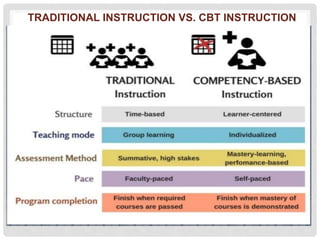
This document discusses competency-based training (CBT), which focuses on what learners can do rather than time spent learning. In CBT, mastery of specific skills determines progression, unlike traditional education where time is the unit of progression. CBT assesses if learners can perform skills to a set standard under certain conditions. It emphasizes outcomes over process and ensuring learners gain knowledge, skills, and attitudes to a competent level. CBT features include being able to do one's job properly, knowing what to do if things go wrong, and adopting the right approach. Key principles of CBT include basing training on competency standards and allowing recognition of prior learning.