liquids in cells, or gases in gas cells. The infrared region is divided into functional group and fingerprint regions that are used for structure elucidation and identification of compounds, drugs, polymers, and more. Molecular vibrations occur as stretching and bending modes. Factors like hydrogen bonding, conjugation, and inductivity affect vibrational frequencies.

![It occurs when atoms in a molecule are in periodic motion while the molecule as a whole has constant
translational and rotational motion.
The frequency of the periodic motion is known as a vibration frequency.
The value of stretching vibrational frequency of a bond can be calculated by the application of hooke’s law.
ν/c = ν¯ = 1/2пc[k/m1m2/m1+m2]1/2
= 1/2пc√k/μ
Where, μ→ reduced mass
m1&m2 →masses of the atoms
k →force constant
c →velocity of radiation
Factors influencing vibrational Frequencies
Calculated value of frequency of absorption for a particular bond is never exactly equal to its experimental
value.
There are many factors which are responsible for vibrational shifts
1)Vibrational coupling:
•it is observed in compounds containing –CH2 &
-CH3.
EG. Carboxylic acid anhydrides , amides , aldehydes
2) Hydrogen bonding:
Hydrogenbonding brings about remarkable downward frequency shifts.
Strongerthe hydrogenbonding,greateris theabsorptionshift towards lower wave length than thenormal
value.
There is 2 types of hydrogen bonding
a) inter molecular→ broad bands
b) intra molecular → sharp bands
•hydrogen bonding in O-H and N-H compounds deserve special attention.
•Eg: alcohols & phenols , enols & chelates
3) Electronic effects:
In this the frequency shifts are due to electronic effects which include conjugation, mesomeric effect,
inductive effect.
a) conjugation: conjugation lowers the absorption frequency of C=O stretching whether the conjugation
is due to α,β- unsaturation or due to an aromatic ring.
b) mesomeric effect: a molecule can be represented by 2or more structures that differ only in the
arrangement of electrons.
c) inductive effect: depends upon the intrinsic tendency of a substituent to either release or withdraw
electrons.
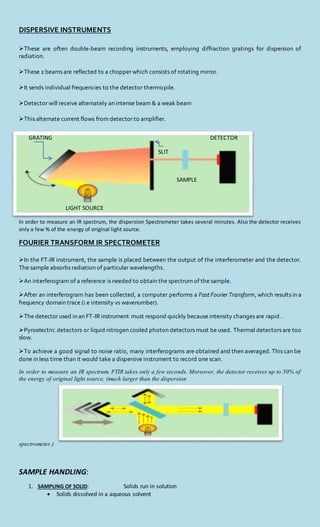
TYPES OF INSTRUMENTATION:
There are 2 types of infrared spectrophotometer, characterized by the manner in which the ir frequencies are
handled.
1) dispersive type (IR)
2) interferometric type(FTIR)
In dispersive type the infrared light is separated into individual frequencies by dispersion, using a grating
monochromator.
In interferometric type the ir frequencies are allowed to interact to produce an interference pattern and this
pattern is then analyzed, to determine individual frequencies and their intensities.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/irspectroscopyautosaved-191010155403/85/Ir-spectroscopy-PRESENTED-BY-DIPSANKAR-2-320.jpg)