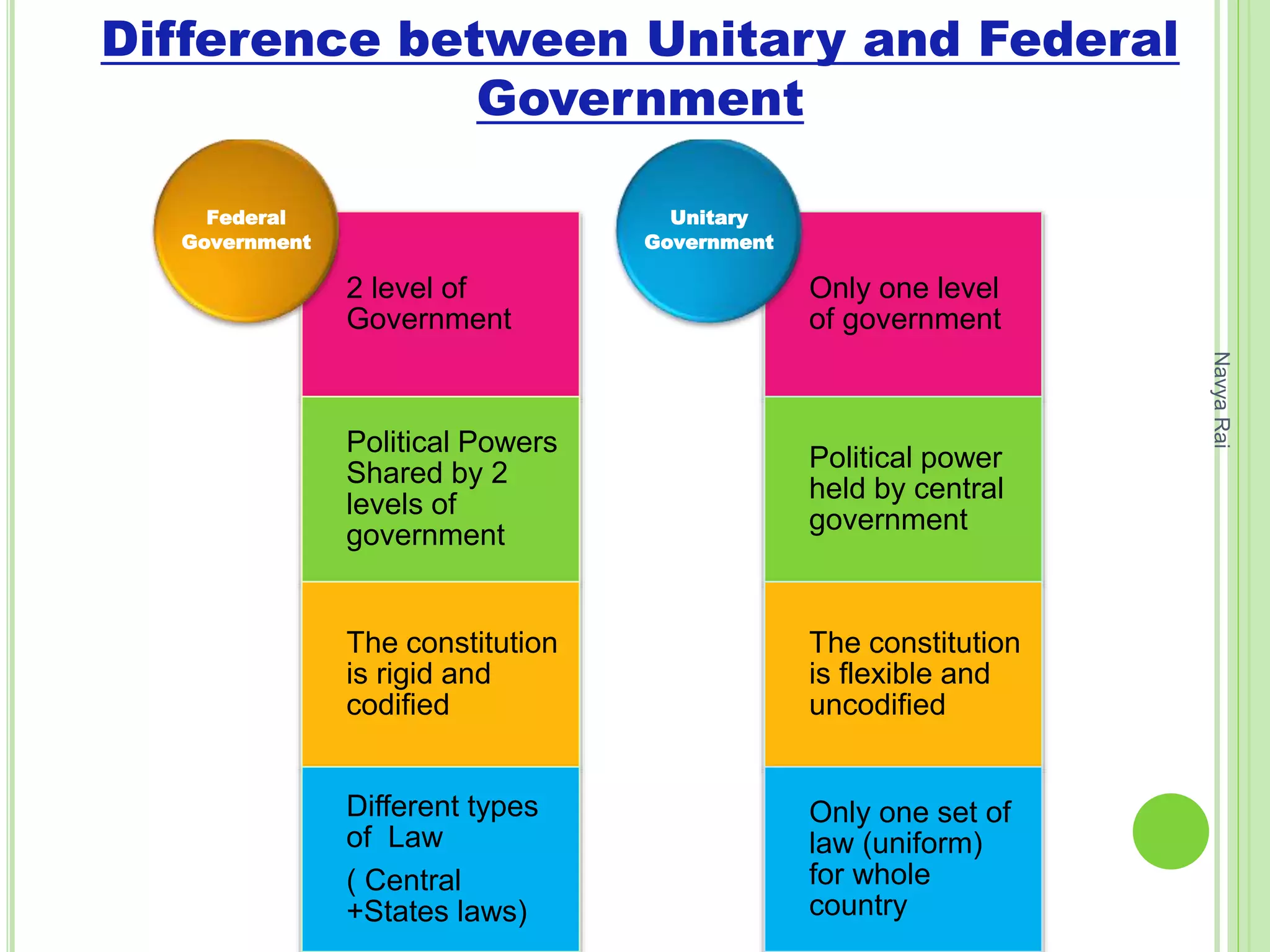
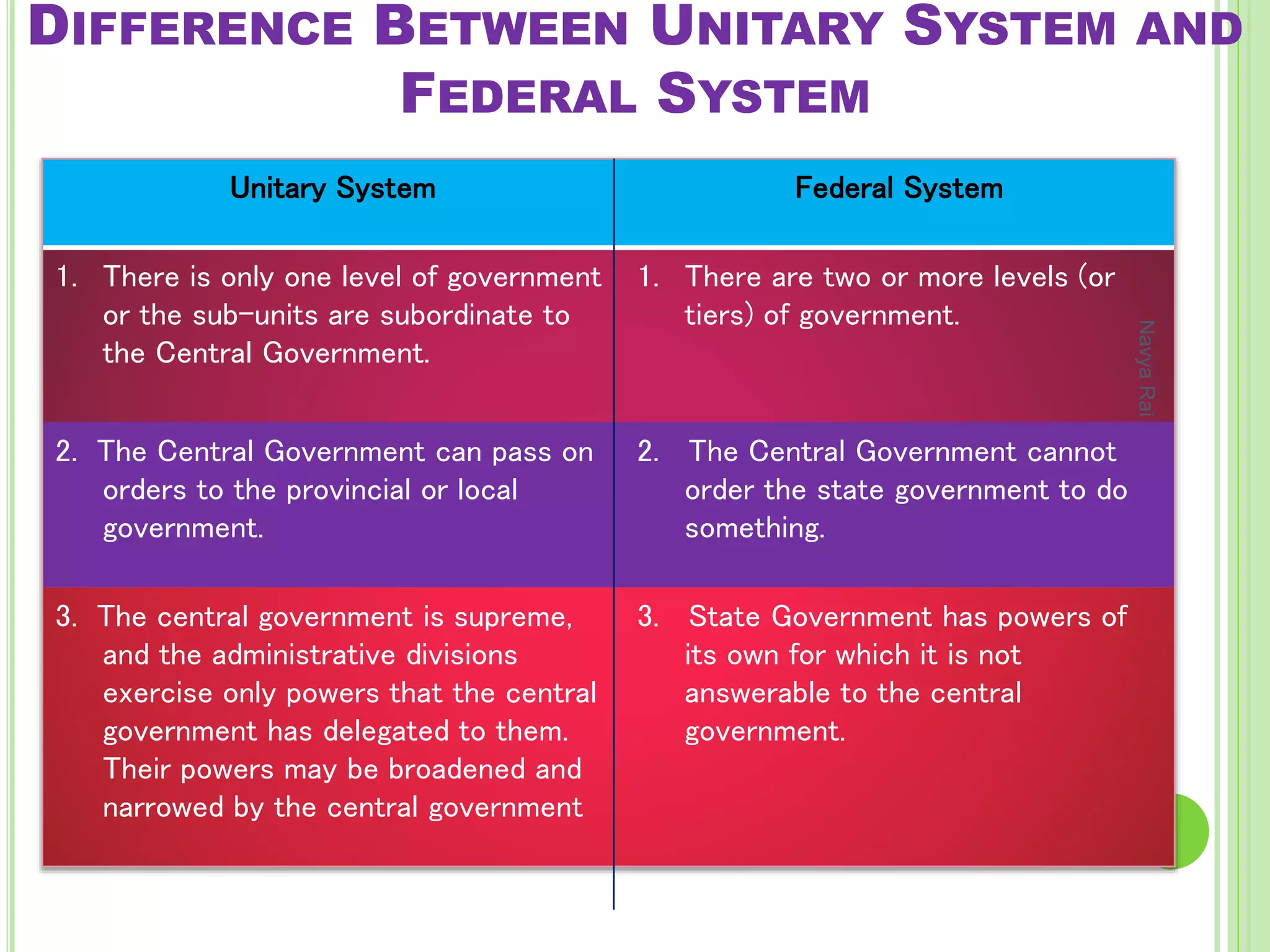
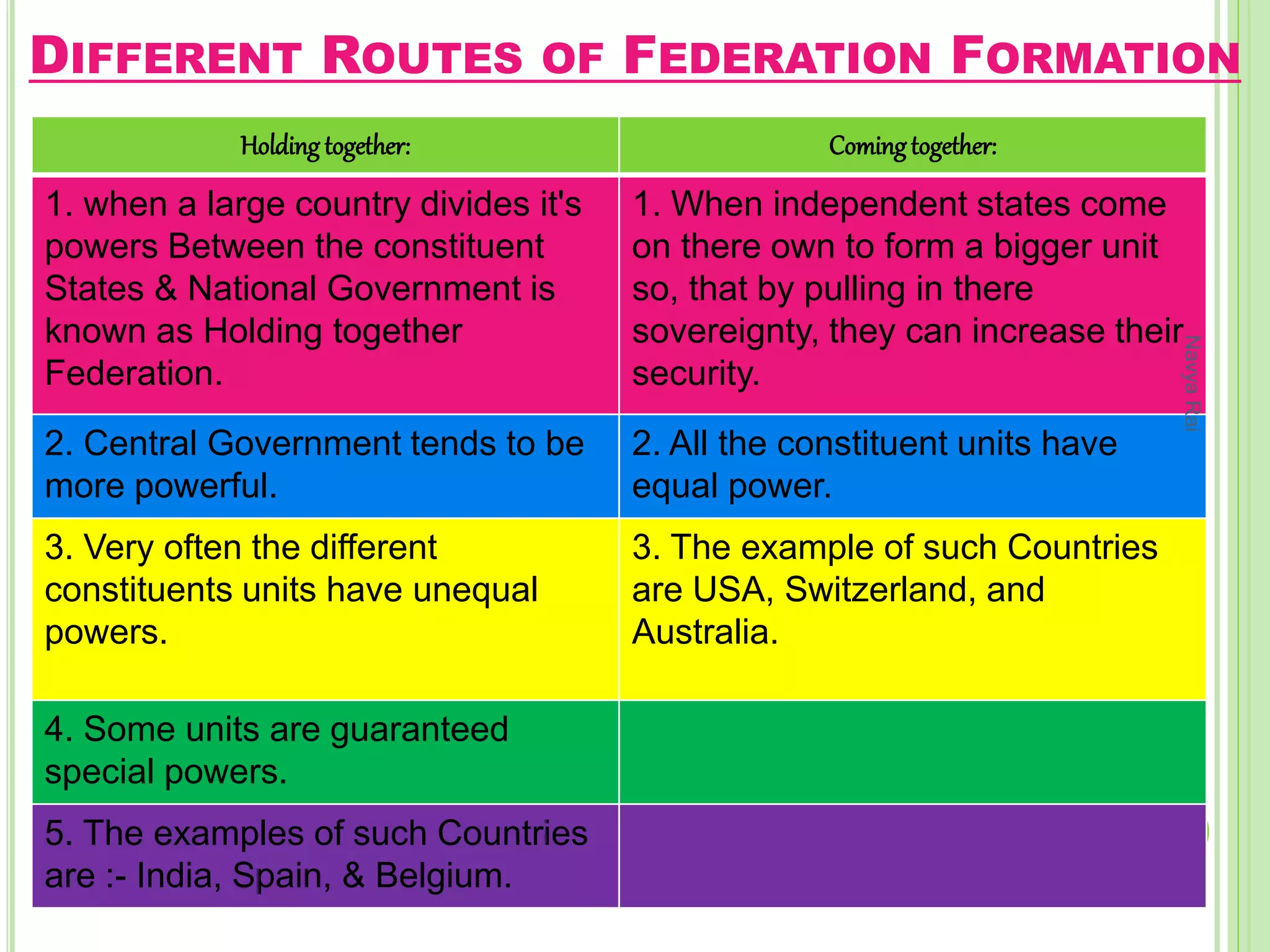
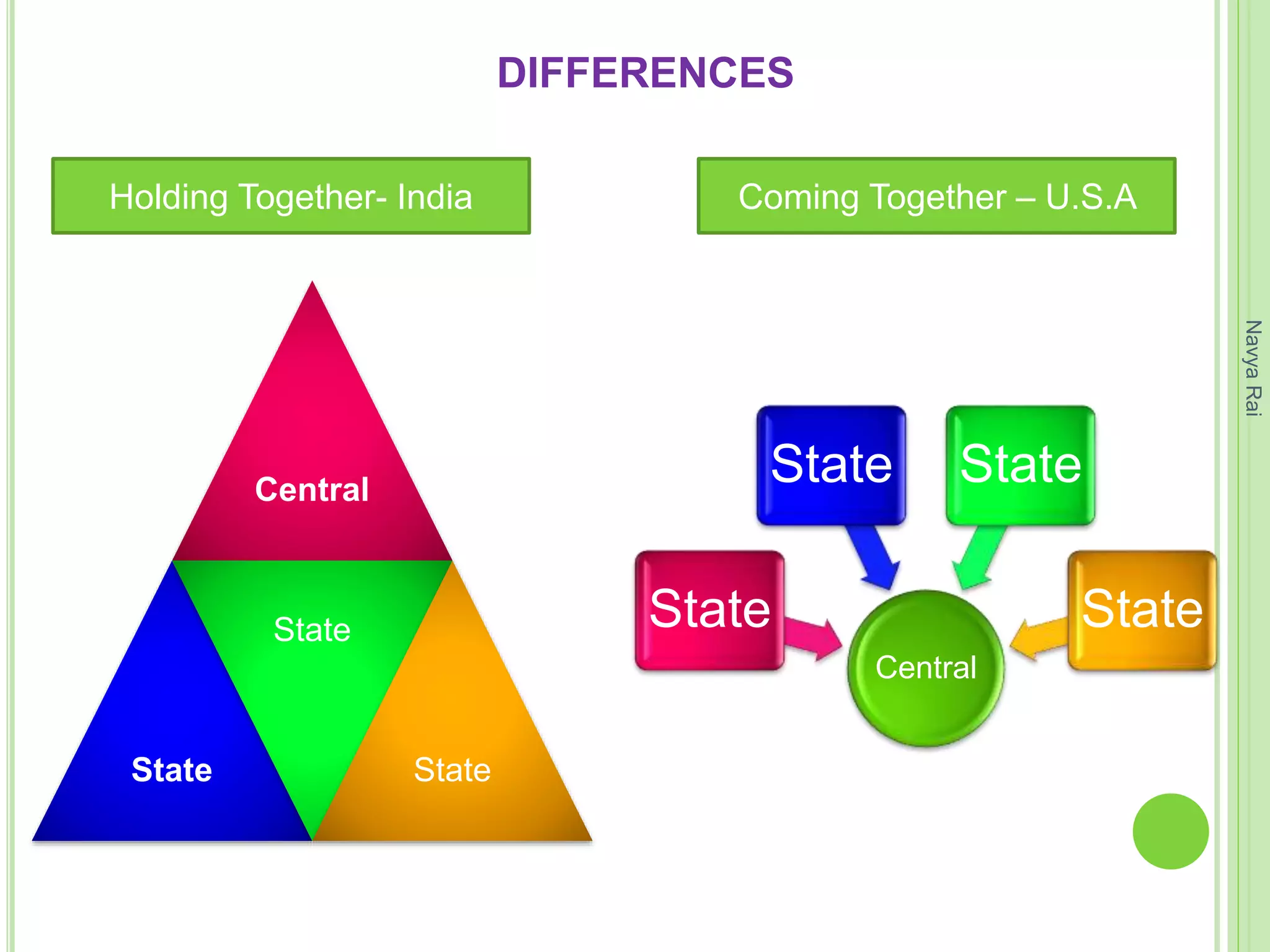
