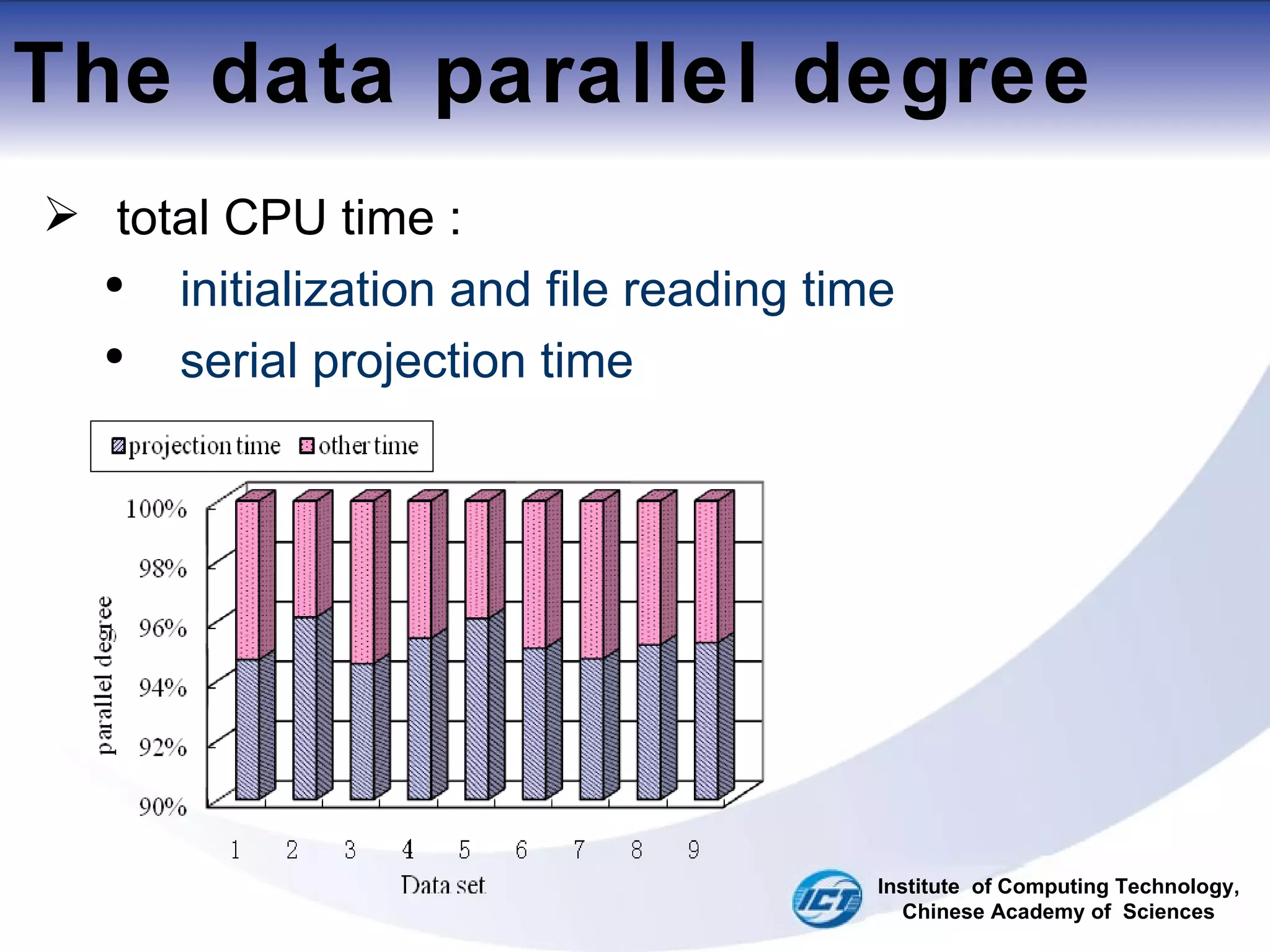
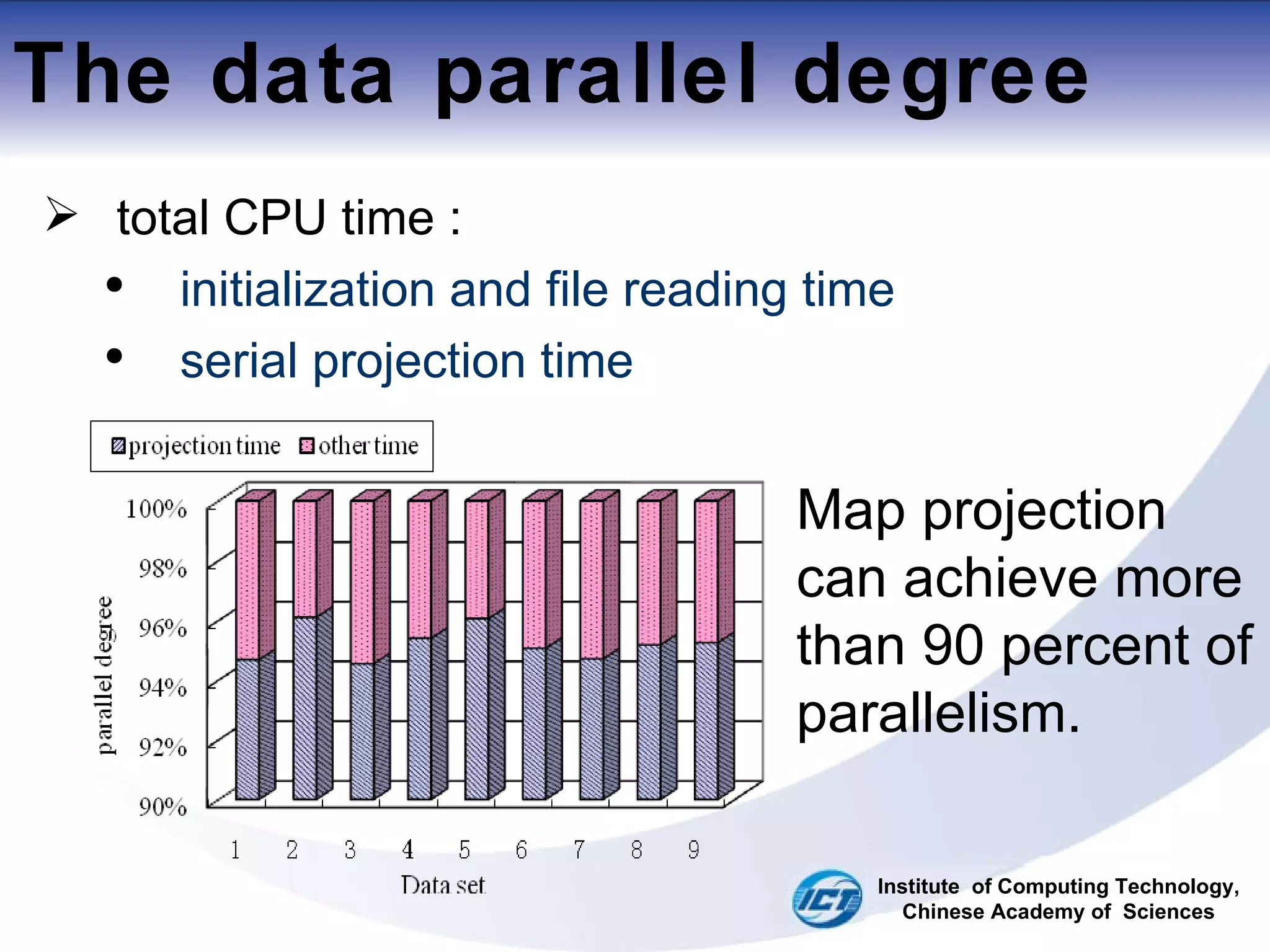
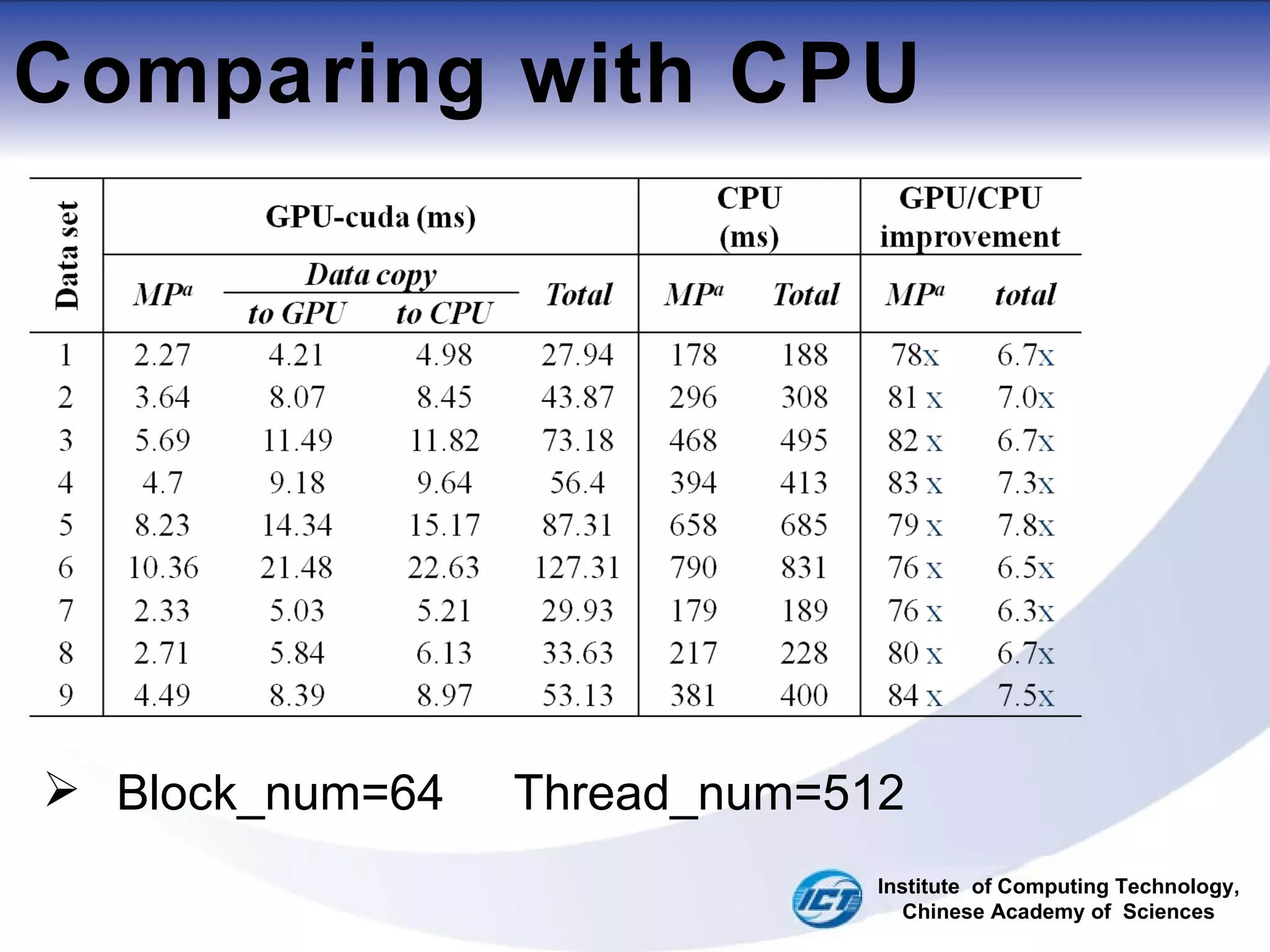
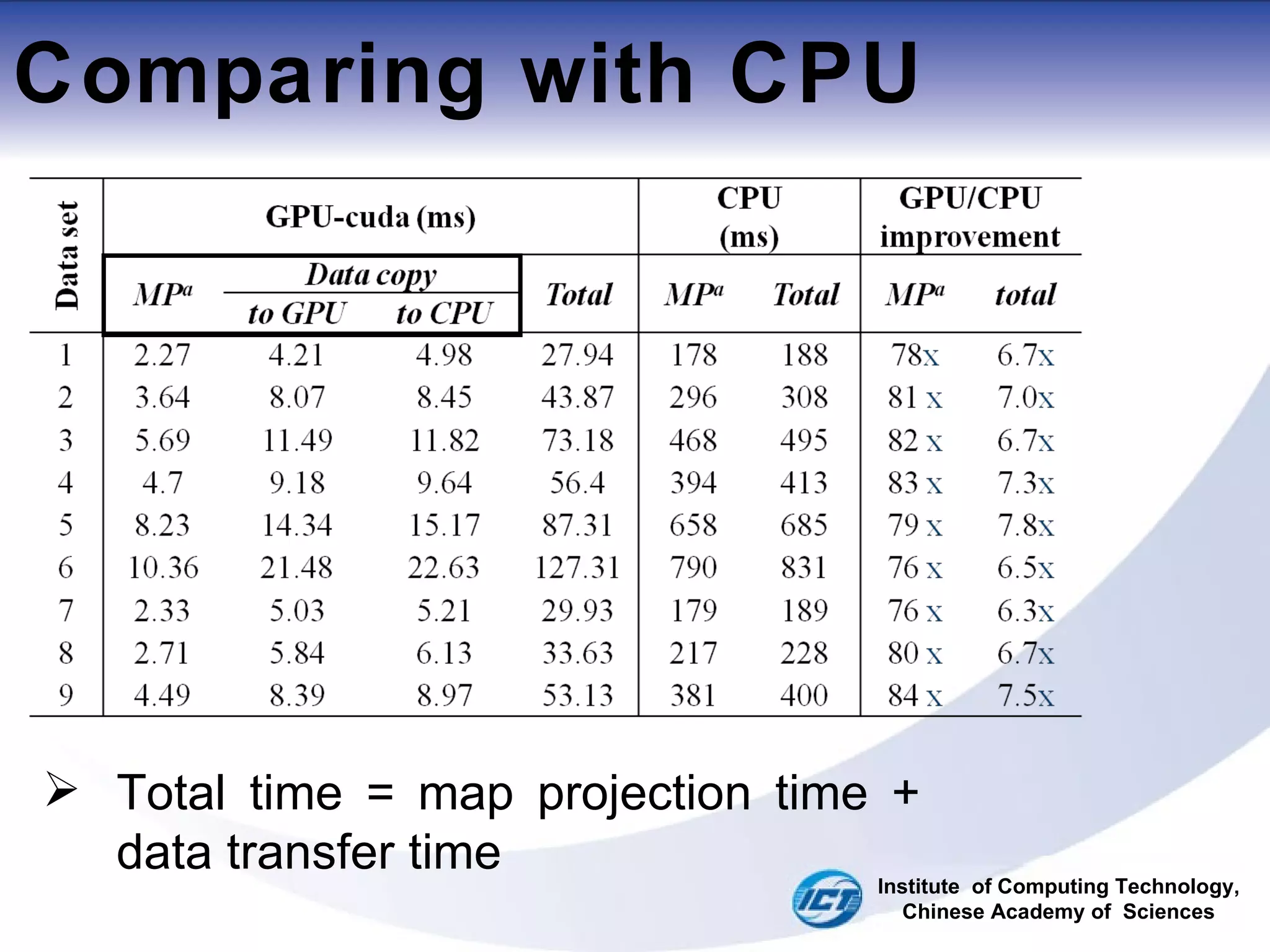
