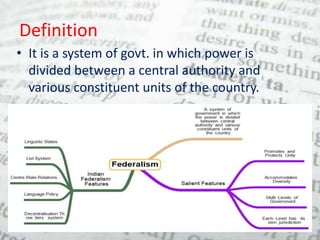
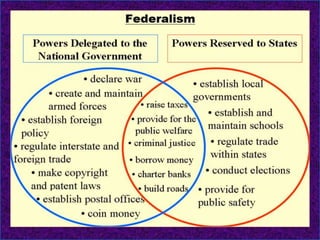
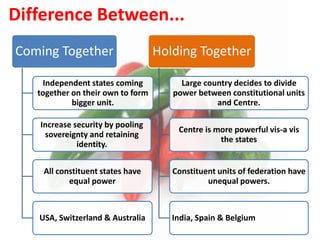
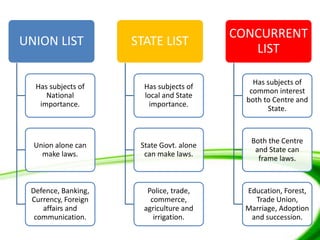
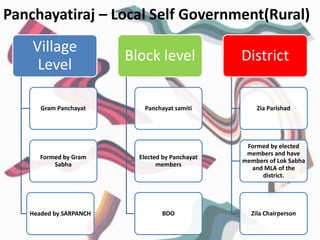
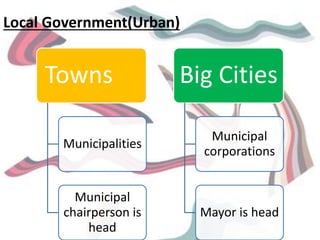
This document discusses federalism and decentralization in India. It defines federalism as a system of government where power is divided between a central authority and constituent units. India practices federalism through its three-tier structure of government with power shared between the central, state, and local governments. While India started as a "holding together" federation with an initially stronger center, power sharing has increased over time through the formation of new states along linguistic lines, the three-fold division of legislative powers, and recognition of regional political parties. Decentralization to local governments through the Panchayati Raj system aims to solve problems at the local level through increased participation and delegation of powers, though challenges remain in fully implementing this framework.