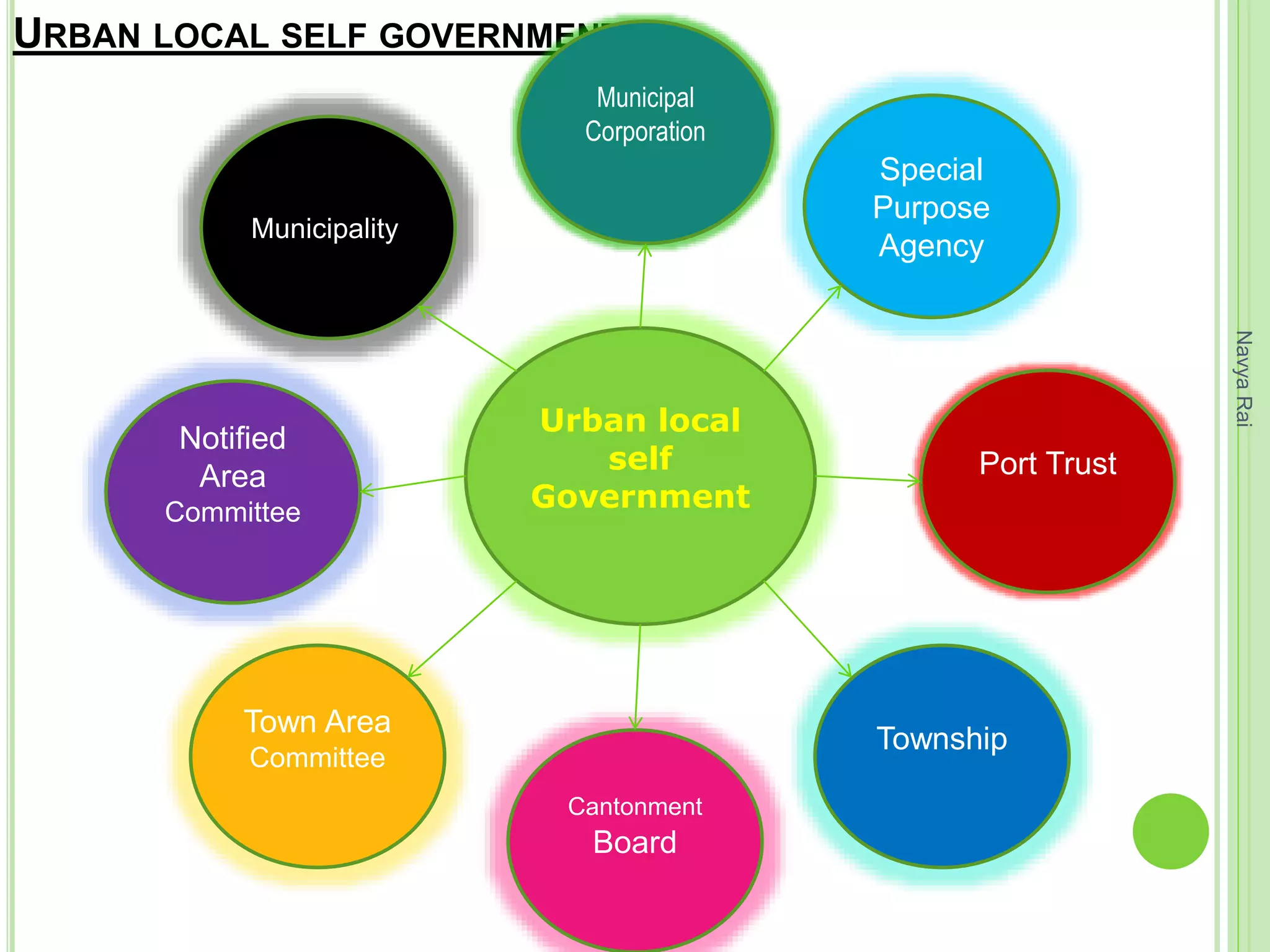
The document discusses federalism as a system of government where power is divided between central and state authorities, highlighting key features such as jurisdiction, constitutional guarantees, and revenue autonomy. It examines the differences between federal and unitary systems, the formation of federations, particularly in the Indian context, and the practice of federalism through linguistic states, center-state relations, and decentralization. Furthermore, it outlines the structure of local self-government in India, detailing the three-tier system and the roles of rural and urban local bodies.