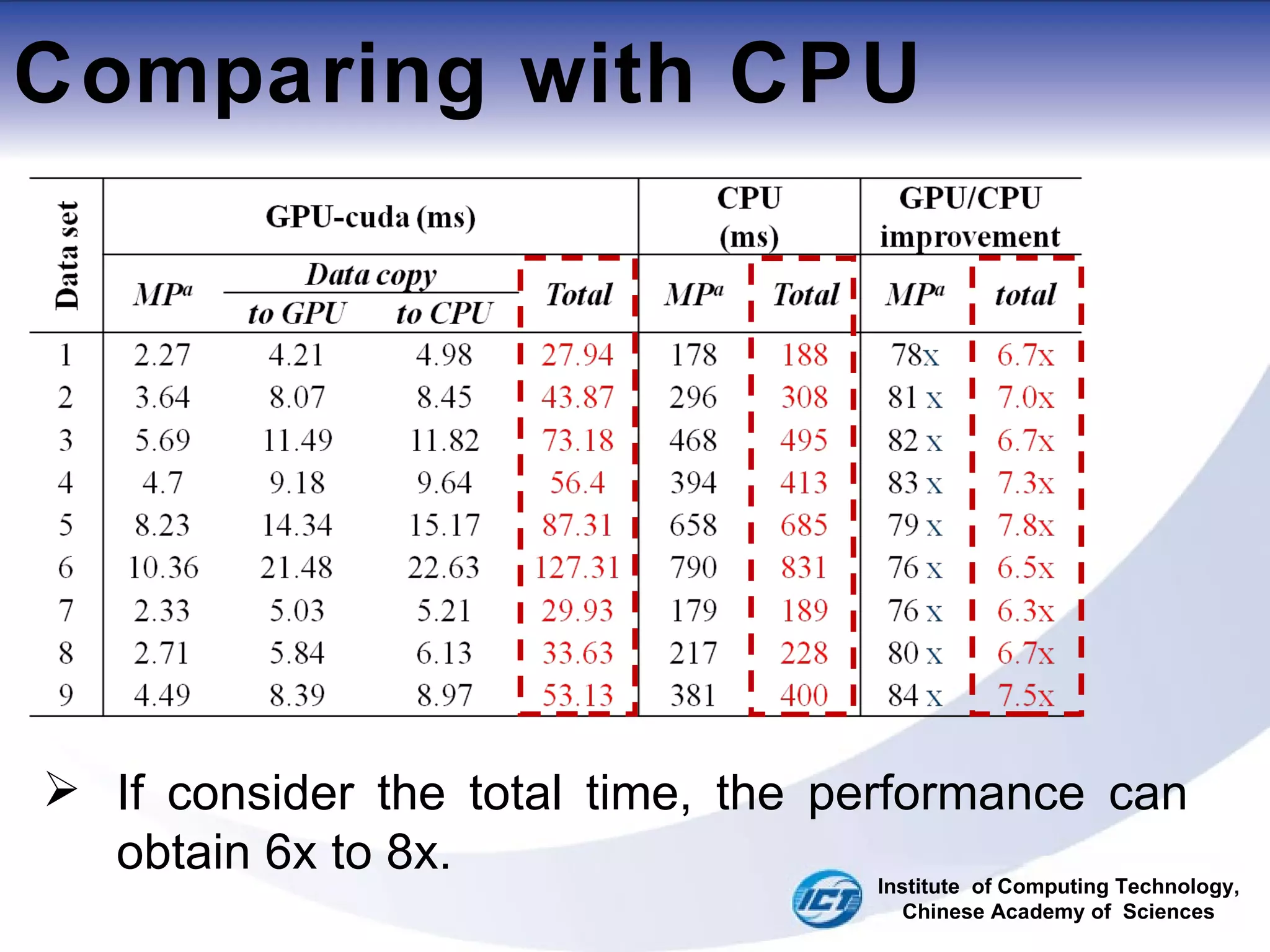
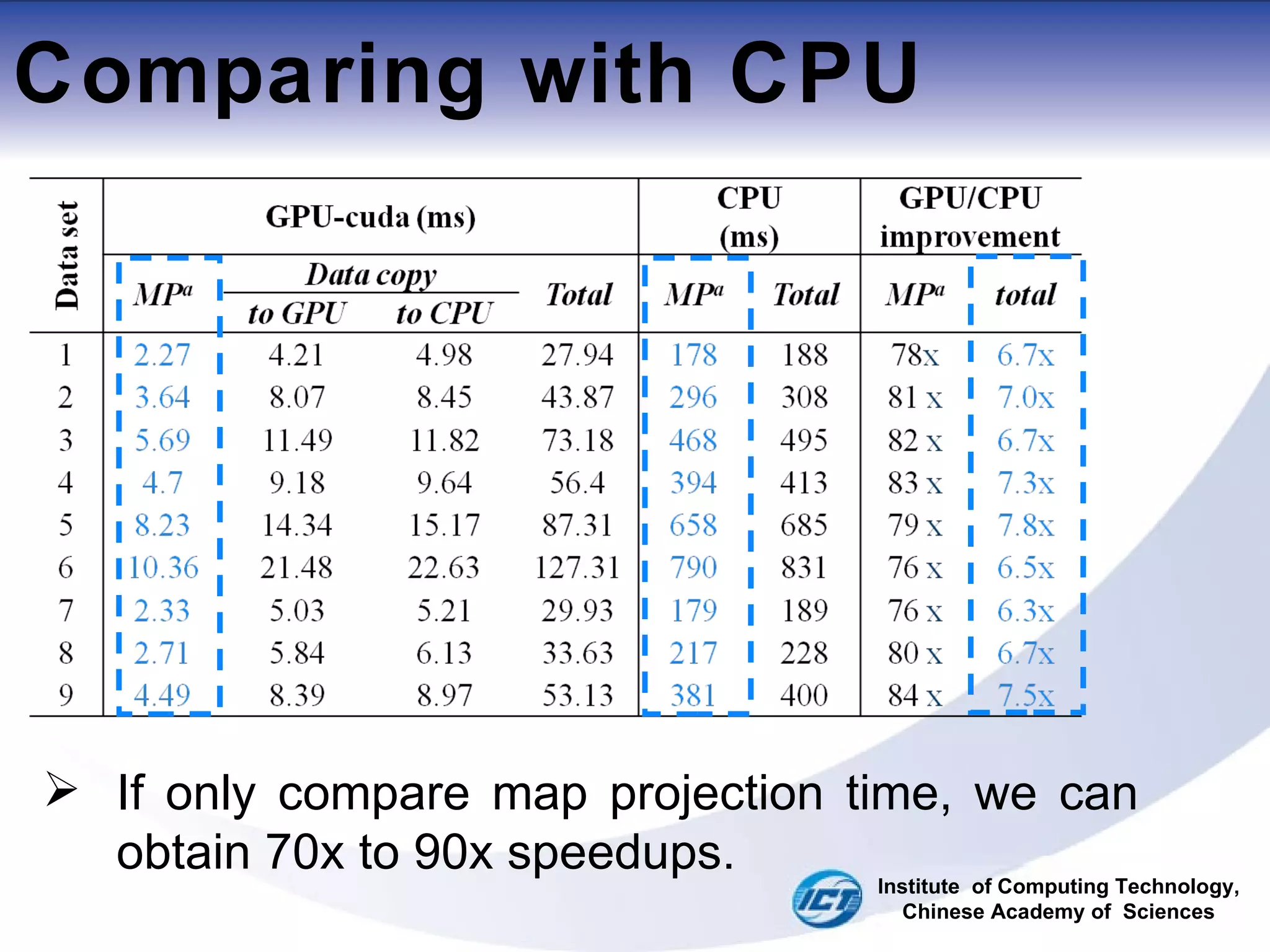
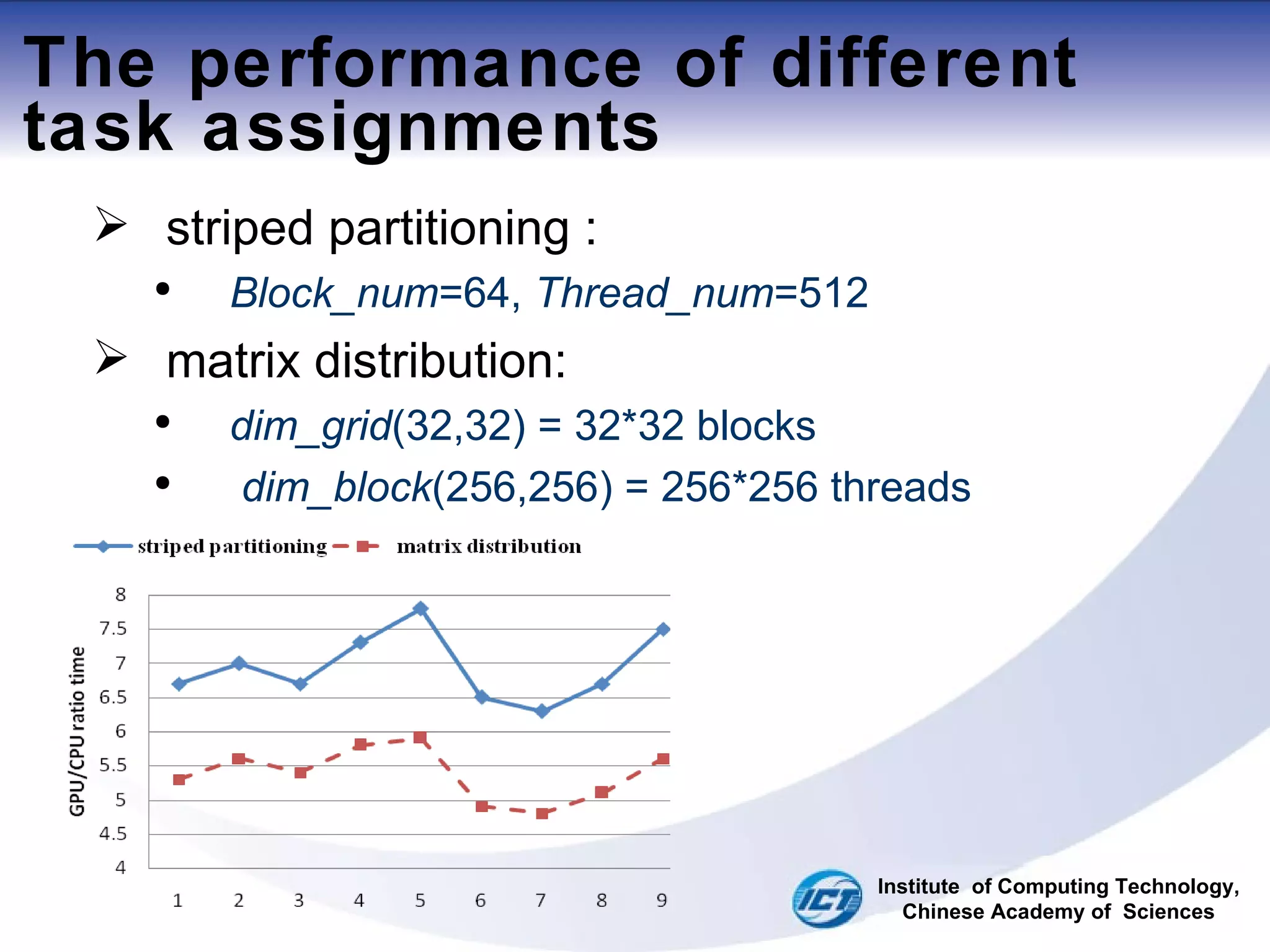
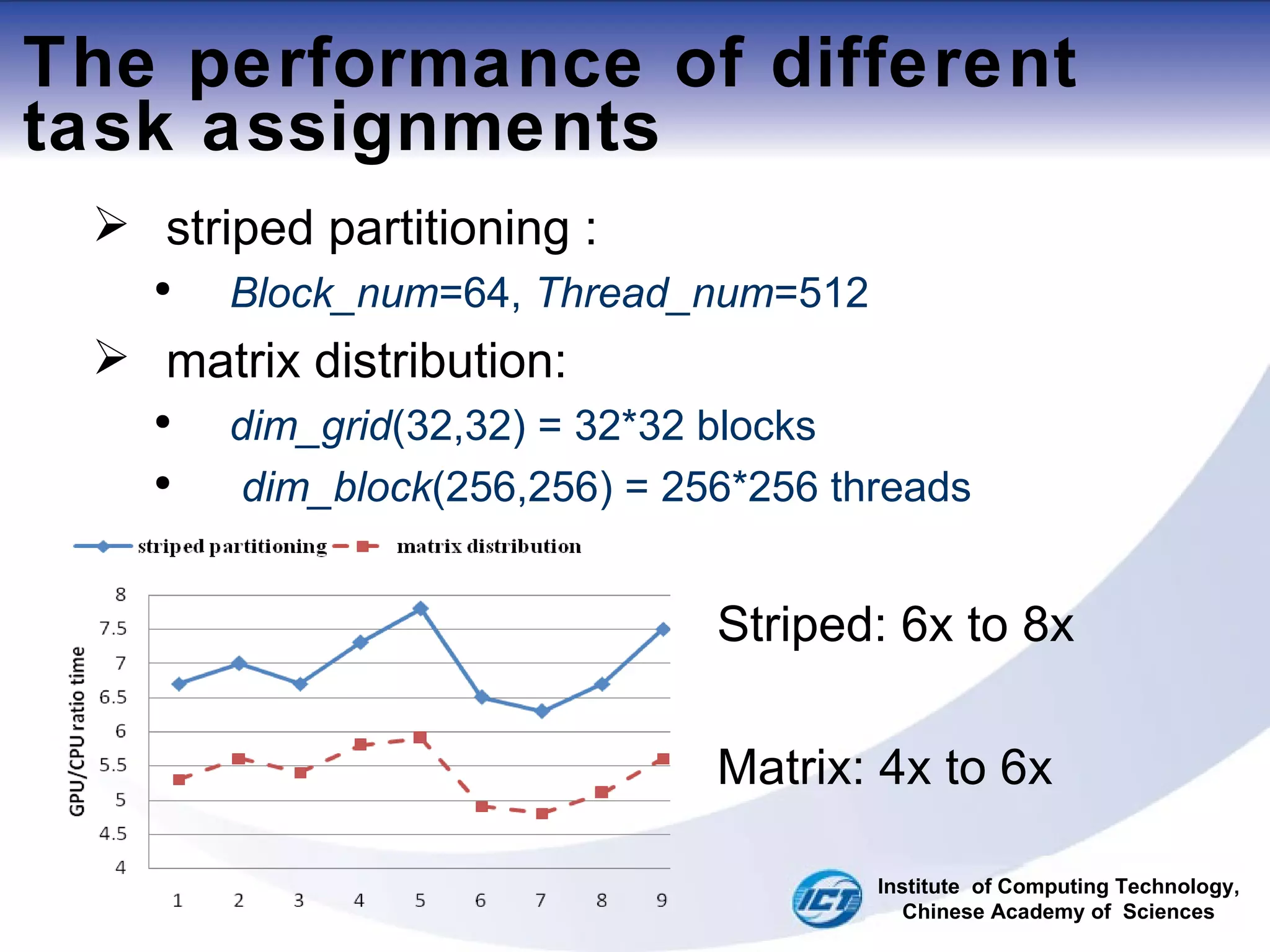
