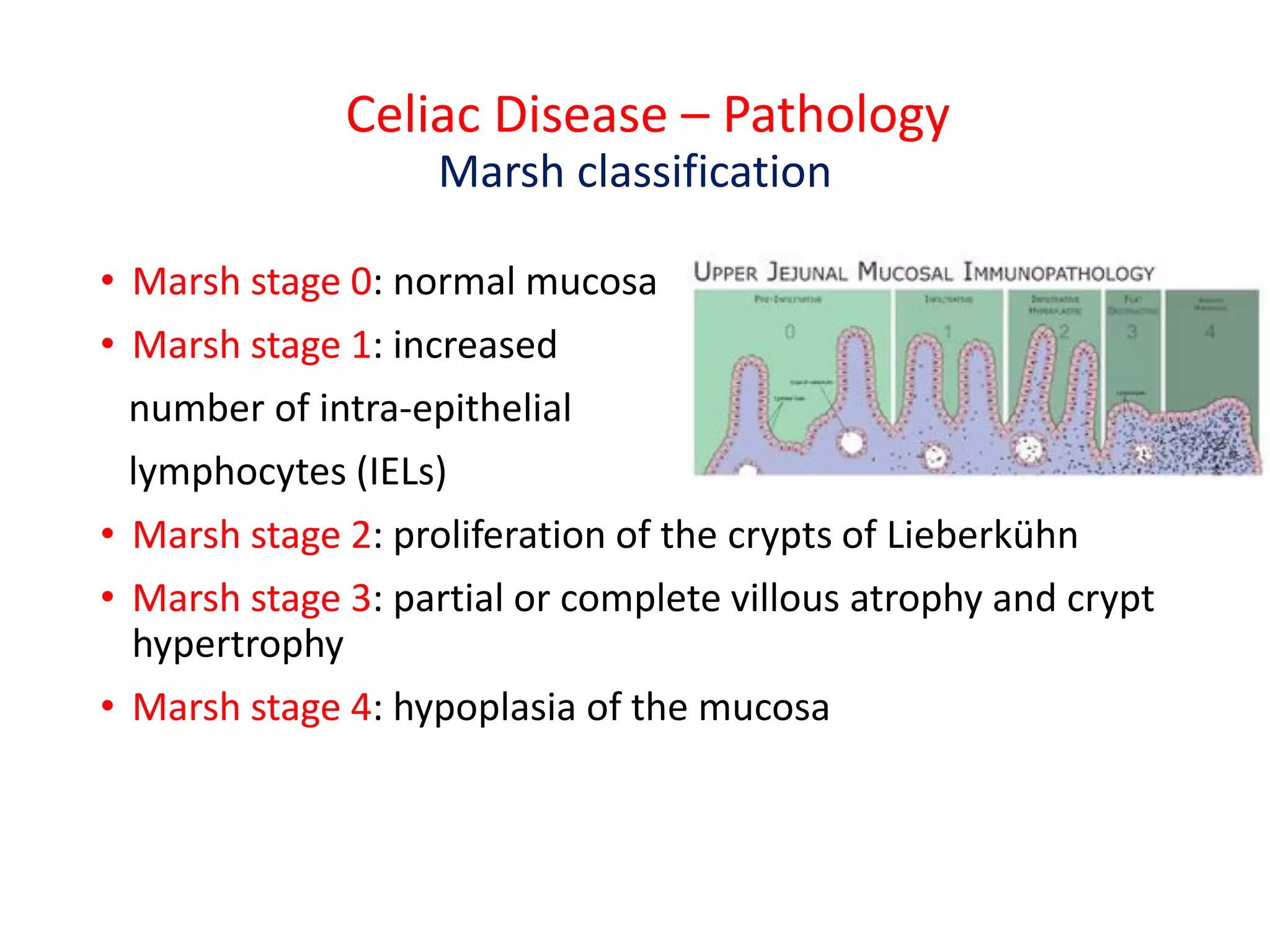
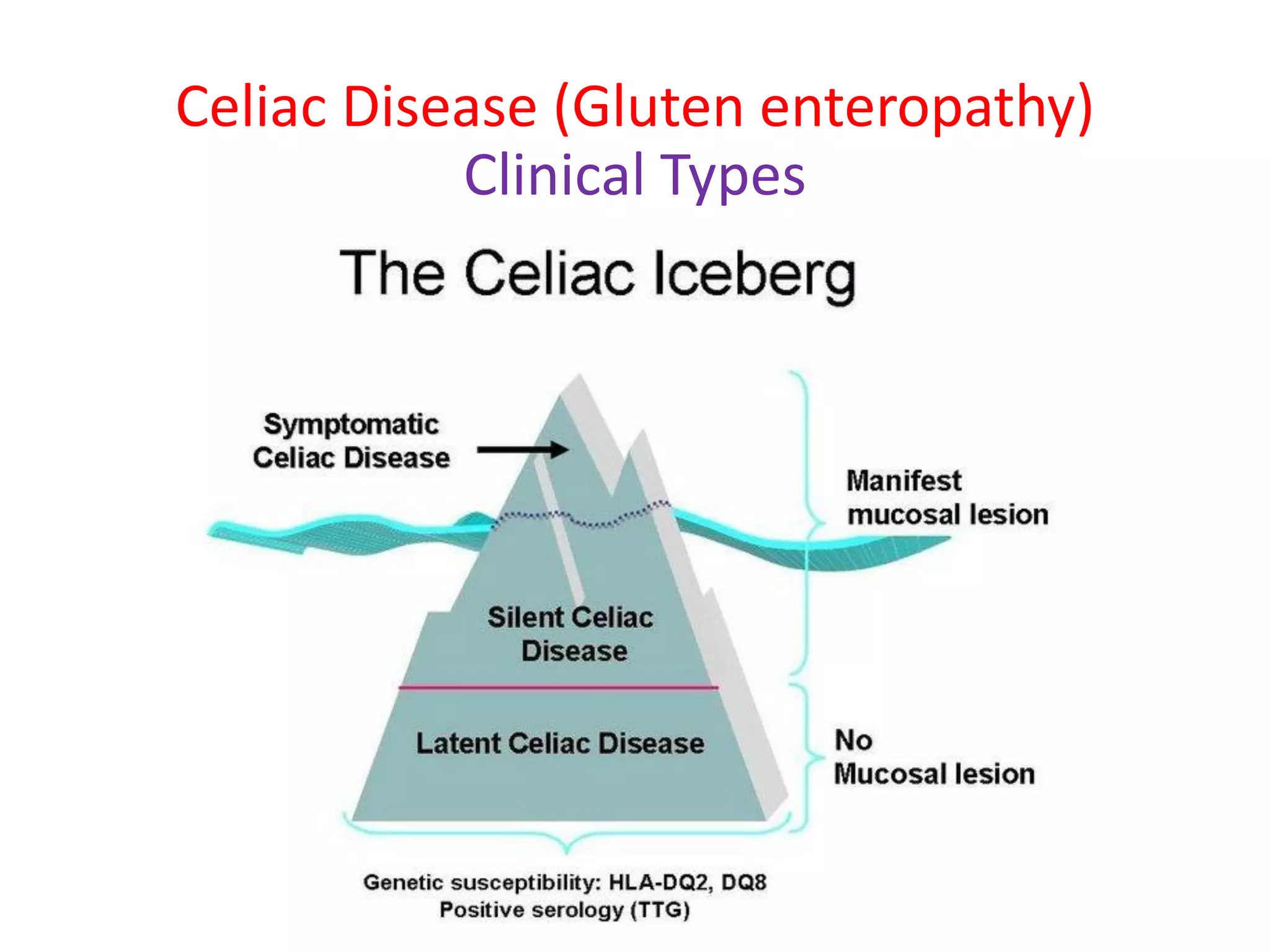
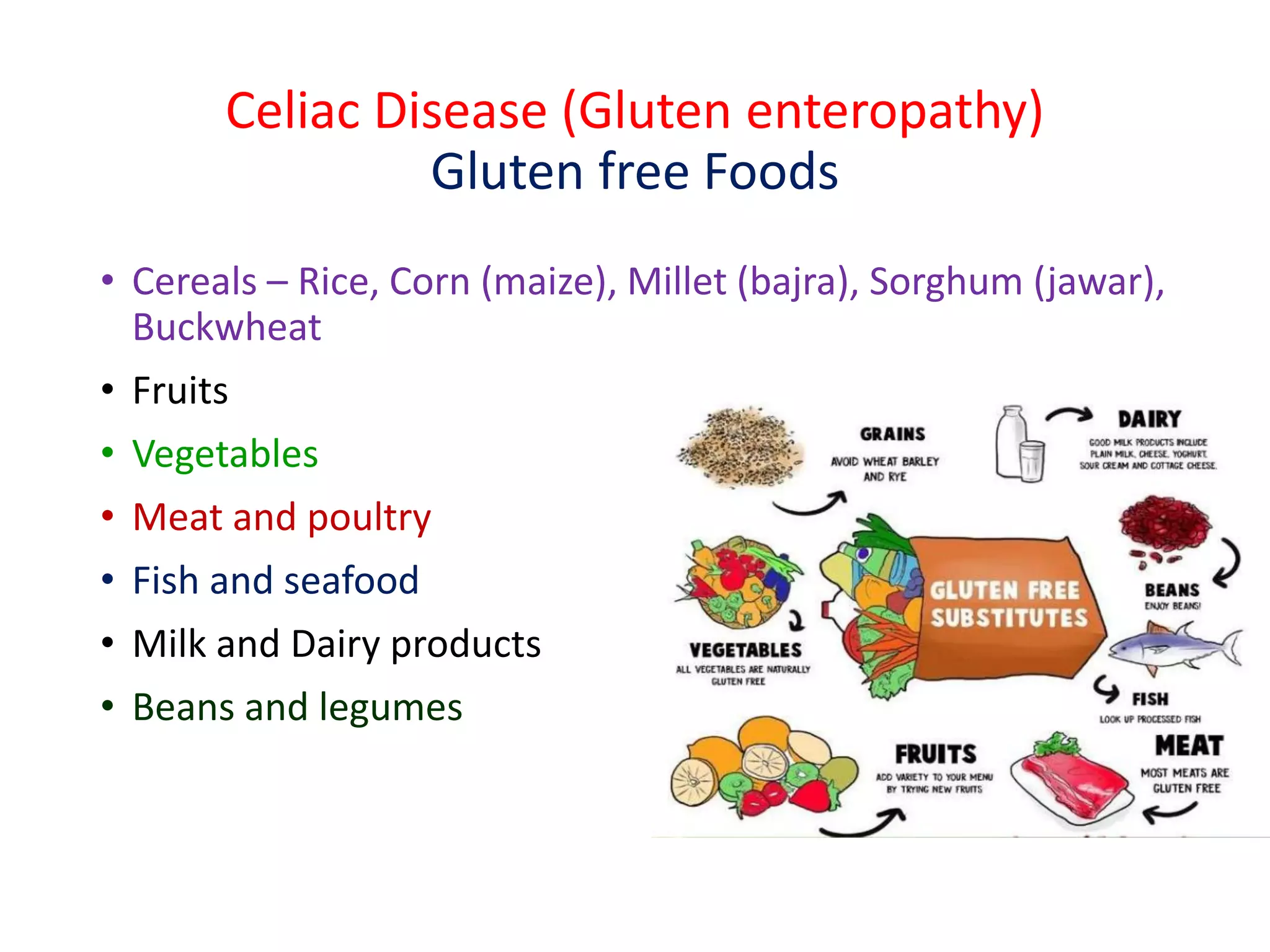
This document provides information on celiac disease in children, including its classification, epidemiology, etiology, clinical features, complications, management, prognosis and prevention. Celiac disease is a genetically predisposed autoimmune disease caused by an immune reaction to gluten, resulting in damage to the small intestine and inability to absorb nutrients. It commonly presents with diarrhea, failure to thrive and malnutrition. Diagnosis involves antibody testing and biopsy of the small intestine. The only treatment is a lifelong gluten-free diet, which can resolve symptoms and heal intestinal damage. Untreated celiac disease can lead to complications like anemia, osteoporosis and intestinal lymphoma.