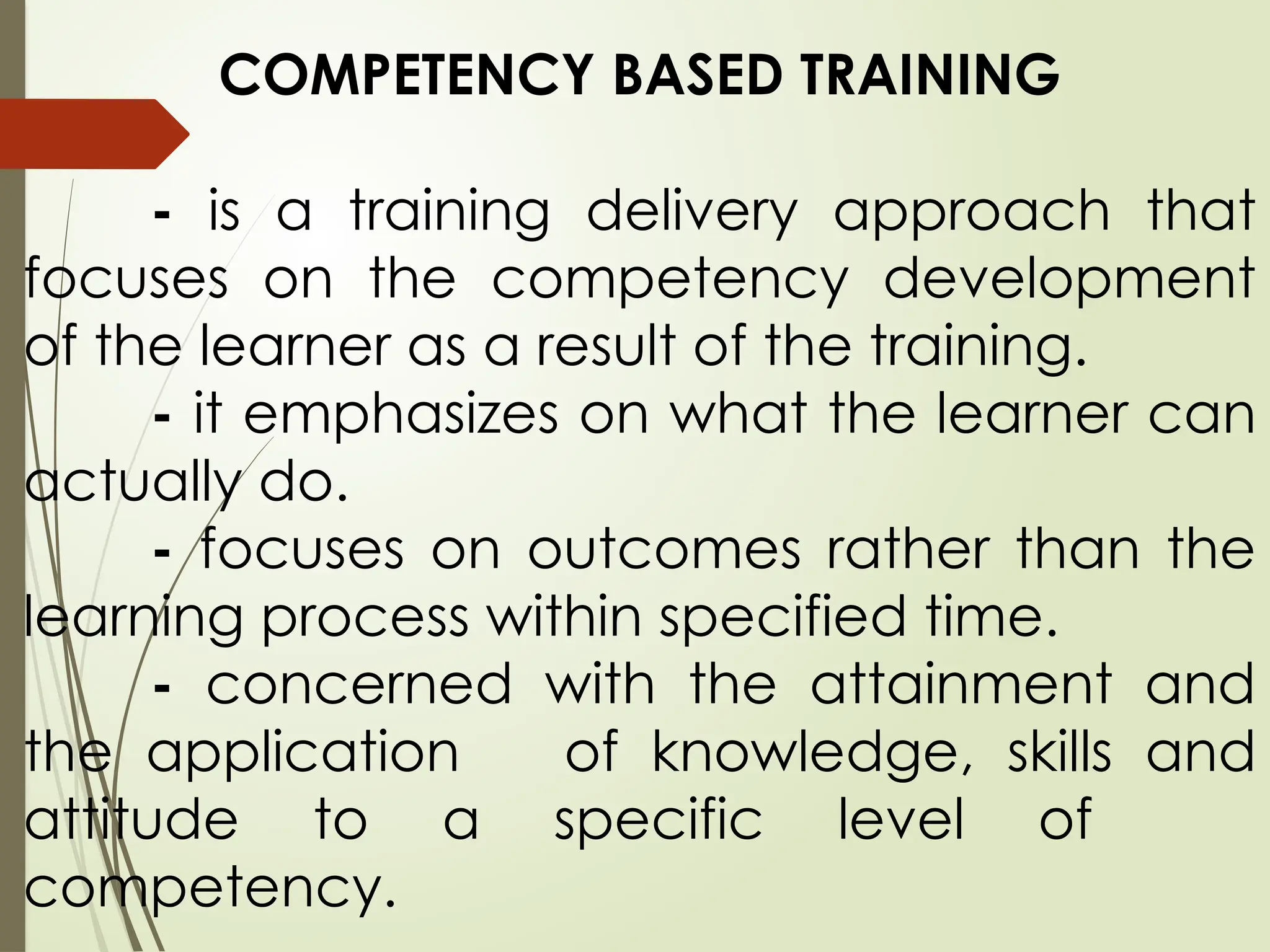
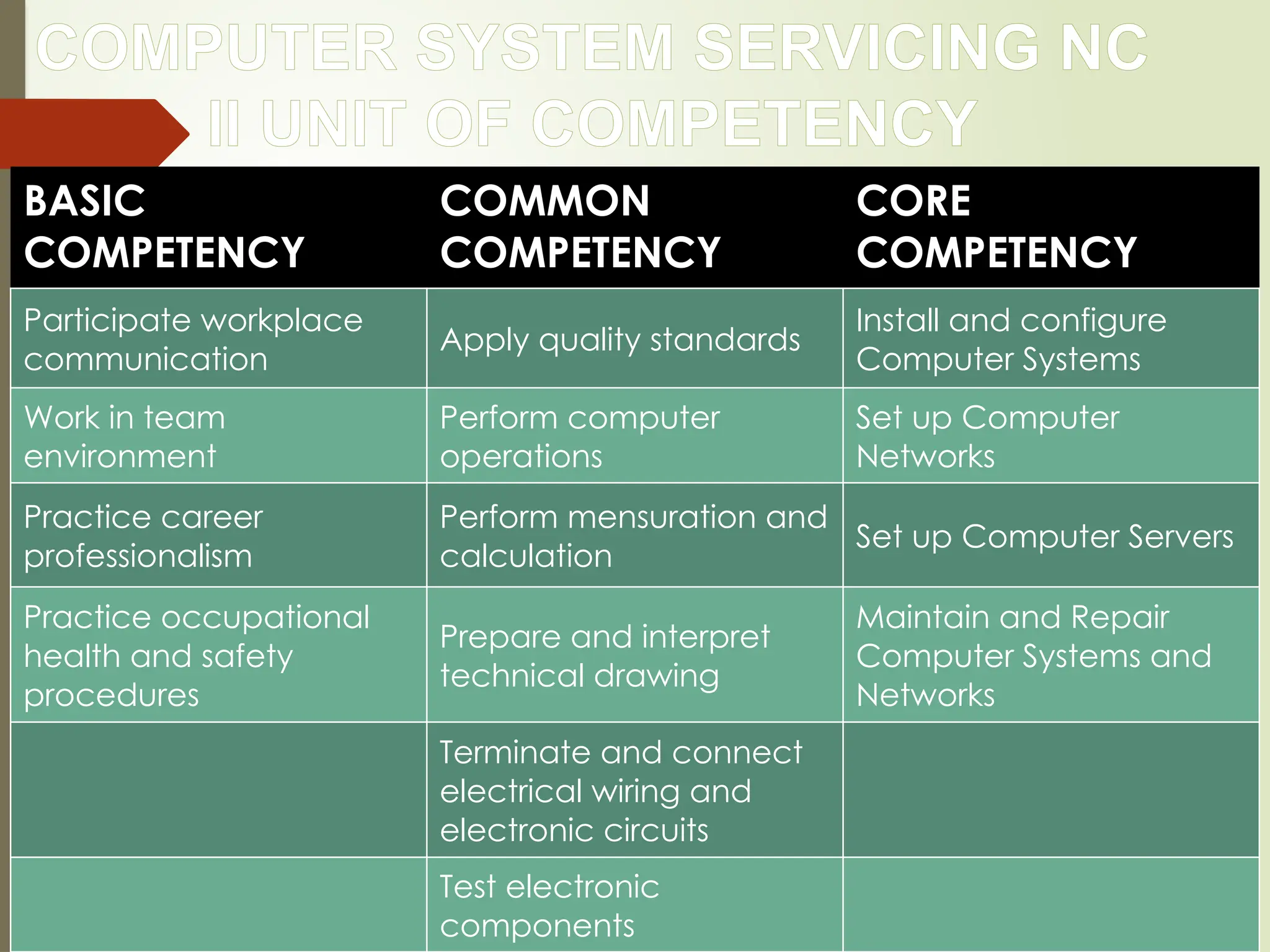
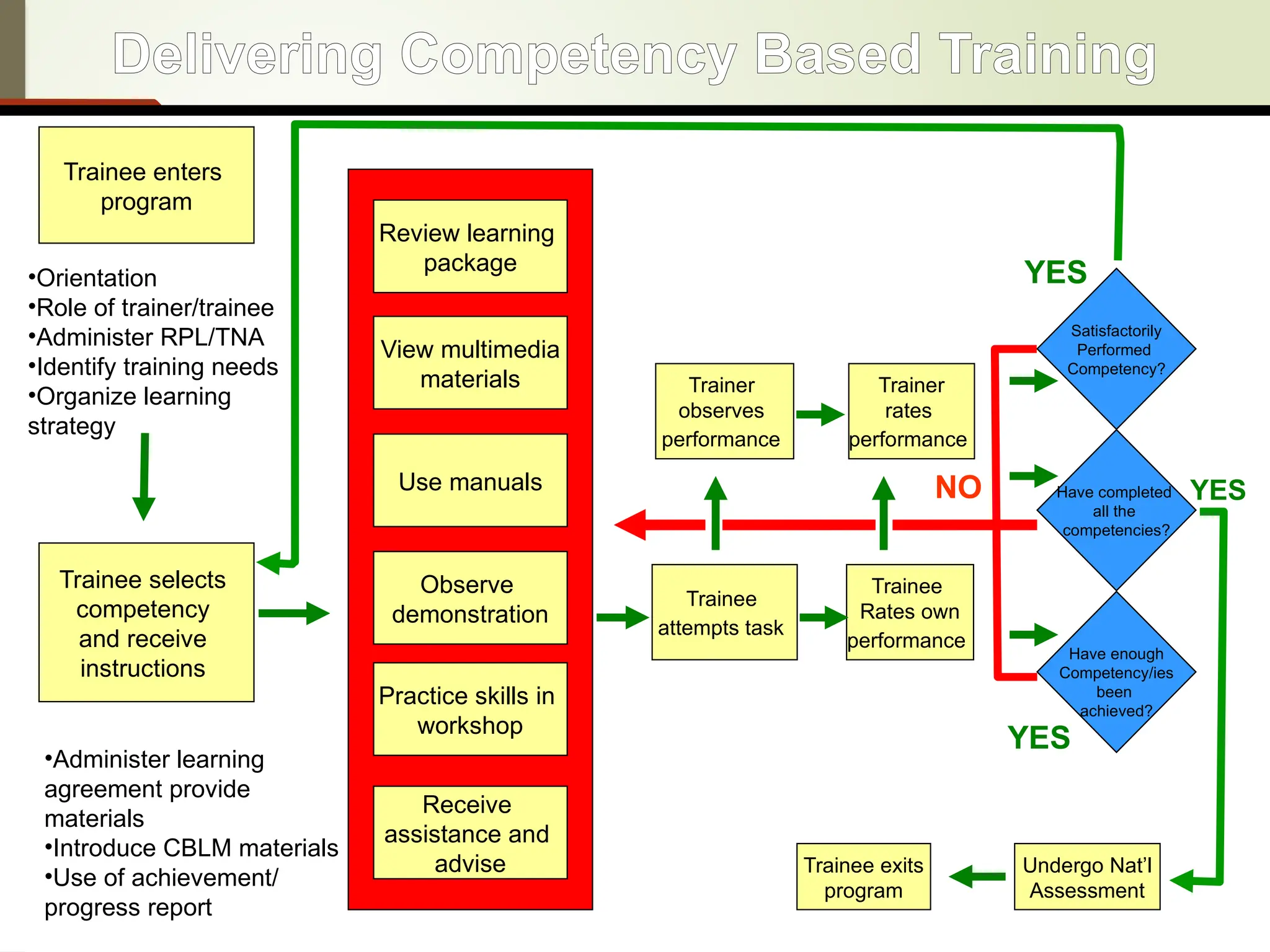
Competency-Based Training (CBT) is a training approach focused on the development of learners' competencies through self-paced, modular learning that prioritizes outcomes over process. Trainers facilitate individualized learning experiences while trainees have the autonomy to choose their learning paths, progressing at their own pace. CBT is structured around well-defined competencies, with assessments based on demonstrated performance relevant to industry standards.