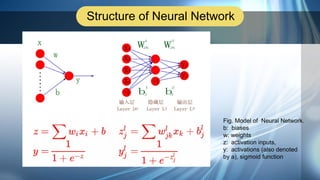
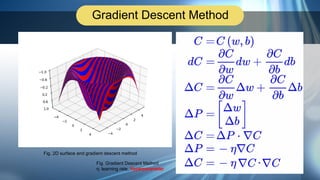
1. The document introduces neural networks and the backpropagation algorithm. It discusses the structure of neural networks and how they are trained on data to learn parameters through methods like gradient descent.
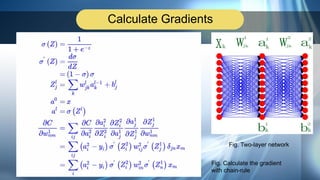
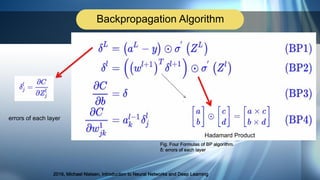
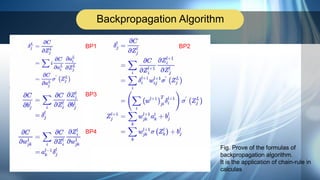
2. Backpropagation is introduced as an efficient method to calculate gradients in neural networks using chain rule. Diagrams show the calculations and flow of backpropagation.
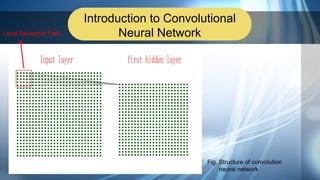
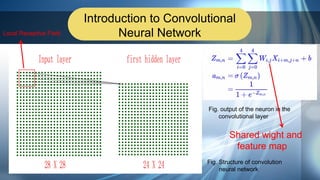
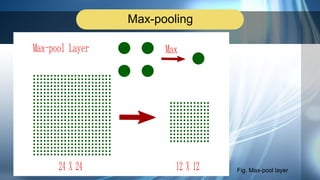
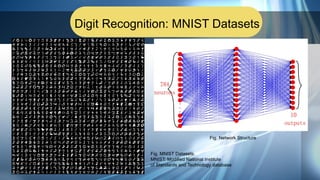
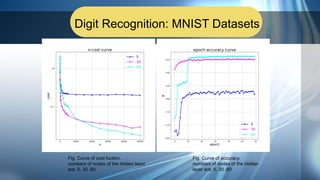
3. Applications of neural networks like convolutional neural networks and digit recognition using the MNIST dataset are demonstrated. AlexNet, an early CNN model for image recognition, is discussed.