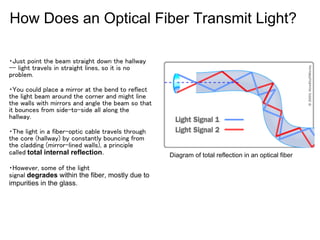
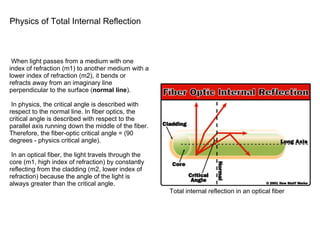
Fiber optics work by transmitting light through thin glass strands called optical fibers. Light travels down the core of the fiber via total internal reflection from the cladding layer. There are two main types of optical fibers: single-mode fibers which transmit infrared laser light using a small core, and multi-mode fibers which transmit infrared light from LEDs using a larger core. Fiber optic systems transmit digital data over long distances using a transmitter to encode light signals, fibers to conduct the signals, and a receiver to decode the signals. Fiber optics offer advantages over copper wires like lower signal degradation, higher data capacity, and ability to carry digital signals for computer networks.