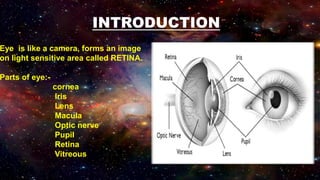
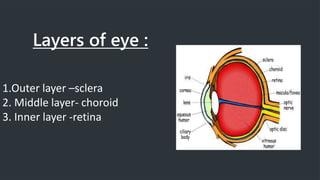
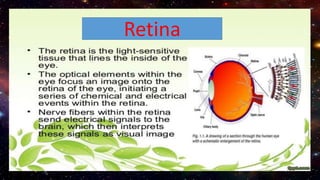
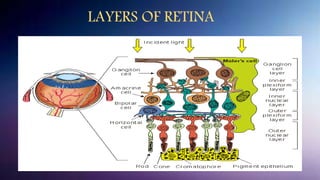
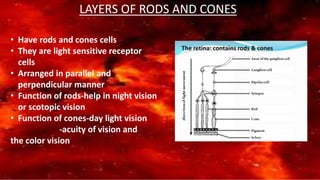
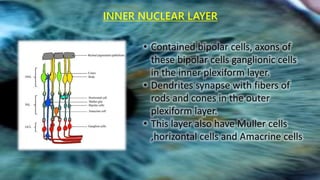
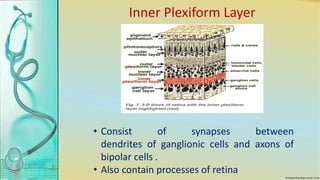
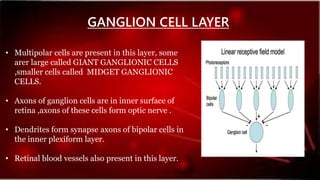
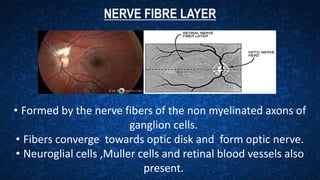
The retina contains 10 layers that process light signals from the eyes. The outermost layer is the retinal pigment epithelium, which absorbs light and prevents reflection. Next are the layers of rods and cones, the light-sensitive cells responsible for vision. Moving inward are the outer limiting membrane, outer nuclear layer, outer plexiform layer, inner nuclear layer, inner plexiform layer, ganglion cell layer, nerve fiber layer, and internal limiting membrane. Each layer has specialized cells and functions that allow light signals to be transmitted via the optic nerve to the brain for visual perception and interpretation. Damage to the retina can cause diseases like retinitis pigmentosa, macular degeneration, and diabetic or hypertensive ret