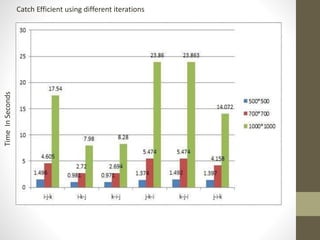
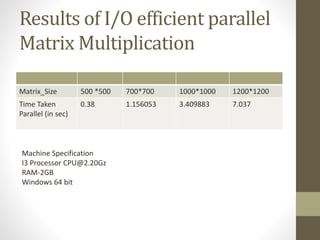
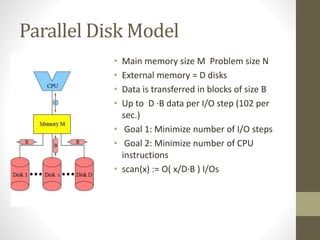
This document presents an overview of making matrix multiplication algorithms more I/O efficient. It discusses the parallel disk model and how to incorporate locality into algorithms to minimize I/O steps. Cannon's algorithm for matrix multiplication in a 2D mesh network is described. Loop interchange is discussed as a way to improve cache efficiency when multiplying matrices by exploring different loop orderings. Results are shown for parallel I/O efficient matrix multiplication on different sized matrices, with times ranging from 0.38 to 7 seconds. References on cache-oblivious algorithms and distributed memory matrix multiplication are provided.




![Assume that the 2-D array matrix is stored in a row-major order
a[0][0],a[0][1],...,a[0][n−1],a[1][0]
,a[1][1],...,a[1][n−1]...a[n−1][n−1]
The accesses into array C are
made in the following order:
• C[0][0] is accessed n times – For the first execution of k loop.
• C[0][1] is accessed n times – For the second execution of k loop.
• C[0][2] is accessed n times – For the third execution of k loop.
• ...
• C[1][0] is accessed n times – For the (n+1)th execution of k loop.
Since the same element is accessed repeatedly and accesses are
made sequentially, both temporal and spatial locality of reference is
observed.
For C, accesses are already optimized for cache!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7266620d-6f02-4342-84e4-6584c798ac1d-160514174353/85/IOEfficientParalleMatrixMultiplication_present-6-320.jpg)
![• The accesses into array A are made in the following order:
• A[0][0],A[0][1],A[0][2],...,A[0][n] – This whole
sequence n times, for each iteration of k loop under a single
iteration of j loop.
• A[1][0],A[1][1],A[1][2],...,A[1][n] – This whole
sequence n times, for each iteration of k loop under a single
iteration of j loop.
• ...
• ...
• A[n][0],A[n][1],A[n][2],...,A[n][n] – This whole
sequence n times, for each iteration of k loop under a single
iteration of j loop.
Hence, each row of array A is accessed n times and each
element in the row is accessed sequentially. We observe good
spatial locality of reference. But the same element is not
referenced repeatedly so no temporal locality.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7266620d-6f02-4342-84e4-6584c798ac1d-160514174353/85/IOEfficientParalleMatrixMultiplication_present-7-320.jpg)
![• The accesses into array B are made in the following order:
• B[0][0],B[1][0],B[2][0],...,B[n][0]
• B[0][1],B[1][1],B[2][1],...,B[n][1]
• ...
• B[0][n],B[1][n],B[2][n],...,B[n][n]
• Then again,
• B[0][0],B[1][0],B[2][0],...,B[n][0]
• B[0][1],B[1][1],B[2][1],...,B[n][1]
• ...
• B[0][n],B[1][n],B[2][n],...,B[n][n]
The whole array is accessed once and only then repetition
starts. So there's no spatial locality or temporal locality for B.
Each element will incur a cache miss on every access made to it.
And thus we have a cache miss on every execution of the
multiplication statement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7266620d-6f02-4342-84e4-6584c798ac1d-160514174353/85/IOEfficientParalleMatrixMultiplication_present-8-320.jpg)

![• C[0][0],C[0][1],C[0][2],...,C[0][n] – This whole sequence n times, for
each iteration of k loop……
• C[n][0],C[n][1],C[n][2],...,C[n][n] – This whole sequence n times, for
each iteration of k loop.
Now C has good spatial locality.
Similarly,
A enjoys good temporal as well as spatial locality.
B now has spatial locality.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7266620d-6f02-4342-84e4-6584c798ac1d-160514174353/85/IOEfficientParalleMatrixMultiplication_present-10-320.jpg)