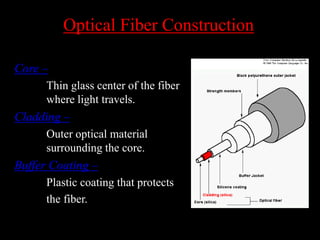
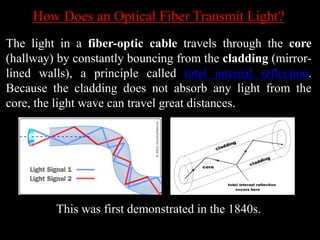
Fiber optic communication is a method of transmitting information via light pulses through optical fibers, which has significantly impacted telecommunications since its development in the 1970s. Optical fibers, made of pure glass, offer advantages such as greater bandwidth, reduced size and weight, enhanced security, and flexibility, though they are more costly and fragile than traditional copper cables. Applications include telecommunications, medical devices, and data networking, highlighting their versatility across various industries.