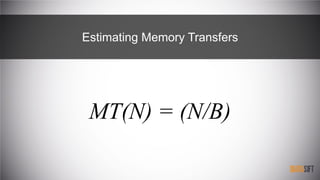
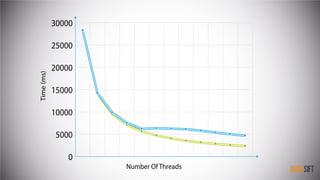
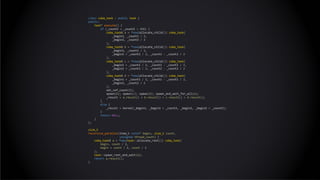
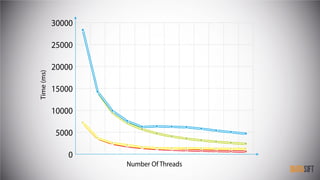
The document provides an introduction to cache-oblivious algorithms, emphasizing that they are efficient on any system regardless of memory hierarchy but do not improve algorithmic complexity. It discusses practical implementations, including parallel processing techniques and memory transfer estimates, utilizing a custom data structure and recursive methods for optimization. Key concepts include the importance of exploiting spatial and temporal locality in these algorithms.