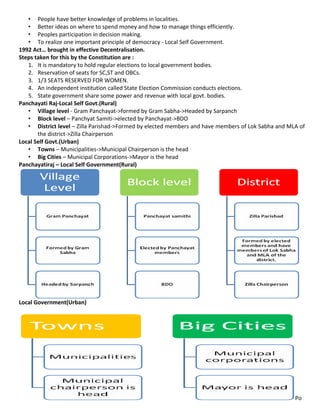
Federalism is a system of government where power is divided between a central authority and constituent units. In India, power is divided between the central government, state governments, and local governments. Key aspects of Indian federalism include a three-tier structure of governance, distribution of legislative powers between union and state lists, and the creation of linguistic states to better represent cultural diversity. However, local governments still face difficulties like irregular village assemblies and lack of resource/power transfers from states.