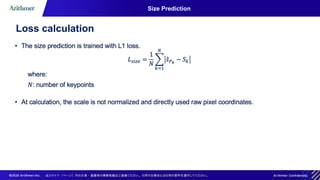
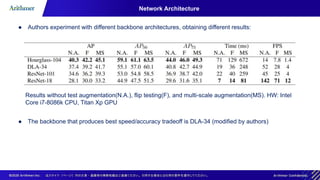
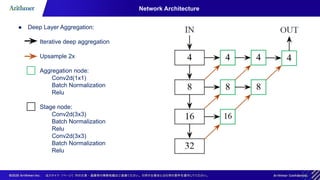
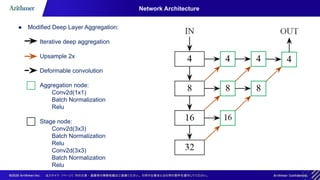
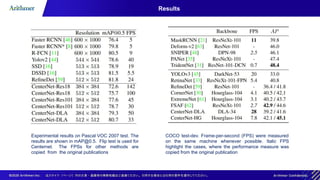
The document discusses the CenterNet approach for object detection that eliminates the need for anchor boxes, making it simpler, faster, and more accurate compared to traditional methods like YOLO and SSD. It covers the training process, keypoint heatmaps, and the architecture modifications used to enhance performance. Experimental results on the COCO dataset demonstrate significant efficiency gains and improved speed-accuracy trade-offs using this anchor-free method.