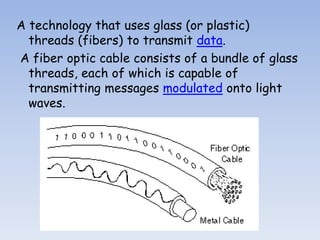
Fiber optics uses glass or plastic threads to transmit data using light. An optical fiber consists of a core that carries light signals, a cladding that keeps light within the core, and a coating that protects the fiber. Total internal reflection guides light down the length of the fiber. Fiber optics has advantages over metal lines like greater bandwidth, less interference susceptibility, thinner cables, and ability to transmit digital data. It is well-suited for long-distance communications due to low light attenuation. Fiber optics has applications in illumination, imaging, spectroscopy, telecommunications, and networking.