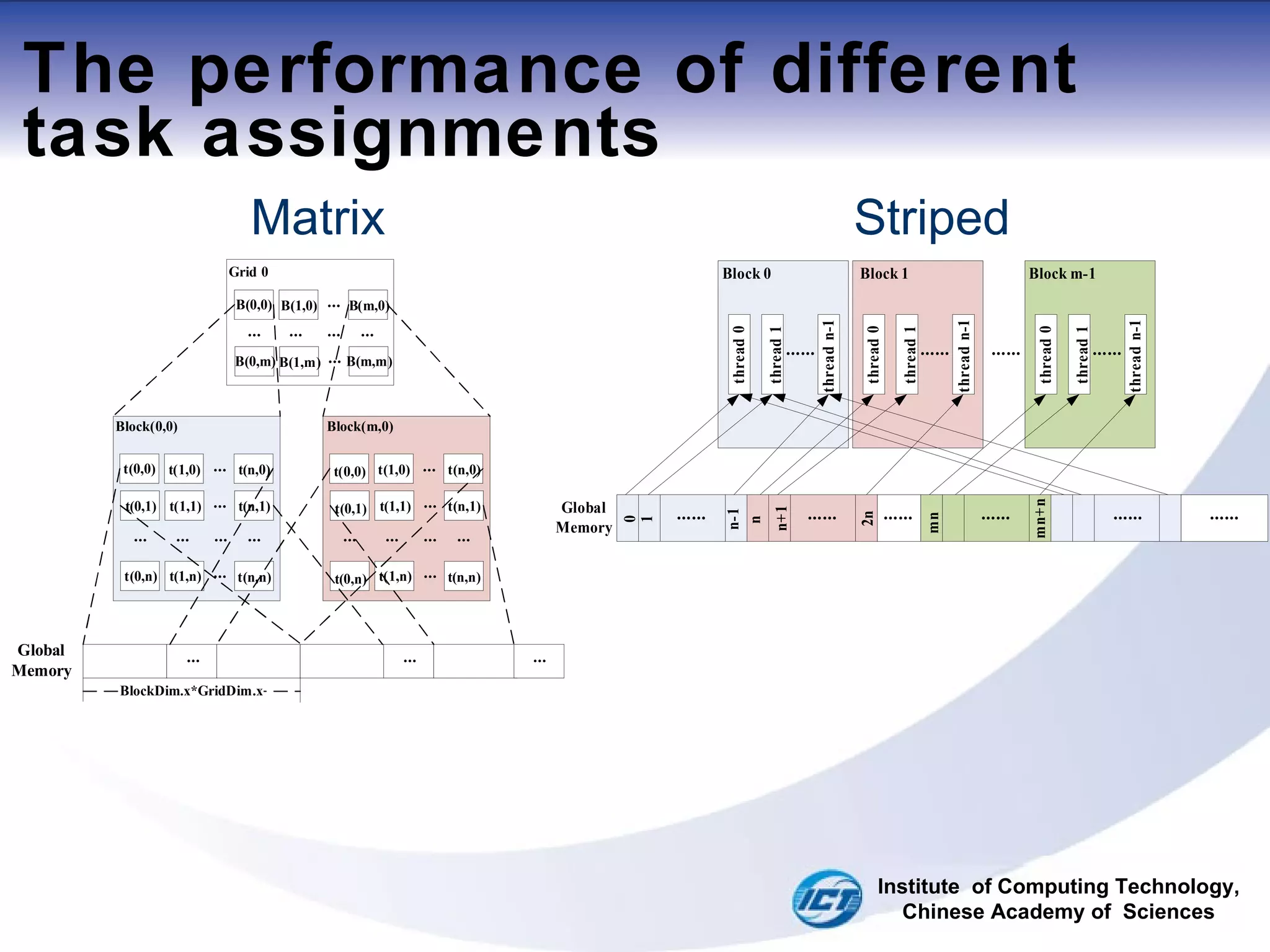
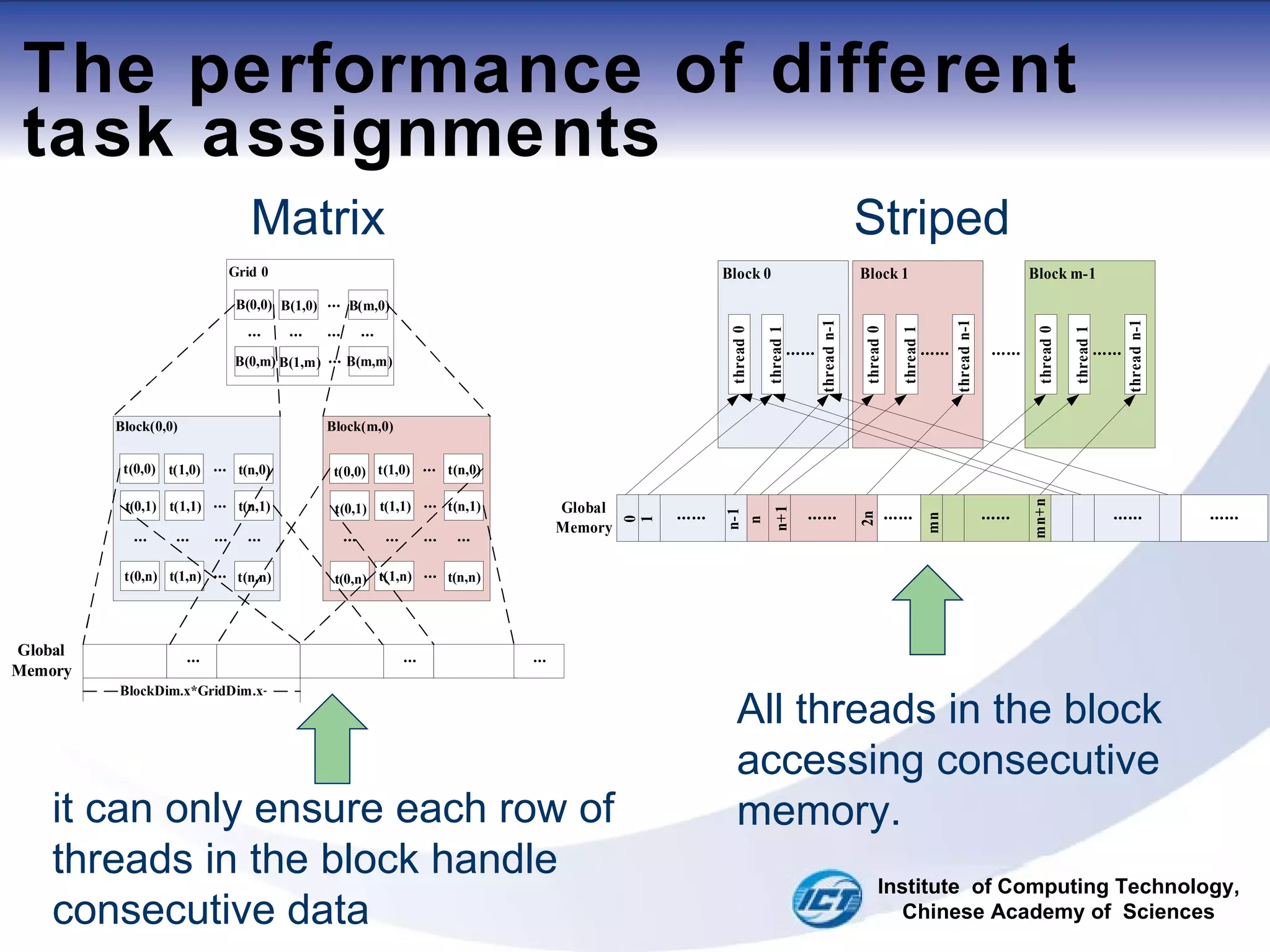
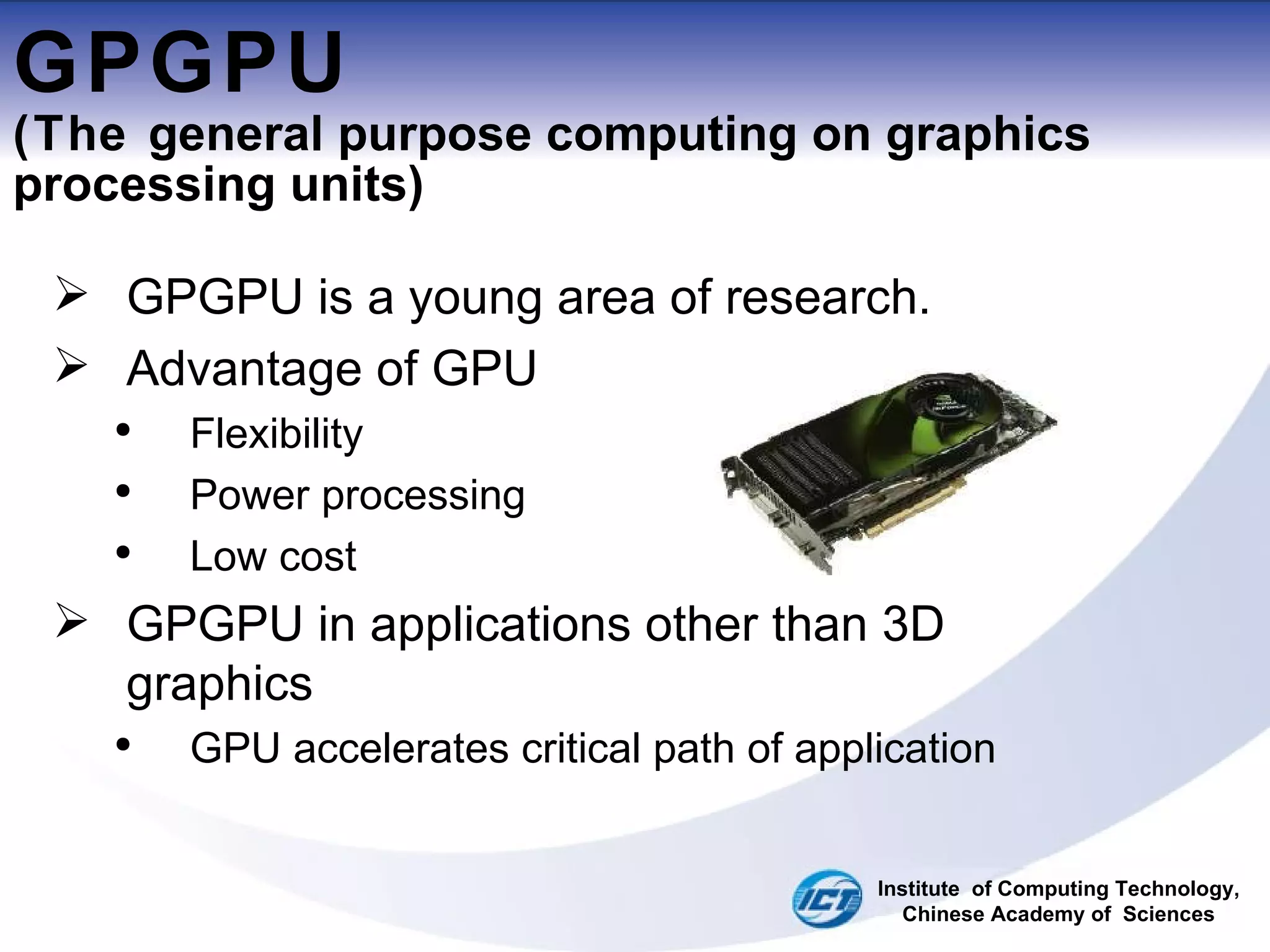
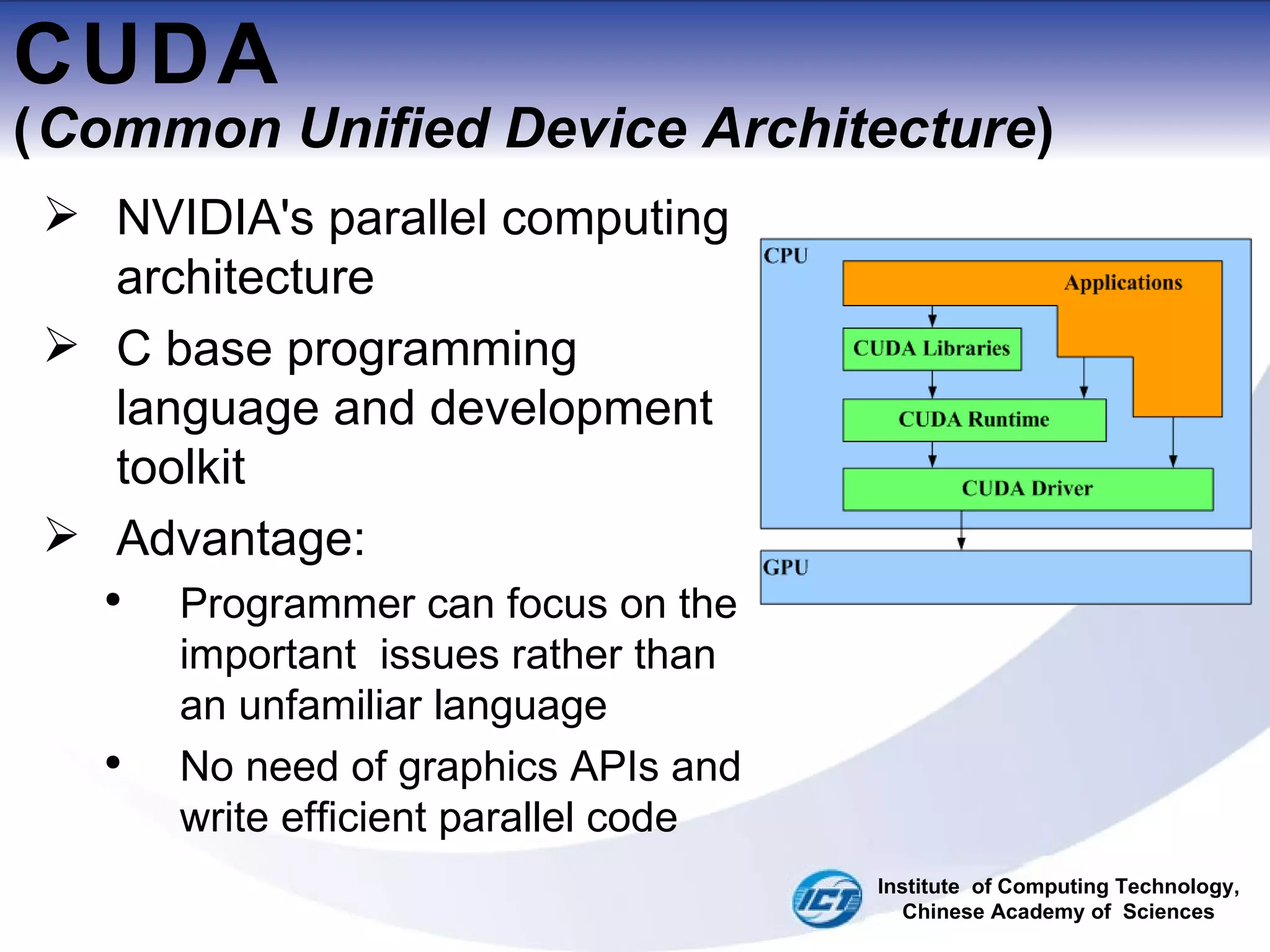
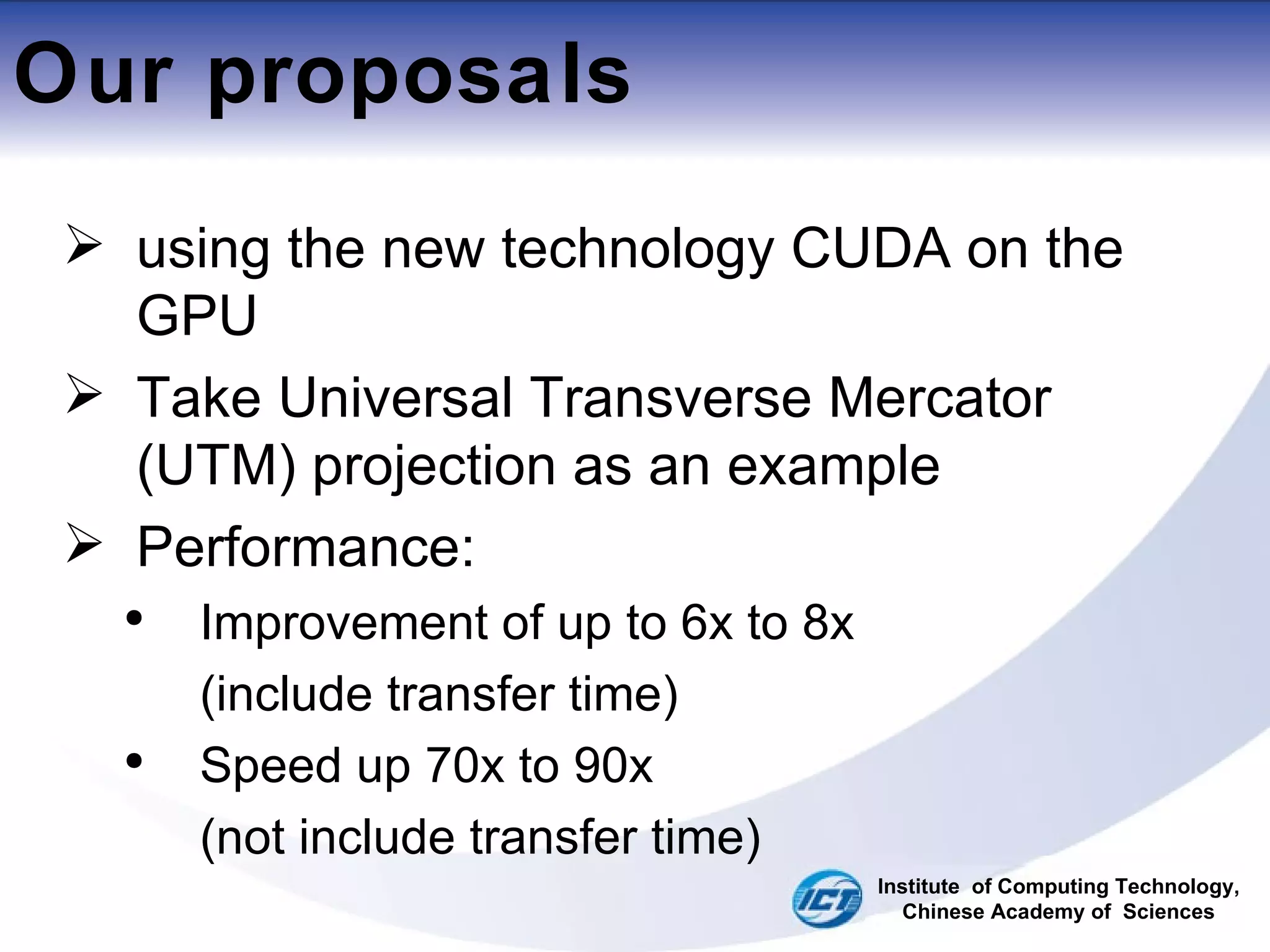
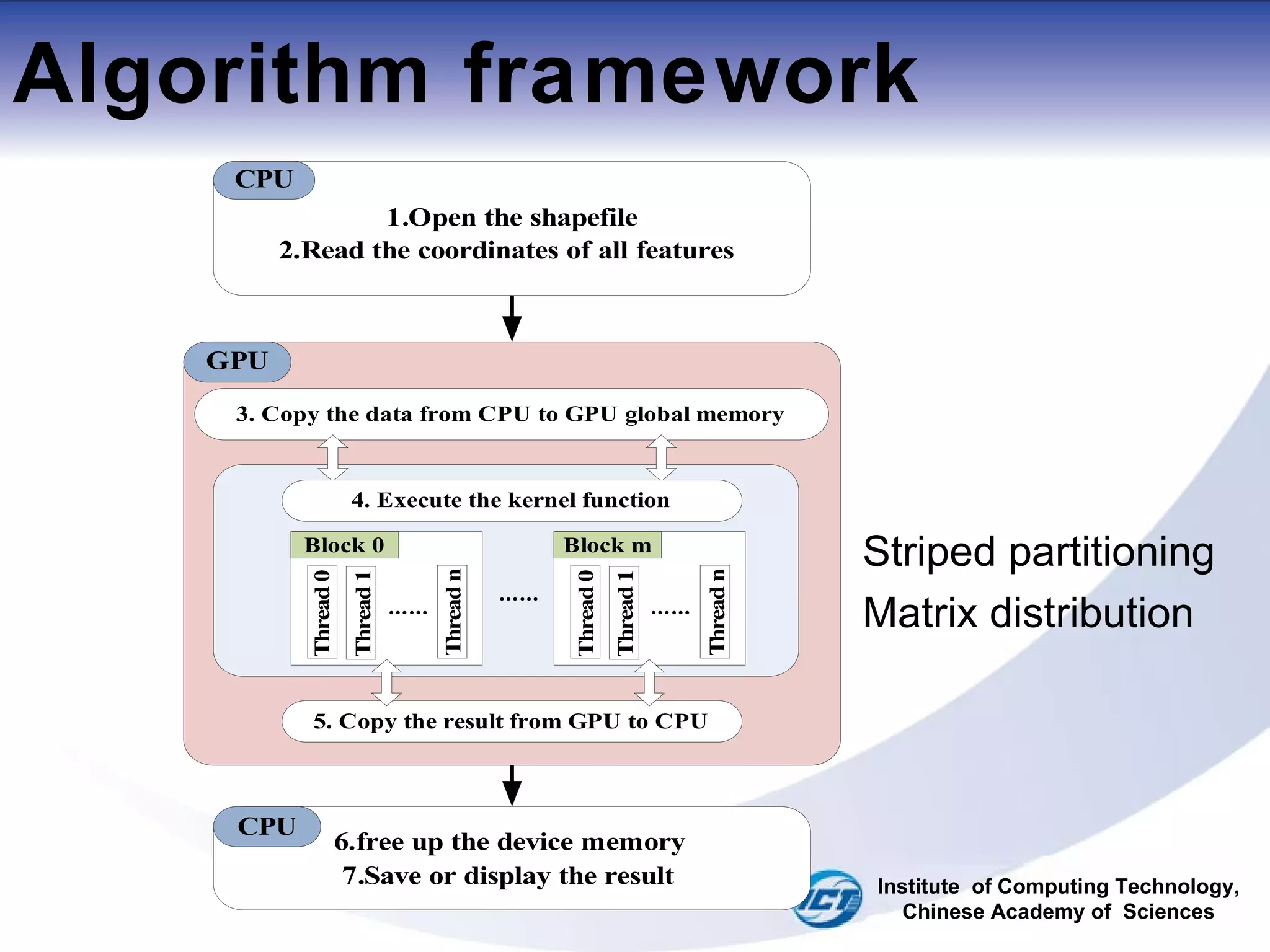
This document discusses using CUDA on GPUs to accelerate map projection calculations. It presents a method for implementing the Universal Transverse Mercator projection on a GPU using CUDA. Experiments show the GPU implementation provides a 6-8x speedup over a CPU version when including data transfer times, and a 70-90x speedup when only considering calculation times. Two task assignment approaches are evaluated, with striped partitioning performing slightly better than a matrix distribution method. Future work is proposed to implement other GIS algorithms on GPUs to take advantage of the significant speed increases possible.



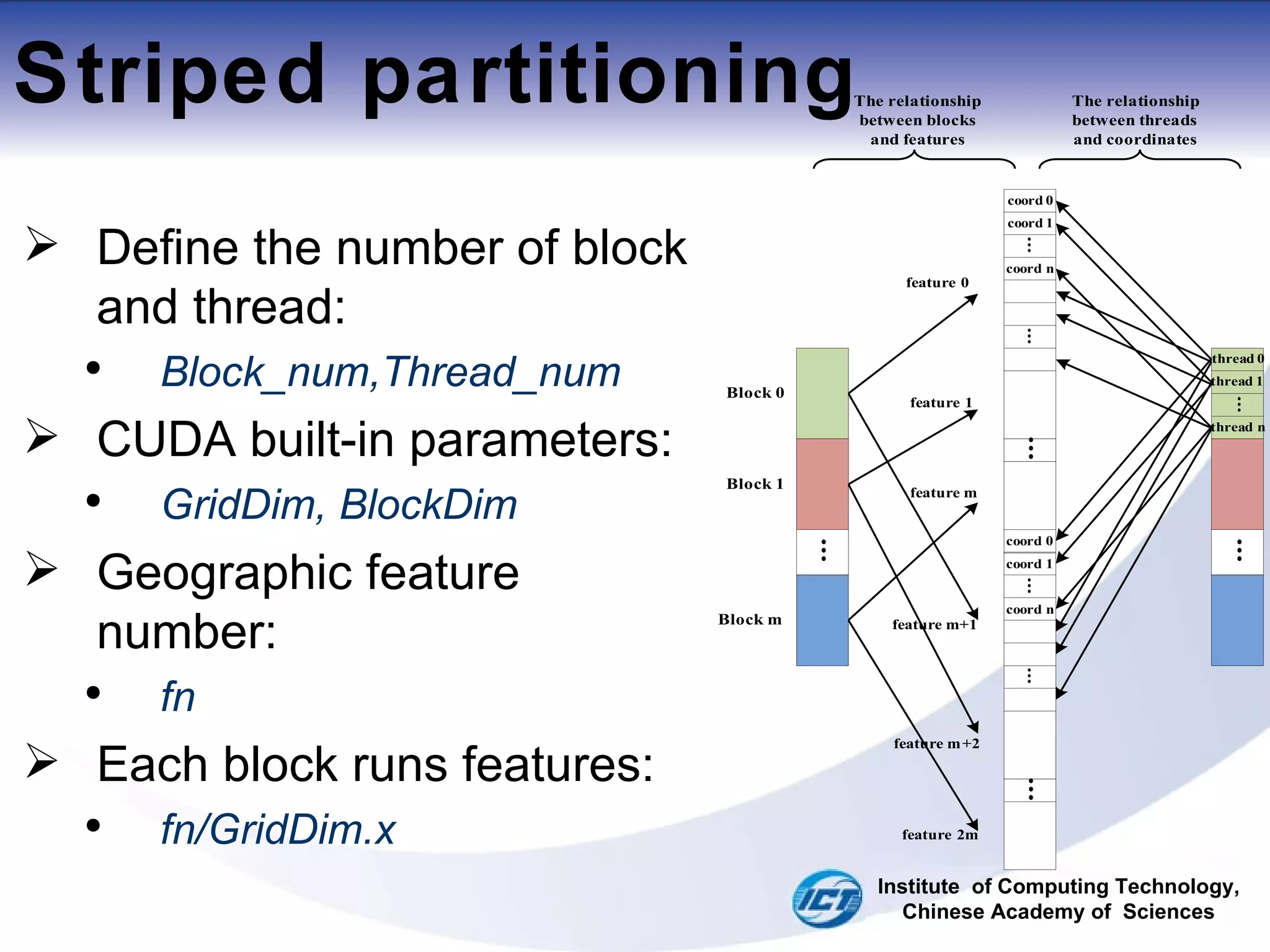
![Striped partitioning For surrounding loop: Blocks and features Block -> Feature[i] i = blockidx.x*(fn/GridDim.x) (1) Block -> next Feature[k] k = i + fn/GridDim.x (2) For inner loop: Threads and coordinates thread->coord[j] j = threadIdx.x thread->next coord[k] k = j +Thread_num Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fast-map-projection-on-cuda-110729103135-phpapp01/75/FAST-MAP-PROJECTION-ON-CUDA-ppt-12-2048.jpg)
![Striped partitioning For surrounding loop: Blocks and features Block -> Feature[i] i = blockidx.x*(fn/GridDim.x) Block -> next Feature[k] k = i + fn/GridDim.x For inner loop: Threads and coordinates thread->coord[j] j = threadIdx.x (1) thread->next coord[k] k = j +Thread_num (2) Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fast-map-projection-on-cuda-110729103135-phpapp01/75/FAST-MAP-PROJECTION-ON-CUDA-ppt-13-2048.jpg)
![Matrix distribution Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences Define the number of block and thread: grid(br,bc), block(tr,tc) Each block run k features, where: (1) Feature[i]: (2) (3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fast-map-projection-on-cuda-110729103135-phpapp01/75/FAST-MAP-PROJECTION-ON-CUDA-ppt-14-2048.jpg)
![Matrix distribution Each block run s coordnates, where: (1) coord[j]: Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fast-map-projection-on-cuda-110729103135-phpapp01/75/FAST-MAP-PROJECTION-ON-CUDA-ppt-15-2048.jpg)